Protein powder has become relatively common in the fitness world, thanks to its numerous fitness benefits, such as promoting muscle gain. But discovering the right protein powder is tricky. We are all different, and our bodies demand different ratios of such ingredients, depending on your fitness goals and other factors. It may feel like if you make one wrong pick, and you can bid your fitness goals goodbye. Of all varieties of protein powder, two of the most common are whey and pea protein powder. They both have a long list of long-term and short-term benefits. But which is the best addition to a health and fitness plan? Find out as we compare and contrast pea protein vs whey protein powder.
Pea Vs Whey Protein Powder
If you frequent the gym, you perhaps have heard of the common debate of which is better between whey and pea protein powder. But to understand the best between the two, you must understand what each protein powder offers. So, let us first familiarize ourselves with each protein powder.
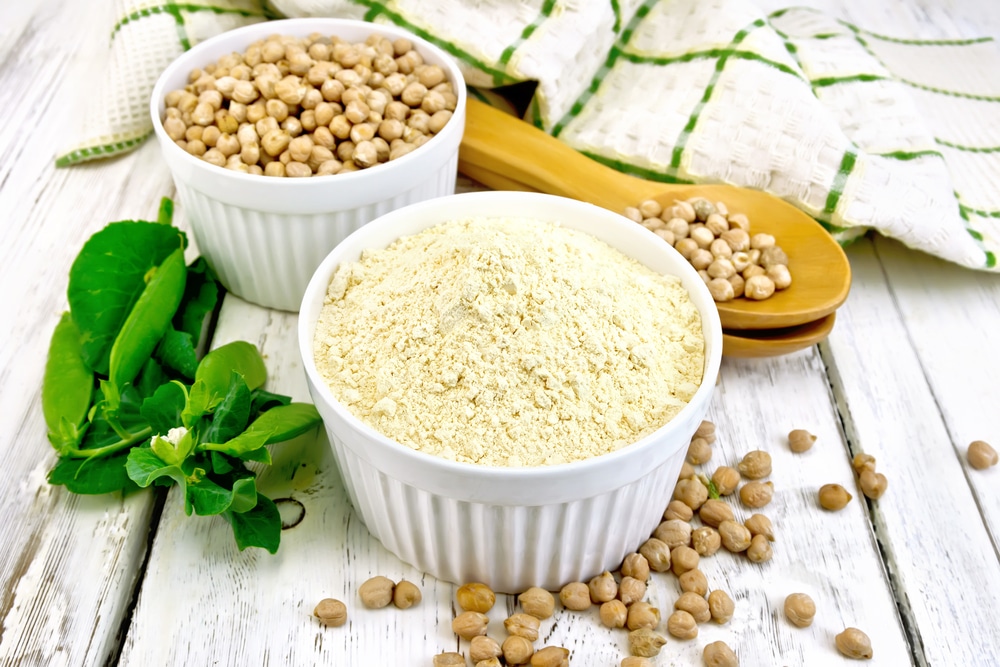
What Is Pea Protein Powder?
As the name implies, it refers to protein powder obtained from peas. Peas are among the most nutritious types of legumes. They are packed with protein, antioxidants, and other vitamins and minerals.
They are suitable protein sources, making them excellent protein powder sources. Pea protein in and of itself is not a complete protein, meaning it does not contain significant amounts of all 9 essential amino acids. This isn’t a problem as long as you consume other varied sources of protein throughout the day. Some pea protein brands also modify their products to improve the amino acid profile.
Pea protein powder is relatively common in many households due to its many benefits. Evidence suggests it can help with (6), (4):
- Boosting your protein levels when added to smoothies or shakes.
- Easing digestion and promoting faster absorption of fiber.
- Providing you with all essential amino acids.
- Promoting weight loss by increasing satiety.
