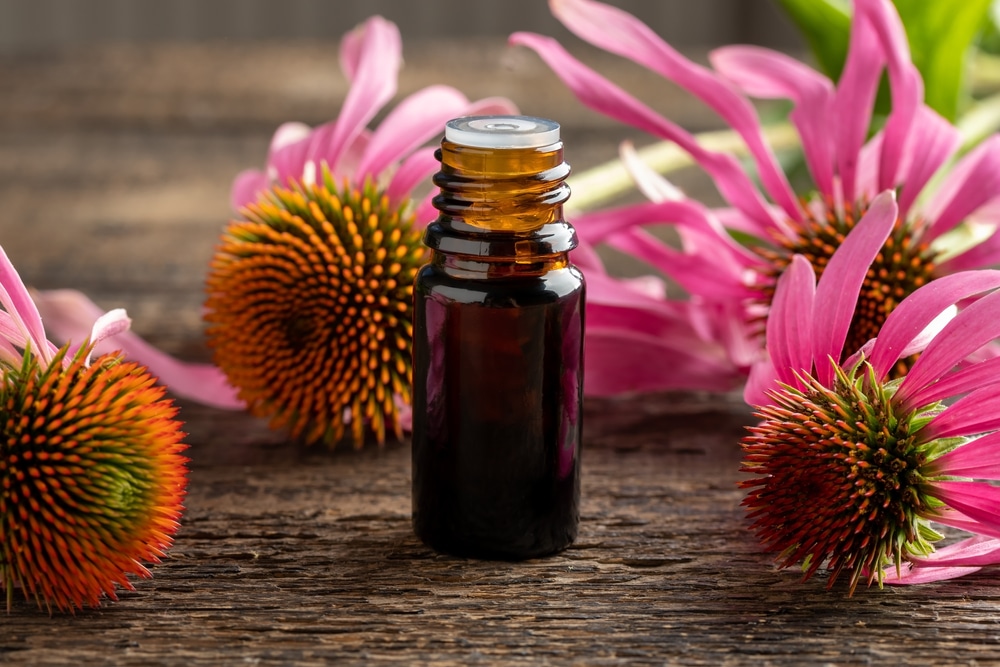
As far as herbal remedies go, echinacea is one of the most popular – and for good reason. It’s been used traditionally to treat everything from the common cold to more serious conditions like cancer (2). This purple flower is native to North America and has been used by Native Americans for centuries. The main active ingredient in echinacea is a compound called echinacin, which is thought to boost the immune system. Echinacea is most commonly taken as a tea or tincture, but it can also be found in capsules, tablets, and even topical creams.
Get your personalized
meal plan!
Here are some of the most common echinacea benefits:
1. Boosts Immune System
The main benefit of echinacea is that it is thought to boost the immune system. This may help you fight off infections, viruses, and diseases (10).
Echinacea is often taken at the first sign of a cold or other infection. It’s thought to help reduce the severity and duration of the illness.
2. Reduces Inflammation
Echinacea is also known for its anti-inflammatory properties. This might be helpful for conditions like arthritis, eczema, and psoriasis (7).
Due to chronic inflammation’s possibility of leading to serious health problems, echinacea may also help prevent some of these diseases (3).
3. Heals Wounds
Echinacea has been shown to speed up the healing of wounds in mice. This is likely due to its anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties (1).
4. May Help Fight Cancer
Cancer is caused by the abnormal growth of cells. Some animal studies suggest that echinacea may help fight cancer by stopping the growth of cancer cells (4).
5. Reduces Pain
Echinacea is sometimes used as a natural pain reliever. This is likely due to its anti-inflammatory properties (12).
Read More: Chicory: Everything You Need To Know About Its Benefits And Side Effects
6. May Reduce anxiety
It is also thought to help with anxiety. Research on this possible effect is still in its early stages(7) (15).
7. Protects Skin
Echinacea is often used in natural skin care products. It is thought to improve the health of the skin and even help fight acne (13) (14).
8. May Promote Heart and Metabolic Health
One test tube study suggests that echinacea may have properties which could help manage high blood sugar and blood pressure.
How To Use Echinacea?
