When you think of getting your vitamins, you usually think of vitamin C and other common nutrients. But there’s one vitamin that should be getting more attention– vitamin K2. This vitamin is crucial for several bodily functions, but unfortunately often overlooked due to its relative obscurity. This three-part guide is designed to help you learn about vitamin K2, its forms and functions, and the best sources of it. We’ll answer questions you might have after, like, how much of it you need and how to make sure you’re getting enough. So buckle up as it’s time for a crash course in vitamin K2!
What Is Vitamin K2?
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin, which means that it’s stored in your body’s fatty tissues and it can take a while for your body to get rid of it. There are two forms of Vitamin K: K1 (phylloquinone) and K2 (menaquinones) (22). Both are important for your health, yet they have some differences.
Both types of vitamin K help to activate proteins involved in blood clotting, bone health, and heart health – however vitamin K2 may be better absorbed and may circulate longer in the body, possibly increasing its effects (15, 25).
While K1 is found in leafy green vegetables and plant oils, K2 can be harder to come by. This is because K2 is mostly made by bacteria in the intestine, and is only found in a few animal products and fermented foods, such as natto, cheese and egg yolks.
What’s Vitamin K2 Good For?
K2 is essential for several bodily processes, and we’ll take a closer look at each one below:
1. Bone Mineralization
Bone mineralization is a process that helps your bones absorb calcium and other minerals. K2 aids in this process by activating proteins, specifically Matrix GLA Protein (MGP) and Osteocalcin, that help your bones get the nutrition they need to stay strong (19).
Will this process happen without K2? Yes, but not as effectively. Some studies have suggested that people with lower dietary intake of K2 tend to have a higher risk of fractures, or that supplementing with vitamin K may increase bone mineral density or reduce the risk of fractures in those with osteoporosis (10). The research is not entirely conclusive yet, however.
Who benefits from this the most? K2 may be especially important for older people and post-menopausal women, as they’re at a higher risk of bone density loss. This is not to say that young people should skip out on their K2 either; getting enough vitamin K2 from childhood can help build strong bones for life.
Read More: Discover 6 True Vitamin E Benefits For Hair And Scalp
2. Calcification And Heart Health
K2 also helps regulate calcification, which is a process that occurs when calcium and other minerals build up in body tissues and organs. This can cause serious health problems, such as hardened arteries and plaque buildup in the heart (21).
K2 helps keep calcification levels under control by activating proteins that reduce the buildup of calcium and other minerals. This helps keep your heart healthy and can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease (24). Vitamin K1 does these things as well, but K2 may be better at it.
It doesn’t just end there! As K2 still does more for heart health. Studies have also found that it may help reduce inflammation and bad cholesterol, both of which are important in maintaining a healthy heart.
3. Cancer Prevention
K2 has been linked to cancer prevention as well. Studies have found that people who get enough K2 have a lower risk of certain forms of cancer, such as prostate, lung, and liver (16).
It’s believed to help reduce cancer risk by activating proteins that help break down mutated cells, which can otherwise lead to the development of cancer.
It also has anti-inflammatory properties that help protect against cell damage, which might further reduce cancer risk.
4. Improved Brain Function
K2 might also help improve brain function. Limited studies have found that people with higher levels of K2 tend to have better cognitive function and score higher on cognitive tests, although the overall research is not conclusive (20).
This may be because vitamin K helps produce sphingolipids, which are a type of fat found in the brain (20). Sphingolipids play an important role in cell communication and memory, so getting enough K2 might help enhance your mental clarity and focus (18).
5. Hope For Parkinson’s Disease
Research into defective mitochondria and vitamin K2 also suggests that it may help improve energy production in people with Parkinson’s Disease (9). This offers hope to those struggling with Parkinson’s. Although, more research is needed to explore the connection further.
BetterMe app will kick you out of the mental funk, shake off your extra weight, rid you off your energy-zapping habits, and help you sculpt the body of your dreams. Intrigued? Hurry up and change your life for the better!
6. Elastin Production
K2 also helps your body produce elastin, a protein that’s responsible for keeping skin and other organs flexible (1). Elastin is especially important for skin health since it helps keep your skin looking firm and youthful. It combats the effects of aging and helps your skin stay wrinkle-free (4).
7. Dental Health
K2 also plays an important role in dental health. It helps strengthen teeth and bones in your jaw, which can reduce the risk of cavities and tooth decay (2).
It also helps produce saliva, which is important for keeping your mouth clean and healthy (23). Saliva helps neutralize acids in the mouth and helps keep bacteria levels under control.
Read More: Vitamin B12 Benefits For Men Who Want Vitality And Prime Well-Being
Where Can You Get Vitamin K2?