Interestingly, pea protein powder is prepared from different types of peas. Some of these include:
Green Peas (Garden Peas)
Perhaps these are the best known types of peas. They have low saturated fat content, cholesterol, and salt. Additionally, they are excellent sources of protein, fiber, vitamins B6, C, A, and K, magnesium, and folate (6). One cup (160 g) of cooked green peas provides (6):
- Calories- 134
- Protein- 8.6 g
- Carbs- 25 g
- Fiber- 8.8 g
- Fat- 0.4 g
Snow Peas
These are also referred to as sugar snap peas. They also have low cholesterol, saturated fat, and salt content. Similarly, they are rich in vitamins A, B6, C, and K, and magnesium, folate, and potassium (6). A cup (160 g) of these peas provides (6):
- Calories- 67
- Carbs- 11.3 g
- Protein- 5.2 g
- Fiber- 4.5 g
- Fat- 0.4 g
Black-Eyed Peas
These are also known as cowpeas. Mature cow peas are low in fat, salt, and cholesterol and are an excellent source of iron, fiber, protein, magnesium, folate, and thiamin (6). A cup serving (185 g) of frozen black-eyed peas provides (6):
- Calories- 278
- Carbs- 42.6 g
- Protein- 15.2 g
- Fat- 5. 88 g
- Fiber- 11.5 g
Read More: Brown Rice Protein: The Best Muscle Building Protein Powder?
Chickpeas
Chickpeas are relatively common in most households, thanks to their nutritional profile. They are low in cholesterol, saturated fat, and salt. However, they are excellent sources of folate, protein, manganese, fiber, and copper (6). A cup (164 g) of cooked chickpeas contains (6):
- Calories- 269
- Carbs- 45 g
- Protein- 14.5 g
- Fiber- 12.5 g
- Fat- 4.3 g
Pigeon Peas
The last type of peas is pigeon peas or red gram peas. They are low in natural sugars, saturated fat, carbs, and salt. However, they are a good source of protein, folate, fiber, manganese, and copper. A cup (168 g) of cooked, mature red gram peas contains (6):
- Calories- 203
- Carbs- 39 g
- Protein- 11.4 g
- Fiber- 11.3 g
- Fat- 0.6 g
Pea Protein Powder Varieties
You will find several varieties of this powder in the market. Some of them include (4):
- Pea Protein Isolate. This variety removes a significant number of other pea compounds, leaving behind only the protein (4).
- Pea Protein Concentrate. This variety still contains a decent amount of the other pea and high protein content (4).
- Pea Protein Hydrolysates. Hydrolysates are products that are partially made by using specific processes such as acid, heat, or enzymes to break down the protein (4).
How To Determine The Best Pea Protein Powder
There are several varieties of pea protein powder, as we have seen above. This explains why choosing even one variety of protein powder is tricky. But to help you choose a variety, there are several things you must consider. They include:
- Your Needs. Your needs highly influence the variety you pick, especially because of its nutritional profile. If, for example, you are following a high-protein diet, you would have to pick a pea protein powder variety with high protein content. So, consider your needs before making a purchase.
- Additives. Read through the labels to check the nutrition profile of each variety. It may be critical to you to avoid getting something that has high contents of artificial flavors, added sugars, colorings, or sweeteners.
- Flavor. It is also important to consider the flavor profile when picking your protein powder. But remember that pea protein powder is not sweet but has a nutty, grassy, or earthy taste. Taste a few brands before purchasing because you may settle on one and have a bad experience with it.
What Is Whey Protein?
It is the protein obtained from whey, which is the watery portion of milk that separates from the curds during cheese preparation. Typically, milk is made of two proteins, whey and casein (5). Whey is separated from the casein in milk during cheese making or formed as a by-product. Whey protein is a complete protein because it contains all 9 essential amino acids. Additionally, it has low lactose content (5).
Looking for a way to break the vicious cycle of weight loss and tone up all the jiggly parts? Watch the extra pounds fly off and your muscles firm up with the BetterMe app!
