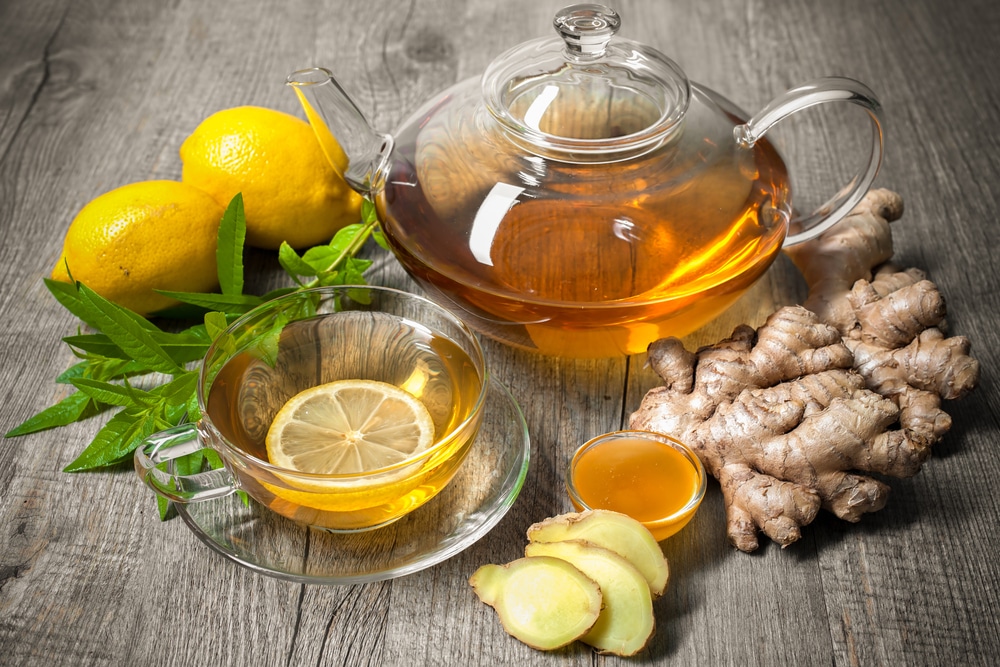
Ginger has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese and Indian Ayurvedic medicine to treat everything from colds and flu to indigestion, arthritis pain, nausea, and motion sickness. With such a long list of potential benefits, it’s not surprising that ginger is one of the most commonly consumed spices today.
Lemon is also a well-known and highly beneficial fruit. It’s a great source of vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants. When combined, ginger and lemon make a delicious and healthy tea that offers a variety of health benefits.
Get your personalized
meal plan!
Lemon Ginger Tea Nutrition Facts
There are several beneficial nutrients in a cup of lemon ginger tea (10). They include:
- Vitamins B6, C, and E
- Manganese
- Magnesium
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Caffeine
- Antioxidants
Lemon contains flavonoids, phenolic acids, citral, and limonoids which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties (4). Ginger contains a wealth of substances that contribute to its health benefits. There are at least 40 different chemical compounds, including (1):
- Zingerone – which is an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory substance that reduces the risk for diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
- Gingerols – which have strong anti-inflammatory properties that may ease arthritis, menstrual discomfort, and pain from nerve damage.
- Shogaols – a pungent substance that can reduce pain, nausea, joint inflammation, and autoimmune diseases such as lupus.
Lemon Ginger Tea Health Benefits
Drinking a ginger-lemon concoction is good for you because it:
Soothes Indigestion
A cup of ginger lemon tea may be a great tonic if you’re dealing with chronic indigestion or discomfort after a heavy meal. Both ginger and lemon contain compounds that alleviate indigestion, nausea, and diarrhea.
Ginger contains shogaols, which stimulate the secretion of gastric juices in your stomach. Shogaols can also cause minor contractions in your stomach, which means that they promote digestion by moving food through the digestive system more quickly (9). A compound called gingerol in ginger is also thought to help quell nausea and other stomach upsets (13).
Lemon also contains a plant compound called limonene, which aids digestion by helping move food along your digestive tract (4).
Alleviates Nausea
Ginger lemon tea is also useful for alleviating nausea. Nausea can be caused by a variety of factors, including pregnancy, motion sickness, the flu, hangovers, or stomach flu. Drinking ginger lemon tea is soothing because it has gingerol, a plant compound that is effective in alleviating nausea (13).
Reasons why BetterMe is a safe bet: a wide range of calorie-blasting workouts, finger-licking recipes, 24/7 support, challenges that’ll keep you on your best game, and that just scratches the surface! Start using our app and watch the magic happen.
Reduces Nasal Congestion
If you’re congested, drinking a hot cup of ginger lemon tea can help clear your sinuses. Ginger has antihistamine and decongestant properties, while lemon contains vitamin C, which helps to fight infection (8).
Boosts the Immune System
Vitamin C is also important for boosting your immune system. Lemon is a good source of this nutrient, and a cup of ginger lemon tea will give you a good dose. The antioxidants in lemon also help to fight off infection and improve your overall health (6).
