Due to the skyrocketing popularity of healthy lifestyles, fitness, and weight loss, the media is swarming with hundreds of various methods for toning up and shedding pounds. For those whose goal is to lose a couple of inches from their waist, the choice of a correct nutritional and workout plan can become more difficult with the appearance of each new popular diet.
As you’re probably aware, everyone has a different body type and requires a different approach to losing weight or packing on muscle. And such a large number of fad diets only confuses people and may even lead to health damage.
ntermittent fasting is just one of these current trending diets, however there is some research backing this method. The 18:6 intermittent fasting method in particular may show results that you can benefit from!
What Is Intermittent Fasting?
The main rule of intermittent fasting nutritional concept is to limit the time when you can eat during a day or a week (11).
Different types of intermittent fasting have an eating window when you can consume the food of your choice.
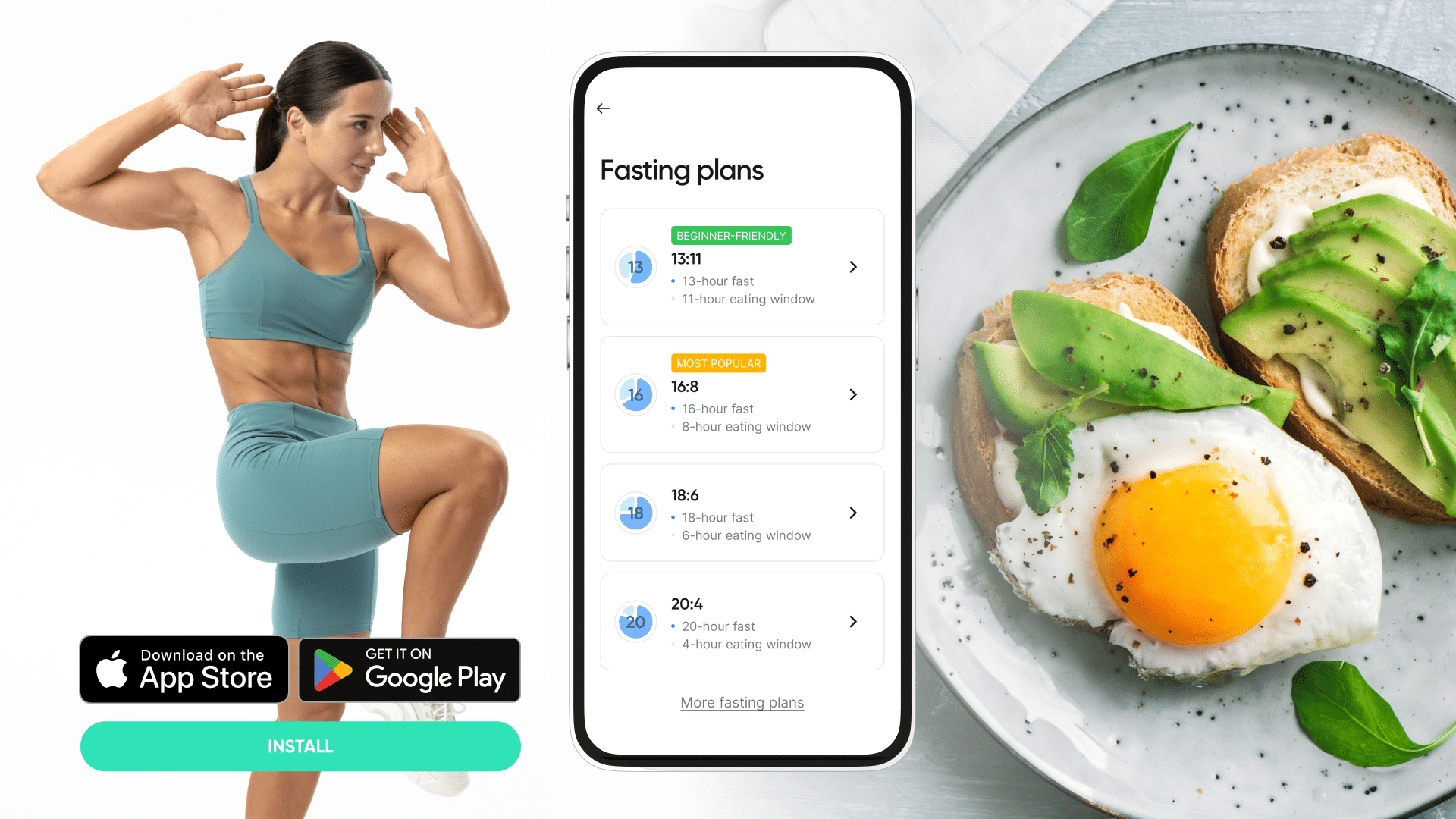
Types of Intermittent Fasting (15):
5:2 fasting
5:2 fasting allows you to eat a normal diet for 5 days and you fast on 2 other days of the week, restricting your daily energy consumption to 600 calories for men and 500 for women.