Types Of Whey Protein
There are three types of whey protein. They include:
- Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC). This type of whey protein has low amounts of carbs and fat (5). As for the protein levels, Medical News Today states that it varies depending on the WPC concentration. You will find that lower-end concentrates have 30% protein while the higher end has up to 90% (5).
- Whey Protein Isolate (WPI). WPIs differ from the other types, particularly because of how they are processed. According to Medical News Today, WPIs are further processed to remove all the fat and lactose. But they usually contain at least 90% protein (5).
- Whey Protein Hydrolysate (WPH). WPH is the “predigested” form of whey protein because it undergoes partial hydrolysis. This is a process which normally takes place in the GI tract and is required for the body’s absorption of protein. So, unlike WPIs and WPCs, WPHs do not require much digestion (5). Because of its improved digestibility and reduced allergen potential, you will find WPH mostly in infant formulas and medical protein supplements (5)
Health Benefits Of Whey Protein
Most people commonly use whey protein to boost their athletic performance and increase strength. But it has many other potential benefits, some of which you may not have explored. They include (5):
Aiding Weight Loss
Because of the many potential health problems associated with excessive weight gain and obesity, most people are trying to shed pounds. Besides exercise, a good diet is considered an effective way of trimming down. Whey protein is considered a great addition to any weight loss diet.
A 2008 study published in the Nutrition and Metabolism Journal found that 158 people on a reduced calorie diet who were given a whey protein drink lost significantly more body fat and less lean body mass than those given a control drink, although both groups lost weight.
Reduced Cancer Risk
Whey protein is believed to have anti-cancer properties that may make it a good supplement to be used along with medical and surgical cancer treatments. But that theory is based on the promising results of a study report, and more research is required to support it (5).
Better Athletic Performance
According to WebMD, individuals who regularly consume whey protein while regularly working out report increased muscle strength and better athletic performance (8). However, the two must be done consistently to bear fruits.
Reducing Cholesterol Levels
A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that participants who were given whey supplements reported a significant decrease in total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol compared with casein supplementation and controls (5).
Asthma Management
One study suggests whey protein could help improve the immune response in children with asthma. This small uncontrolled study found a modest improvement in immune response among 11 children with asthma who were supplemented with whey protein for a month (5). More rigorous research needs to be done to support this idea.
Reduced Blood Pressure And Cardiovascular Disease Risk
One study has found that drinks supplemented with whey protein significantly reduced blood pressure in patients with prehypertension (5). Controlling blood pressure can help reduce the risk of stroke and heart disease.
Reduced Weight Loss In Individuals With HIV
Unfortunately, people with HIV often report weight loss, especially as their disease progresses. Some evidence suggests consuming whey protein may help reduce weight loss among HIV-positive patients (5).
Read More: Crispy Tofu Recipes That’ll Make You Love This Plant-Based Protein
Differences Between Pea And Whey Protein
There are several differences between these two protein powders, some obvious, others not. Let us look into them:
Form And Source
Pea protein is plant-based as it is obtained from legumes, peas. However, whey is animal-based because it is derived from milk.
Flavor Profile
Pea protein has an earthy, nutty, and raw taste. However, as for whey protein, its flavor is bland and milky, as it is obtained from milk.
Texture
Pea protein has a smooth and creamy texture, while whey protein has a thin texture that looks like milk.
Suitable Diet Plan
Pea protein is suitable for most diet plans, unlike whey protein. Pea protein is suitable for a vegan diet, unlike whey protein. Remember that whey is derived from milk, an animal product, which is not recommended in a vegan diet plan (7).
What’s Better Pea Or Whey Protein?
A lot has been said about the best protein powder for muscle gain or weight loss between pea and whey protein. The running theory is that whey protein is better than pea protein for muscle building. Similarly, most people believe pea protein is better for weight loss when comparing pea protein powder vs whey.