Lemon is also a source of potassium, which helps to regulate blood pressure and support the nervous system (12).
May Relieve Constipation
Ginger is a natural stimulant and can help to get your digestive system moving if you’re constipated (5). When combined with lemon, it makes a gentle tea that can help to relieve constipation.
May Help Prevent Cancer
Ginger has been shown to have anti-cancer properties. A compound called 6-gingerol, which is found in ginger, has been found to suppress the growth of cancer cells (1). While more research is needed, early findings suggest that ginger may help to prevent certain types of cancer, including ovarian cancer.
Improves Heart Health
Lemon is a good source of potassium, which is important for heart health. A diet high in potassium can help to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease (12). The antioxidants in lemon also help to protect your heart from damage.
Improves Mood and Concentration
Drinking ginger lemon tea can help to improve your mood and concentration. That’s because both ginger and lemon contain caffeine, which is a psychostimulant that increases your attention span (2).
Prevents Kidney Stones
If you’re prone to developing kidney stones, drinking ginger lemon tea may help to prevent them. The citric acid in lemon helps to break down the calcium oxalate that is a common component of kidney stones (11).
Read More: Matcha Tea Side Effects: 9 Reasons Why You May Want To Drink Less Of This Beverage
Promotes Weight Loss
Ginger lemon tea is a calorie-free beverage that can help you lose weight. The gingerol in ginger helps to boost your metabolism, and the antioxidants in lemon help to reduce inflammation and improve your overall health (14).
Helps Improve Liver Function
The lemon in ginger lemon tea helps to improve liver functions. The citric acid in lemon helps to detoxify the liver, and the antioxidants help to protect it from damage (3).
Soothes Pain, Menstrual Cramps, and Inflammation
Ginger has long been used as a natural pain reliever. It contains gingerols, which are powerful anti-inflammatories (1). Menstrual cramps and other types of pain can be relieved by drinking a cup of ginger lemon tea.
Improves Skin Health
The antioxidants in lemon help to protect your skin from damage (4). Lemonade has been used as a natural skin toner for centuries. Drinking ginger lemon tea can help to improve the appearance of your skin and reduce wrinkles.
Promotes Hair Growth
Lemon ginger tea is full of vitamins and minerals that are important for hair growth. The vitamin C in lemon helps to produce collagen, which is essential for strong hair (15).
Lemon Ginger Tea Side Effects
This tea is generally well-tolerated, but it may cause some side effects. Ginger should be avoided if you have a blood clotting or bleeding disorder or diabetes. Ginger may also interact with blood thinners and drugs for hypertension and diabetes (7). So make sure you talk to your doctor before you start taking this tea if you have any of the above conditions.
If you’re pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant, you should avoid drinking this tea. Animal studies suggest that high doses of ginger can affect fertility and lower testosterone levels in males.
You shouldn’t drink this tea if you’re eight years old or younger, as there isn’t enough research to know whether it’s safe for children under the age of eight. The caffeine in ginger may also increase your risk of side effects, especially if you’re sensitive to caffeine.
The Bottom Line
Ginger lemon tea is a popular beverage that can benefit your overall health. It can boost your mood, reduce inflammation and pain, improve liver function, and promote hair growth. The caffeine in ginger may help you to lose weight by boosting your metabolism, while the antioxidants in lemon protect your skin from damage. If you’re prone to developing kidney stones, drink this tea to help break them down. However, ginger lemon tea may not be safe for everyone to drink, so consult with a doctor before starting any new tea regimen.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ginger in Health and Physical Activity: Review of Current Evidence (2013, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Caffeine: Cognitive and Physical Performance Enhancer or Psychoactive Drug? (2015, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Citric Acid Effects on Brain and Liver Oxidative Stress in Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Mice (2014, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Citrus limon (Lemon) Phenomenon—A Review of the Chemistry, Pharmacological Properties, Applications in the Modern Pharmaceutical, Food, and Cosmetics Industries, and Biotechnological Studies (2020, mdpi.com)
- Constipation and herbal medicine | Pharmacology (2015, frontiersin.org)
- Effects of Citrus Fruit Juices and Their Bioactive Components on Inflammation and Immunity: A Narrative Review (2021, frontiersin.org)
- ginger | Michigan Medicine (n.d., uofmhealth.org)
- Ginger extract versus Loratadine in the treatment of allergic rhinitis: a randomized controlled trial – BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies (2020, biomedcentral.com)
- Ginger in gastrointestinal disorders: A systematic review of clinical trials (2018, onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- Lemon Ginger Tea: Health Benefits, Nutrients per Serving, Preparation Information, and More (2020, webmd.com)
- Medical and Dietary Therapy for Kidney Stone Prevention (2014, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Role of potassium in regulating blood flow and blood pressure (2006, journals.physiology.org)
- The Amazing and Mighty Ginger – Herbal Medicine (2011, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The effects of ginger intake on weight loss and metabolic profiles among overweight and obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (2019, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The Role of Vitamins and Minerals in Hair Loss: A Review (2018, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)