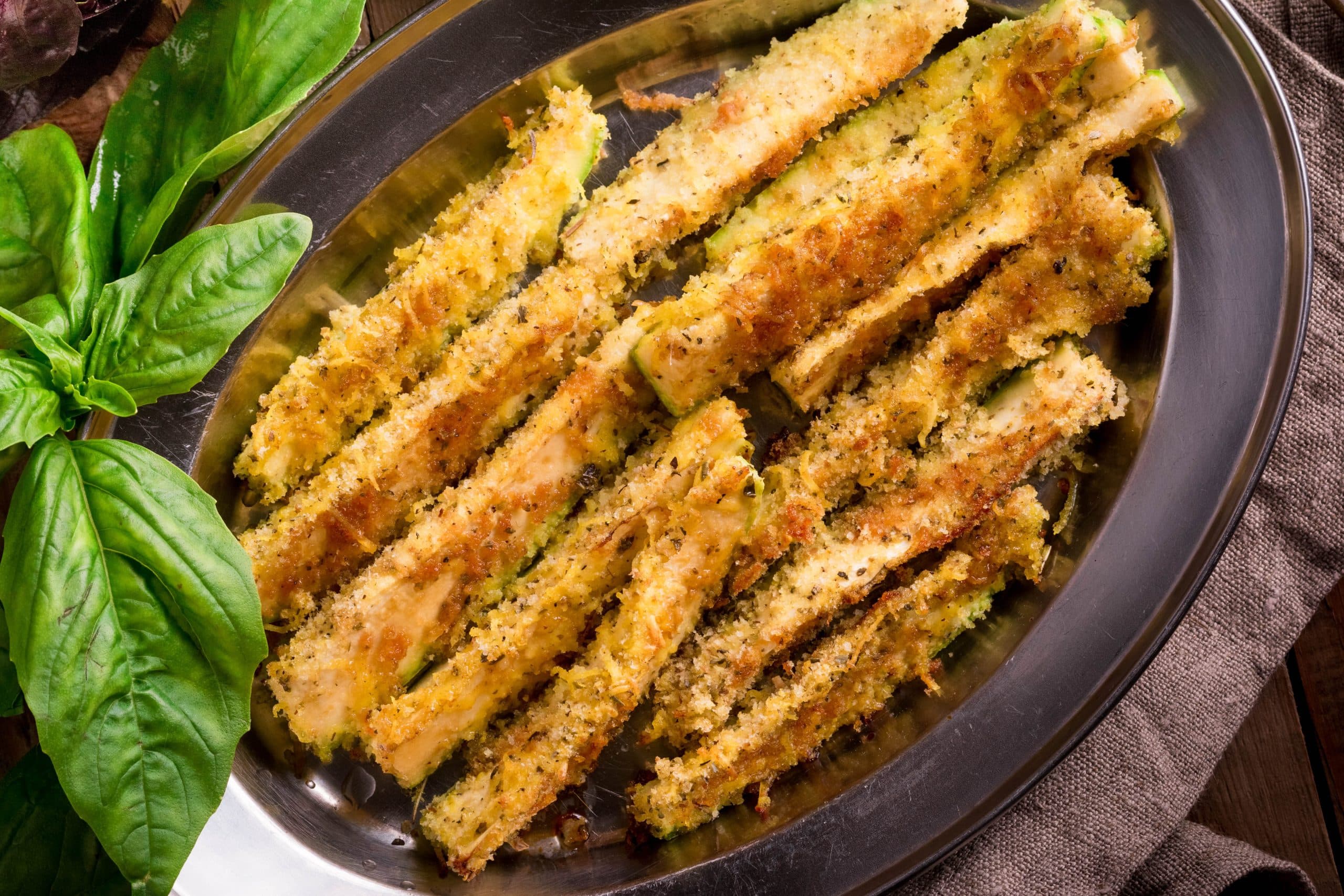
If you’re like me who’s always eyeing the appetizers at restaurants but never order them because they’re usually deep fried, then this oven fried zucchini recipe is for you! Crispy, slightly salty and just plain delicious, these zucchini rounds are the perfect low carb side dish or appetizer. And since they’re baked, not fried, they’re actually pretty healthy too!
Oven Fried Zucchini Recipe (3)
Coated with Panko bread crumbs and Parmesan cheese, these zucchini rounds are baked in the oven until golden brown and crispy. Serve them as a side dish or appetizer with a dipping sauce of your choice.
Ingredients:
- 2 medium size zucchini
- Cooking spray
- ¼ cup grated Parmesan cheese
- ½ teaspoon dried Italian seasoning
- 1 cup Panko bread crumbs
- 2 large eggs, beaten
- Salt and pepper, to taste
- 1 cup marinara sauce
Instructions:
- Preheat the oven to 400 degrees F. Line a baking sheet with parchment paper and set aside.
- Prepare the zucchini: trim off the ends and slice into ¼-inch thick rounds.
- In a shallow bowl, combine Parmesan cheese, Italian seasoning, Panko bread crumbs, and salt and pepper.