16:8 fasting
This type of fasting requires you to fast for 16 hours a day and consume all your calories during the remaining 8 hours. Usually, people choose one of the following eating windows: 9 a.m.–5 p.m., 10 a.m.–6 p.m., or noon–8 p.m. (1)
Alternate day fasting
This is as simple as it sounds. You eat your regular diet for a day, then restrict your energy intake the next day (18).
18:6 intermittent fasting
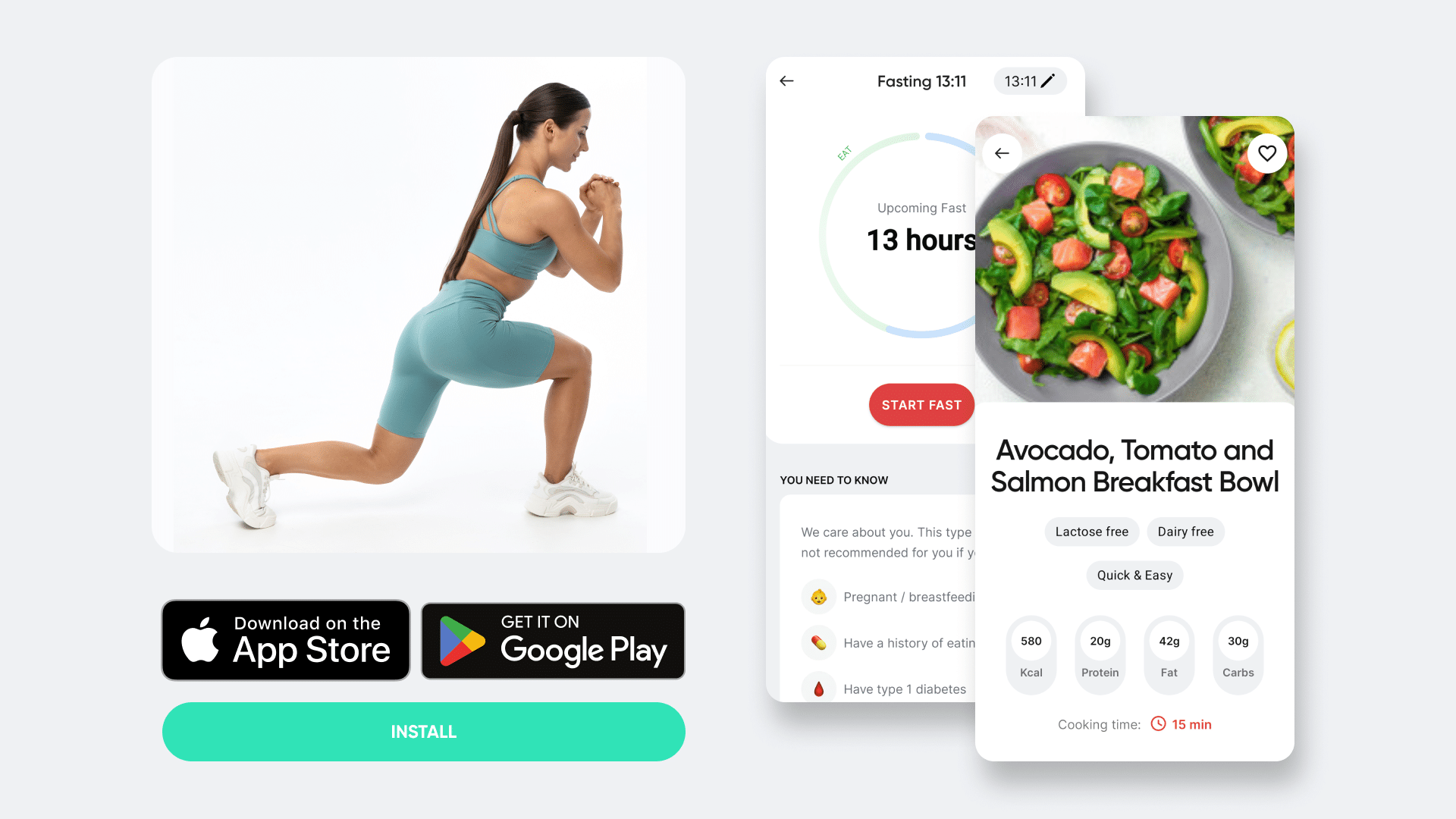
This type of fasting, which is the main topic of this article, is similar to 16:8 intermittent fasting, but your eating window is smaller, so you need to manage to consume all your calories during 6 hours of your day. In this period, you can eat 2 full meals and a snack.