But despite these running theories, there is no scientific evidence to back up any of these theories. Instead, most studies show that pea protein is equally as effective and comparable to whey protein.
A 2019 study found that consuming pea and whey protein produced similar outcomes in several measurements. These include muscle thickness, body composition, force production, workout of the day (WOD) performance and strength following 8-weeks of high-intensity functional training (HIFT) (3). This suggests that pea protein can be equally helpful in muscle gain and weight loss as whey protein.
How To Consume Pea Or Whey Protein
People often consume either protein powder by adding a substantial amount to their shakes or smoothies. Alternatively, others add them to their muffins, oatmeal, and pancakes. However, here are examples of recipes where both of these protein powders are not used in shakes or smoothies but in other products:
Recipe 1: Coconut & Whey Protein Balls (1)
As the name suggests, this recipe uses whey protein powder. The recipe entails:
Ingredients (1):
- 30 g soft prunes
- 10 g desiccated coconut
- 3 scoops (75 g) of rolled oats
- ½ banana
- 40 g Vanilla Impact whey protein (or your favorite flavor)
Preparation (1):
- Mash the banana, then add the prunes.
- Put in the microwave for two minutes, then mash again.
- Add the whey protein and oats, then mix well. Add some water if the mixture is too thick.
- Roll the mixture into bite-size snack balls. Eight balls will do.
- Wet the outside of the balls lightly, then roll them in the coconut.
- Store in an airtight container in the fridge.
If you tend to let yourself off the hook, raise the white flag when things get tougher than you expected, send yourself on an unconscious binge-eating trip – BetterMe app is here to help you leave all of these sabotaging habits in the past!
Recipe 2: Pea Protein Overnight Oats (2)
Elevate the nutritional profile of your morning oats by adding a scoop of pea protein powder. Here is a recipe to guide you:
Ingredients (2):
- 1 ¼ cups vanilla-flavored whey protein powder
- 1 cup whole wheat flour
- 1 (10 oz.) bag of chocolate chips
- 1 cup unsalted butter, softened
- 2 large eggs
- ¾ cup white sugar
- 6 tbsp. sucralose and brown sugar blend (such as Splenda brown sugar blend)
- 1 tsp. baking soda
- 1 tsp. salt
- 1 tsp. vanilla extract
- 1 cup chopped walnuts (Optional)
Preparation (2):
- Mix the rolled oats, almond milk, chia seeds, pea protein powder, yogurt, and hemp seeds (optional) in a bowl.
- Let the mixture sit in the refrigerator overnight to allow the oatmeal to soak up the liquid.
- Remove from the refrigerator and top as desired.
Nutrition Profile (2):
- Calories: 400
- Total fat: 14 g
- Total carbs: 37 g
- Protein: 36 g
- Fiber: 8 g
The Bottom Line
There has been a debate for the longest time about the most effective protein powder when comparing and contrasting pea protein vs whey. The running theory is that pea protein is better for weight loss while whey is better suited for muscle building.
But there are no studies to justify these theories. Instead, evidence shows that pea protein is equally comparable and effective to whey protein in muscle building and weight loss. However, pea protein is fit for a vegan diet, unlike whey protein, because it is animal-derived. Please talk to a professional if you are interested in adding either protein to your diet.
Get your personalized
meal plan!
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- Coconut & Whey Protein Balls | On The Go Snack (2016, myprotein.co.in)
- Pea Protein Overnight Oats (2022, pulses.org)
- The Effects of Whey vs. Pea Protein on Physical Adaptations Following 8-Weeks of High-Intensity Functional Training (HIFT): A Pilot Study (2019, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- What are some of the best pea protein powders? (2021, medicalnewstoday.com)
- What are the benefits and risks of whey protein? (2017, medicalnewstoday.com)
- What are the health benefits of peas? (2022, medicalnewstoday.com)
- What Is a Vegan Diet? (2021, webmd.com)
- Whey protein – Uses, Side Effects, and More (2020, webmd.com)