- In another shallow bowl, beat the eggs.
- Dip each zucchini round in the egg mixture, then coat with the bread crumb mixture.
- Place on the prepared baking sheet. Spray lightly with cooking spray.
- Bake for 20-25 minutes, or until golden brown and crispy.
- Serve with marinara sauce or your favorite dipping sauce.
Nutrition: Calories 114kcal, Carbohydrates 11g, Protein 8g, Fat 5g, Saturated Fat 2g, Cholesterol: 99mg, Sodium 497mg, Potassium 503mg, Fiber 2g, Sugar 6g, Vitamin A 650IU, Vitamin C 22mg, Calcium 120mg, Iron 2mg
This recipe is courtesy of jerseygirlcooks.com
Read More: Eggplant Lasagna Keto: A Delicious Low Carb Alternative
How Do You Keep Zucchini From Getting Soggy When Roasting
There are several reasons why zucchini gets soggy when you roast it. Here are some solutions for you:
Mistake 1: Not Preheating The Oven
If you don’t preheat your oven, the slow climbing heat will cause the zucchini’s moisture to wick out and the vegetables will cook in their own juices, leading to soggy results. Always preheat your oven before roasting vegetables.
Mistake 2: Overcrowding The Pan
Crowding vegetables too closely prevents hot air from circulating around them, leading to steamed vegetables instead of roasted ones. Make sure to give your vegetables enough space on the pan so they can roast evenly.
Divide your zucchini coins into two separate sheet pans if necessary.
Mistake 3: Overbaking
Zucchini has a high water content, so it can quickly go from perfectly roasted to overcooked and soggy. To prevent this, keep a close eye on your zucchini while it’s roasting. Remove the zucchini from the oven as soon as it’s tender and starting to brown.
Alternatively, make oven fried zucchini sticks. As they have a larger surface area, they will cook faster and are less likely to overcook.
Mistake 4: Not Using A Baking Rack
While a sheet pan is essential for roasting vegetables, using a baking rack on top of the pan will help to further circulate hot air around the zucchini and prevent it from getting soggy.
Arrange your zucchini coins on the baking rack, making sure they’re not touching each other, and roast as usual. These tips should help you achieve perfectly roasted zucchini every time!
How Do You Reheat Fried Zucchini In The Oven?
Preheat your oven to 350 degrees Fahrenheit. Place the fried zucchini on a baking sheet and bake for 5-10 minutes, or until heated through. You can also reheat fried zucchini in the microwave, but be careful not to overcook it or it will become soggy.
If you wish to cinch your waist, tone up your bat wings, blast away the muffin top – our fitness app was created to cater to all your needs! BetterMe won’t give excess weight a chance!
Do You Peel Zucchini Before Roasting?
No, you do not need to peel zucchini before roasting. The skin of the zucchini is edible and contains nutrients that are good for you. Just make sure to wash the zucchini well before cooking.
Do You Need To Salt Zucchini Before Roasting?
No, you do not need to salt zucchini before roasting. The vegetables will release some of their moisture as they roast, and the salt will help to draw out even more water, leading to soggy results. If you want to add flavor to your roasted zucchini, try sprinkling on some herbs or spices or even salt, but after it comes out of the oven.
What Temperature Should Zucchini Be Cooked At?
Zucchini should be roasted at a high temperature, between 400 and 425 degrees Fahrenheit. This will help to create a crispy exterior while keeping the zucchini tender on the inside.
Are Zucchini Fries Healthier Than French Fries?
Zucchini fries are a healthier alternative to French fries as they contain less fat and calories. They are also a good source of fiber and vitamins. However, fried zucchini still contains some fat and calories, so it should be eaten in moderation. Baked zucchini fries would be an even better choice.
Below are some specific health benefits of zucchini that make them a healthier choice than French fries:
Rich In Many Nutrients
According to the USDA, 100 grams of cooked zucchini contains the following nutrients (13):
- Calories: 17
- Protein: 1 gram
- Fat: less than 1 gram
- Carbs: 4 grams
- Sugar: 1 gram
- Fiber: 1 gram
- Vitamin A: 1% of the Daily Value (DV)
- Manganese: 10% of the DV
- Vitamin C: 4% of the DV
- Potassium: 4% of the DV
- Magnesium: 3% of the DV
- Vitamin K: 4% of the DV
- Folate: 2% of the DV
- Copper: 5% of the DV
- Phosphorus: 2% of the DV
- Vitamin B6: 3% of the DV
- Thiamine: 3% of the DV
Rich In Antioxidants
Antioxidants are compounds that may help protect your cells from damage. They scavenge harmful toxins known as free radicals, which can damage cells and might contribute to chronic diseases like cancer, heart disease and Alzheimer’s (1).
Zucchini is an excellent source of antioxidants (17).
In fact, it contains several different kinds, including carotenoids like zeaxanthin and lutein (17). These two nutrients are important for eye health and have been linked to a lower risk of age-related macular degeneration, the leading cause of blindness in older adults (12).