You can choose to either skip breakfast and have an early dinner, skip dinner and have a late lunch, or basically adjust your eating schedule to your personal preference with the condition that your meals should be within the 6-hour window.
Some people are skeptical about such an eating approach and some wonder, “Is 18:6 intermittent fasting safe?” The answer is yes. This type of fasting is safe, as long as you eat enough calories during your eating hours.
If you struggle to even flirt with the idea of giving up your favorite foods or working out till your legs give way – BetterMe app is here to breathe a fresh perspective into the way you view the weight loss process! Check out the app and experience the fun side of fitness and dieting with BetterMe!
What Is the Best Intermittent Fasting Schedule?
The best intermittent fasting schedule is the one you’re able to stick with in the long term. This is because you’ll only see results from intermittent fasting if you’re consistent. It’s not a quick fix or a crash diet – it’s a lifestyle change.
There are many different ways to approach intermittent fasting and the best schedule for you may depend on your individual needs and preferences.
Some people prefer to fast for 16 hours and then have an 8-hour eating window every day, while others may choose to fast for longer periods, such as 20 hours with a 4-hour eating window. The key is finding what works best for your body and fits into your daily routine.
For example, if you’re someone who enjoys breakfast and feels more energized when you eat earlier in the day, a 16:8 schedule may work well for you. However, if you tend to eat larger meals and feel satisfied with only two meals a day, a longer fasting period such as 20:4 may be more suitable.
We also advise that you work your way up to longer fasting periods, as it can be challenging for your body to adjust if you’ve never fasted before. Start with a 12-hour fast and gradually increase the length of your fasting window until you find what works best for you.
Is an 18-Hour Fast Better Than 16?
Fasting for 18 hours a day for a month may have more pronounced health benefits than fasting for 16 hours a day. This is due to the longer period of time your body is in a fasted state, which may allow it to fully reap the benefits of intermittent fasting.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that consistency is key when it comes to intermittent fasting. It’s important to find a schedule that you can maintain in the long term rather than trying to push your body to fast for longer periods of time. If you find an 18-hour fast too challenging, then stick with a 16-hour fast and focus on being consistent with it.
As time goes on and your body becomes more accustomed to fasting, you may find that you’re able to increase the length of your fasts. However, you should always listen to your body and make sure you’re not pushing yourself too hard.
What to Eat when Following 18:6 Intermittent Fasting
People often ask, “What can I have while intermittent fasting 18:6?” Obviously, you’re not allowed to eat anything during your 18-hour fasting period. And for the rest of the day, you must stick to a healthy well-balanced diet if you want to improve your wellness and slim down a couple of sizes. Try to avoid sugary foods and drinks, junk food, and other products filled with unhealthy components such as trans and saturated fats and refined carbohydrates.
Your diet should consist of fruits, vegetables (fresh and fermented), lean meats, poultry, fish and seafood, eggs, dairy, beans and legumes, nuts and seeds, and whole grains. Make sure you consume enough essential nutrients, including:
Protein
Proteins are the building blocks of your body. Without protein, your body won’t be able to function properly. That’s why it’s important to consume plenty of this macronutrient.
If you want to lose weight, you should eat plenty of protein, as it prolongs the feeling of satiety and ensures that you burn fat and don’t break down muscles (2).