Now that you know the possible benefits of vitamin K2, let’s look at some of the best sources.
First, we should highlight the relationship between gut bacteria and K2. The bacteria in your gut have the ability to convert K1 into MK-4 and MK-7, which are forms of vitamin K2 that your body can use (6).
So say you consume leafy greens, they are a good source of K1 but lack K2. Your gut bacteria can convert some of the K1 into K2, so you still get a bit of the vitamin from eating leafy greens.
Having a healthy balance of gut bacteria is important for your overall health, but it’s especially crucial for getting enough Vitamin K2 (17). This means, eating foods that encourage healthy gut bacteria, such as fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi.
You can also take probiotic supplements to support your gut.
Now, if you’re looking for a good source of Vitamin K2, there are several different forms of the vitamin that you can find in the foods below:
Natto
The richest source is natto, which is a fermented soybean dish popular in Japan. It is made by boiling soybeans with a bacteria called Bacillus subtilis, which helps the fermenting process and increases vitamin K2 production (14).
Natto typically contains vitamin K2 in the form of MK-7, which is one of the most bioavailable forms. It also has some MK-4, which is another form of K2.
Not sure how to eat natto? It’s a bit of an acquired taste. Natto is usually served with soy sauce, mustard, and scallions over steamed white rice. You can also add it to a breakfast bowl with eggs or use it as a topping for salads.
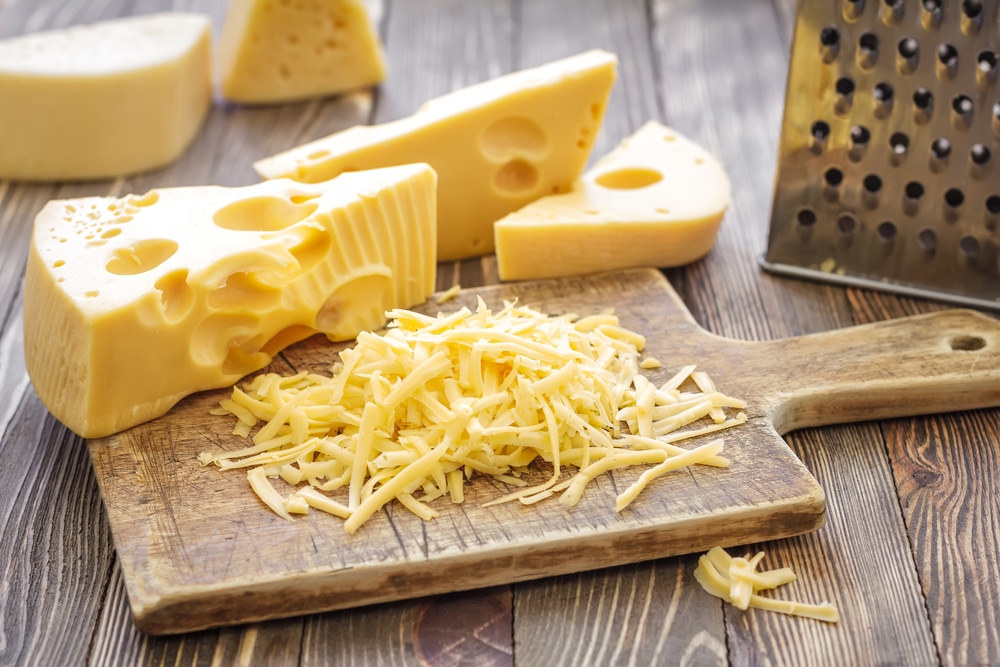
Cheeses
Soft cheeses such as Brie and Gouda are good sources of vitamin K2. They are major sources of MK-4, as are other animal-based foods like egg yolks and the organs of animals (3).
It is important to note, however, that the Vitamin K2 content of animal products may depend on how the animals were fed. Animals that are grass-fed instead of grain-fed are believed to have higher levels of Vitamin K2.
Lean and toned up body isn’t just a far-fetched fantasy. Check out the BetterMe app and watch it propel your weight loss journey into high gear!
Milk And Yogurt
Milk and yogurt are also good sources of Vitamin K2, though the levels vary between brands (13). The best way to get enough Vitamin K2 in your diet is to look for brands that use grass-fed milk and yogurt, as they are thought to have higher levels of the vitamin.
Note that full-fat milk and yogurt are usually higher in vitamin K2 than low-fat or nonfat versions, so look for those if you’re looking to get an extra boost.
Sauerkraut And Kimchi
Fermented vegetables, such as sauerkraut and kimchi, are also good sources of vitamin K2 (11). Both of these are made by fermenting vegetables with beneficial bacteria, which increases the vitamin K2 content.