Read More: 3 Ingredient Peanut Butter Fat Bombs | Healthy Snacks For Keto
May Aid Weight Loss
Zucchini is low in calories but high in water and fiber, both of which are beneficial for weight loss.
Water and fiber are two of the most filling nutrients and can help you eat fewer calories overall. In one study, people who drank 500 ml water (two 8-oz glasses) before each meal and were on a reduced calorie diet lost more weight than those who were on the reduced calorie diet but did not drink the water before meals (18).
A review from 2001 found that increasing fiber intake by 14 grams per day may reduce calorie intake by 10%. This could lead to a weight loss of about 4 pounds (1.9 kg) over a period of just under four months (5).
May Help Manage Diabetes
Zucchini may be beneficial for people with diabetes. This is because it has a low glycemic index (GI), which is a measure of how quickly blood sugar levels rise after eating a food (14).
A food with a high GI raises blood sugar levels more than a food with a low or medium GI. This is important for people with diabetes because knowing how a food may affect their blood sugar can help them control their blood sugar levels (14).
May Boost Heart Health
Zucchini may help to improve heart health. This is because it’s high in potassium, a nutrient that helps to regulate blood pressure (15).
High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease. In fact, it’s estimated that having high blood pressure increases your risk of heart disease significantly (9).
May Promote Healthy Digestion
Zucchini may help promote healthy digestion. This is because it’s a good source of fiber, which is important for regular bowel movements.
Fiber adds bulk to stool and helps food move through the digestive system more quickly. This can help to prevent constipation and other digestive issues like hemorrhoids and diverticulosis (6).
Zucchini also has soluble fiber, which plays a role in promoting a healthy gut microbiome. This type of fiber is fermented by friendly gut bacteria and produces short-chain fatty acids that are beneficial for gut health (12).
May Support Brain Health
Zucchini may help to support brain health. This is because it contains choline, a nutrient that’s important for cognitive function (16).
Choline is involved in the production of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that helps with learning and memory. It’s also necessary for the structure and function of cell membranes (16).
Research shows that choline deficiency can lead to reduced cognitive performance and memory loss. Ensuring adequate choline intake may help to prevent these effects (16).
BetterMe is your fast-track ticket to a long-lasting weight loss! Tailor your fitness journey and maximize your results with just a couple of swipes!
Possible Side Effects
Zucchini is generally safe to eat and has few side effects. However, some people may experience gas or bloating after eating foods that contain soluble fiber, like zucchini.
Soluble fiber can ferment in the gut and produce gas (7). If you’re sensitive to this effect, it may be best to avoid foods that are high in soluble fiber, or increase your intake slowly as your digestive system adjusts.
Zucchini is also a member of the cucurbitaceae family. This family also includes cucumbers, squash, and watermelons. These fruits are all high in a compound called cucurbitacin E.
Cucurbitacin E is thought to have a bitter taste and may cause stomach pain or discomfort for some people (4). If you’re sensitive to cucurbitacin E, it’s best to avoid eating zucchini and other cucurbitaceae fruits.
Conclusion
Oven fried zucchini is a delicious and easy to make low carb side dish. Zucchini is coated in a bread crumb mixture and then baked until golden brown and crispy. Serve with marinara sauce or your favorite dipping sauce.
To prevent soggy results, be sure to preheat your oven, use a baking rack, and don’t overcook the zucchini. You can also reheat leftovers in the oven or microwave.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- Antioxidants (n.d., harvard.edu)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: An Overview(2005, pubmed.gov)
- Crispy Oven Fried Zucchini Chips (2020, jerseygirlcooks.com)
- Cucurbitacins in plant food (2006, diva-portal.org)
- Dietary fiber and weight regulation (2001, pubmed.gov)
- Effect of dietary fiber on constipation: a meta analysis (2012, pubmed.gov)
- Effects of High-Fiber Diets and Macronutrient Substitution on Bloating: Findings From the OmniHeart Trial (2020, nih.gov)
- Evaluation of Cucurbita pepo L. lipophilic extract on androgen-induced prostatic hyperplasia (2006, researchgate.net)
- High Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease (2019, ahajournals.com)
- Lycopene for the prevention and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer: a systematic review (2012, pubmed.gov)
- Potential Role of Carotenoids as Antioxidants in Human Health and Disease (2014, nih.gov)
- Review article: prebiotics in the gastrointestinal tract (2006, pubmed.gov)
- Squash, summer, zucchini, includes skin, frozen, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt (2019, usda.gov)
- The Effect of Dietary Glycaemic Index on Glycaemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials (2018, nih.gov)
- The effect of potassium supplementation on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis (2016, pubmed.gov)
- The relation of dietary choline to cognitive performance and white-matter hyperintensity in the Framingham Offspring Cohort1,2,3,4 (2011, nih.gov)
- Use of visible and near-infrared spectroscopy for predicting antioxidant compounds in summer squash (Cucurbita pepo ssp pepo) (2014, pubmed.gov)
- Water Consumption Increases Weight Loss During a Hypocaloric Diet Intervention in Middle-aged and Older adults (2009, nih.gov)