There is plenty of protein in meats and poultry, fish and seafood, and dairy. Rich plant sources of protein include beans, legumes, and nuts.
Read more: Green Tea Intermittent Fasting: Benefits and Side Effects
Healthy fats
Mono- and polyunsaturated fats, which are known as healthy fats, are an inseparable part of a balanced diet.
Experts recommend that you should reduce your consumption of unhealthy fats to 10% of your daily energy intake and substitute them with unsaturated fats (8). You can find healthy fats in fish and seafood, avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
Complex carbohydrates
Complex carbs are the main source of energy for the human body and can also promote weight loss. Fiber prolongs the feeling of satiety and adds to the glycemic index of a food (7). The best sources of complex carbs are whole-grain products, fruits, and vegetables.
Vitamins and minerals
Micronutrients are as important as macronutrients when it comes to your health and the proper functioning of your body.
Each vitamin and mineral has its purpose and contributes to your wellness. It’s important to consume only the required amount of each micronutrient, as overconsumption of vitamins and minerals can have negative consequences.
Water
The human body cannot survive without water. Proper hydration is incredibly important and promotes better skin, weight loss, and overall wellness (19).
You can try drinking 8 glasses of water a day, but the best indicator is your thirst, so drinking whenever you feel like it is the best choice.
Whether you’re a workout beast or just a beginner making your first foray into the world of fitness and dieting – BetterMe has a lot to offer to both newbies and experts! Install the app and experience the versatility first-hand!
18:6 Intermittent Fasting Benefits
Intermittent fasting has proven to be quite effective at helping people lose weight, managing blood glucose levels, and learning how to manage their time properly (3). As different types of this dietary approach have similar benefits, it is a matter of preference for which one to follow.
Here are some of the main health benefits of intermittent fasting (20):
Reduces inflammation
Studies have suggested that intermittent fasting may be effective at helping you reduce inflammation and improve neurological and pulmonary conditions associated with inflammation (17), such as asthma, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke.
Lowers the risk of type II diabetes
As being overweight and obese are two of the main risk factors for developing type II diabetes, intermittent fasting can have an effect on diabetes prevention due to its weight loss effects. It can also potentially influence other factors that are linked to an increased risk of diabetes.
A 2014 study showed that intermittent fasting can lower blood glucose and insulin levels in people at risk of diabetes (13).
Promotes the prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Studies have implied that intermittent fasting may improve your heart health and reduce the risk of heart disease. A 2016 review showed that this type of eating pattern could reduce blood pressure, heart rate, LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides, all of which add to the risk of cardiovascular diseases (10).
May reduce the risk of cancer
Several animal studies have suggested that intermittent fasting may reduce the risk of cancer (5). Such an effect may be the aftermath of weight loss, reduced inflammation, and insulin levels, which are caused by this eating pattern.
A 2019 review of people with cancer found that fasting reduced some of the side effects of chemotherapy and increased its effectiveness. The review suggested that fasting may deprive cancer cells of nutrients, which makes them more susceptible to the toxins in chemotherapy (6).
18:6 Intermittent Fasting Weight Loss
One of the main benefits of 18:6 intermittent fasting is weight loss. There are many cases of weight loss success with intermittent fasting 18:6, in addition to those where people aren’t satisfied with the 18:6 intermittent fasting results. The result is dependent on how well you adjust to this eating pattern and your choice of food.
There are several ways in which intermittent fasting can help you lose weight, including (9):
Increase in HGH
Intermittent fasting can lead to an increase in human growth hormone HGH (16), which helps the body burn fat and grow muscle (14).
Lower insulin levels
This eating approach has the potential to reduce the levels of insulin, making it easier for the body to use stored fat.
Reduced energy intake
Eating during a set period can help you reduce your energy intake and may boost metabolism.
Various studies have shown that intermittent fasting is efficient at helping people lose weight (12). In some cases, it even had the same effect as conventional dieting with the reduction of daily food intake.
Read more: Intermittent Fasting and Running: A Winning Combination or a Terrible Mistake?
FAQs
With an 18:6 intermittent fasting diet, how many calories can you eat to lose weight?
You can eat to your fill, without restricting any specific food groups. There is no calorie limit during the eating window because intermittent fasting isn’t a diet, but an eating pattern.