It helps that they are fiber-rich, so they are great for supporting your gut microbiome, which in turn supports your Vitamin K2 levels. You can eat these as a side dish with meals, a hearty stew, or eaten in a spoonful every now and then.
Vitamin K2 Supplements
It’s best to get your vitamin K2 from whole foods whenever possible. If you do decide to take a supplement, make sure to get one that is high-quality. Many vitamin K2 supplements are synthetic, meaning they don’t come from real food sources. Look for one that uses natural forms of vitamin K2, such as MK-4 or MK-7.
How Often Should You Take Vitamin K2?
Research suggests that getting some form of vitamin K2 through food every day is beneficial for your health (9). That’s partly because these foods, in addition to having vitamin K2, are usually packed with other nutrients and beneficial compounds.
How much of these foods you need in order to get your daily dose of vitamin K2 depends on the amount that is already in your diet. For instance, if you eat a lot of soft cheeses, you may need to include fewer other food sources in order to get a healthy daily amount.
At the moment, there is no recommended daily amount for vitamin K2. Based on the recommended amount for vitamin K1, which is 90 to 120 mcg per day, some experts suggest that we should be getting around 30 to 45 mcg of vitamin K2 per day (25).
Is There A Best Time To Take Vitamin K2?
There is no scientific evidence that suggests taking vitamin K2 at a certain time of day is more beneficial than another. However, if you are taking vitamin K2 as a supplement, it’s best to take it with food to help ensure better absorption.
Is There Proof Of Vitamin K2 For Weight Loss?
There is not enough scientific evidence to support an association between vitamin K2 intake or supplementation and weight loss at this time.
Conclusion
When it comes to getting enough vitamin K2, the best approach is to get creative with your diet. Eating a variety of fermented foods, such as natto, sauerkraut, and kimchi, is a great way to get them.
Soft cheeses and other animal-based foods can also be good sources of the vitamin, possibly depending on how the animals were raised. And if you do decide to take a supplement, make sure it’s high-quality and uses natural forms of the vitamin.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- [Elastin metabolic indices in various body allowances of vitamin K] (1983, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- A hypothetical role for vitamin K2 in the endocrine and exocrine aspects of dental caries (2015, sciencedirect.com)
- A narrative review of vitamin K forms in cheese and their potential role in cardiovascular disease (2022, onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- Clinical Relevance of Elastin in the Structure and Function of Skin (2021, academic.oup.com)
- Dietary Alteration of the Gut Microbiome and Its Impact on Weight and Fat Mass: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (2018, mdpi.com)
- Dietary vitamin K is remodeled by gut microbiota and influences community composition (2021, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Effect of vitamin K2 administration on depression status in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized clinical trial (2022, biomedcentral.com)
- Effects of MK-7 Supplementation on Glycemic Status, Anthropometric Indices and Lipid Profile in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial (2020, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Growing Evidence of a Proven Mechanism Shows Vitamin K2 Can Impact Health Conditions Beyond Bone and Cardiovascular (2021, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Influence of Vitamin K on Bone Mineral Density and Osteoporosis (2020, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Menaquinones, Bacteria, and Foods: Vitamin K2 in the Diet (2016, intechopen.com)
- Molecular Pathways and Roles for Vitamin K2-7 as a Health-Beneficial Nutraceutical: Challenges and Opportunities (2022, frontiersin.org)
- Multiple Vitamin K Forms Exist in Dairy Foods (2017, sciencedirect.com)
- Nutritional Health Perspective of Natto: A Critical Review (2022, hindawi.com)
- Phytonadione (Vitamin K1) (2021, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Research progress on the anticancer effects of vitamin K2 (2018, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Role of Vitamin K in Intestinal Health (2022, frontiersin.org)
- Sphingolipids: membrane microdomains in brain development, function and neurological diseases (2017, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The Dual Role of Vitamin K2 in “Bone-Vascular Crosstalk”: Opposite Effects on Bone Loss and Vascular Calcification (2021, mdpi.com)
- The Relationships Between Vitamin K and Cognition: A Review of Current Evidence (2019, frontiersin.org)
- Vascular Calcification: Pathophysiology and Risk Factors (2014, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Vitamin K (2023, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Vitamin K2 and its Impact on Tooth Epigenetics (2016, intechopen.com)
- Vitamin K Dependent Proteins and the Role of Vitamin K2 in the Modulation of Vascular Calcification: A Review (2014, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Vitamins K1 and K2: The Emerging Group of Vitamins Required for Human Health (2017, hindawi.com)