Echinacea is available in many forms, including teas, tinctures, capsules, tablets, and topical creams.
For the most benefit, it’s best to take echinacea at the first sign of a cold or infection. However, if you are using echinacea for another purpose, follow the directions on the product you’re using.
Echinacea is generally considered safe for most people. However, there are a few side effects to be aware of. These include upset stomach, diarrhea, headaches, and dizziness. These side effects are common among people who are allergic to other flowers such as daisies (5).
Moreover, if you have a ragweed allergy, you may also be allergic to echinacea (2). If you’re pregnant or breastfeeding, it’s best to avoid echinacea as well. This herb can stimulate the immune system, which can be harmful to a developing fetus or infant. Echinacea is also not recommended for people with autoimmune disorders like lupus and multiple sclerosis. This is because echinacea can further stimulate the immune system (14).
As with any herb, it’s best to talk to your doctor before taking echinacea, especially if you have a medical condition.
If you tend to let yourself off the hook, raise the white flag when things get tougher than you expected, send yourself on an unconscious binge-eating trip – BetterMe app is here to help you leave all of these sabotaging habits in the past!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some common questions about echinacea:
Q: What Is Echinacea?
A: Echinacea is a flowering plant in the daisy family. It’s native to North America and has been used by Native Americans for centuries.
The main active ingredient in echinacea is a compound called echinacin, which is thought to boost the immune system. This herb is available in many forms, including teas, tinctures, capsules, tablets, and topical creams.
Q: What Does Echinacea Do To The Skin?
A: Echinacea is thought to have several benefits for the skin, including reducing inflammation, speeding up wound healing, and fighting bacteria. In addition, echinacea contains antioxidants that can help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals (6).
Q: Does Echinacea Help With Hair Growth?
A: There is some anecdotal evidence that echinacea may help with hair growth. It is said to stimulate the stem cells associated with each hair follicle and promote hair growth. It is also said to increase blood circulation in the scalp, which helps promote hair growth. However, this is not scientifically proven.
Employing shampoos and serums enriched with echinacea extracts may help alleviate itchy scalp due to its anti-inflammatory properties (9).
Q: Is Echinacea Good For Wrinkles?
A: Echinacea contains antioxidants that may help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals. In addition, echinacea has anti-inflammatory properties that might help improve the appearance of the skin (13).
Read More: List Of Adaptogens: Benefits And Side Effects
Q: What Are The Benefits Of Taking Echinacea Daily?
A: Echinacea is thought to boost the immune system, making it a good choice for people who want to prevent or treat infections. In addition, echinacea has anti-inflammatory properties that might help to reduce the severity of conditions like allergies, asthma, and arthritis.
Finally, echinacea is rich in antioxidants, which can help to protect the body from damage caused by free radicals (14). It’s best to talk to your doctor before taking echinacea for any reason.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- Alcohol extract of Echinacea pallida reverses stress-delayed wound healing in mice (2009, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Allergenic Cross-Reactivity between Echinacea and Ragweed (2007, jacionline.org)
- Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span | Nature Medicine (2019, nature.com)
- Echinacea: a Miracle Herb against Aging and Cancer? Evidence In vivo in Mice (2005, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Echinacea (2020, nccih.nih.gov)
- Echinacea purpurea: Pharmacology, phytochemistry and analysis methods (2015, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench: Biological and Pharmacological Properties. A Review (2022, mdpi.com)
- Echinacea purpurea supplementation stimulates select groups of human gastrointestinal tract microbiota (2009, onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- Efficacy of hydrophilic or lipophilic emulsions containing Echinacea purpurea extract in treatment of different types of pruritus (2018, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Enhancement of Innate and Adaptive Immune Functions by Multiple Echinacea Species (2006, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Know Your Risk for Heart Disease (2019, cdc.gov)
- Medicinal properties of Echinacea: A critical review (2003, sciencedirect.com)
- Skin improvement and stability of Echinacea purpurea dermatological formulations (2010, onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- The potential use of Echinacea in acne: control of Propionibacterium acnes growth and inflammation (2011, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The Safety and Efficacy of Botanicals with Nootropic Effects (2021, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Use of echinacea in medicine (2000, sciencedirect.com)