Therefore, there are no strict rules regarding how much food you can eat during your eating window. By restricting your meals to specific hours, you’re automatically limiting the amount of food you consume, which can lead to reduced calorie intake and weight loss.
However, making the right food choices during your eating window can further enhance the benefits of intermittent fasting. This includes choosing whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in nutrients and avoiding highly processed and sugary foods (4).
How fast can you lose weight on intermittent fasting 18:6?
You’ll start to lose weight in 4-8 weeks with an 18:6 intermittent fasting schedule, depending on your individual factors, such as body composition and activity level. However, initial weight loss may be due to water weight and not necessarily fat loss.
As you fast for longer periods, your body may start to burn fat for energy, which leads to sustainable weight loss.
How many days in a row can you do 18/6 intermittent fasting?
You can follow the 18/6 intermittent fasting schedule every day if you choose to. If you’ve worked your way up from a shorter fasting window, your body may be able to handle it without any negative effects.
Over time, you may notice your progress stagnates or you start to feel fatigued from fasting every day. In that case, it’s perfectly fine to take a break and switch to a different intermittent fasting schedule for a few days.
The key is finding what works best for your body and being consistent with it in the long term.
What foods won’t break a fast?
There’s no food that won’t break a fast. By being in a fasted state, your body is getting zero calories. However, some beverages have a lower impact on insulin levels and can be consumed during the fasting window without interrupting the benefits of intermittent fasting. They’re called zero- or low-calorie options and include black coffee, tea, and sparkling water.
It’s important to note that even though these beverages are allowed during the fasting period, it’s essential to remain hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. In addition, you should avoid adding any sugar or creamer to your drinks as they can spike insulin levels and break your fast.
Regarding solid foods, it’s best to stick with water and calorie-free beverages during the fasting window.
Consuming any calories, even in small amounts, will break your fast and can disrupt the metabolic processes that occur during a fasted state. So you should save your meals for your eating window to maximize the benefits of intermittent fasting.
The Bottom Line
18:6 intermittent fasting can be a great option for those who want to slim down. It’s like an advanced version of 16:8 intermittent fasting and has similar benefits, including weight loss, reduced risk of type II diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and reduced inflammation.
The only difference between these two types of fasting is that 18:6 intermittent fasting only includes a 6-hour eating window. As a person will most likely only eat 2 complete meals during this period, some people may find it difficult to stick to this eating pattern.
Those who follow this nutritional approach must remember that they should consume all the required calories during the eating window. This is why you need to carefully plan your meals beforehand if you follow 18:6 intermittent fasting.
Ensure that you consume all the essential nutrients, such as protein, healthy fats, complex carbs, vitamins, and minerals and drink plenty of water. Remember that before you start to follow any new nutritional plan, it’s important that you consult a dietitian or a doctor.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- A guide to 16:8 intermittent fasting (2020, medicalnewstoday.com)
- A high-protein diet for reducing body fat: mechanisms and possible caveats (2014, biomedcentral.com)
- Beneficial effects of intermittent fasting: a narrative review (2023, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Counting calories: Get back to weight-loss basics (2020, mayoclinic.org)
- Effect of fasting on cancer: A narrative review of scientific evidence (2022, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Effects of short-term fasting on cancer treatment (2019, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Health benefits of dietary fiber (2009, academic.oup.com)
- Healthy diet (2020, who.int)
- How to begin intermittent fasting (2019, medicalnewstoday.com)
- Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes (2016, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Intermittent fasting: What are the benefits? (2020, mayoclinic.org)
- Intermittent fasting and weight loss (2020, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Intermittent fasting vs daily calorie restriction for type 2 diabetes prevention: a review of human findings (2014, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Normal Physiology of Growth Hormone in Adults (2019, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Seven Ways to do Intermittent Fasting (2020, medicalnewstoday.com)
- The effect of prolonged fasting on levels of growth hormone-binding protein and free growth hormone (2012, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The regulatory effect of intermittent fasting on inflammasome activation in health and disease (2023, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The ultimate beginner’s guide to intermittent fasting (2020, medicalnewstoday.com)
- Water, hydration, and health (2010, academic.oup.com)
- What are the benefits of intermittent fasting? (2018, medicalnewstoday.com)