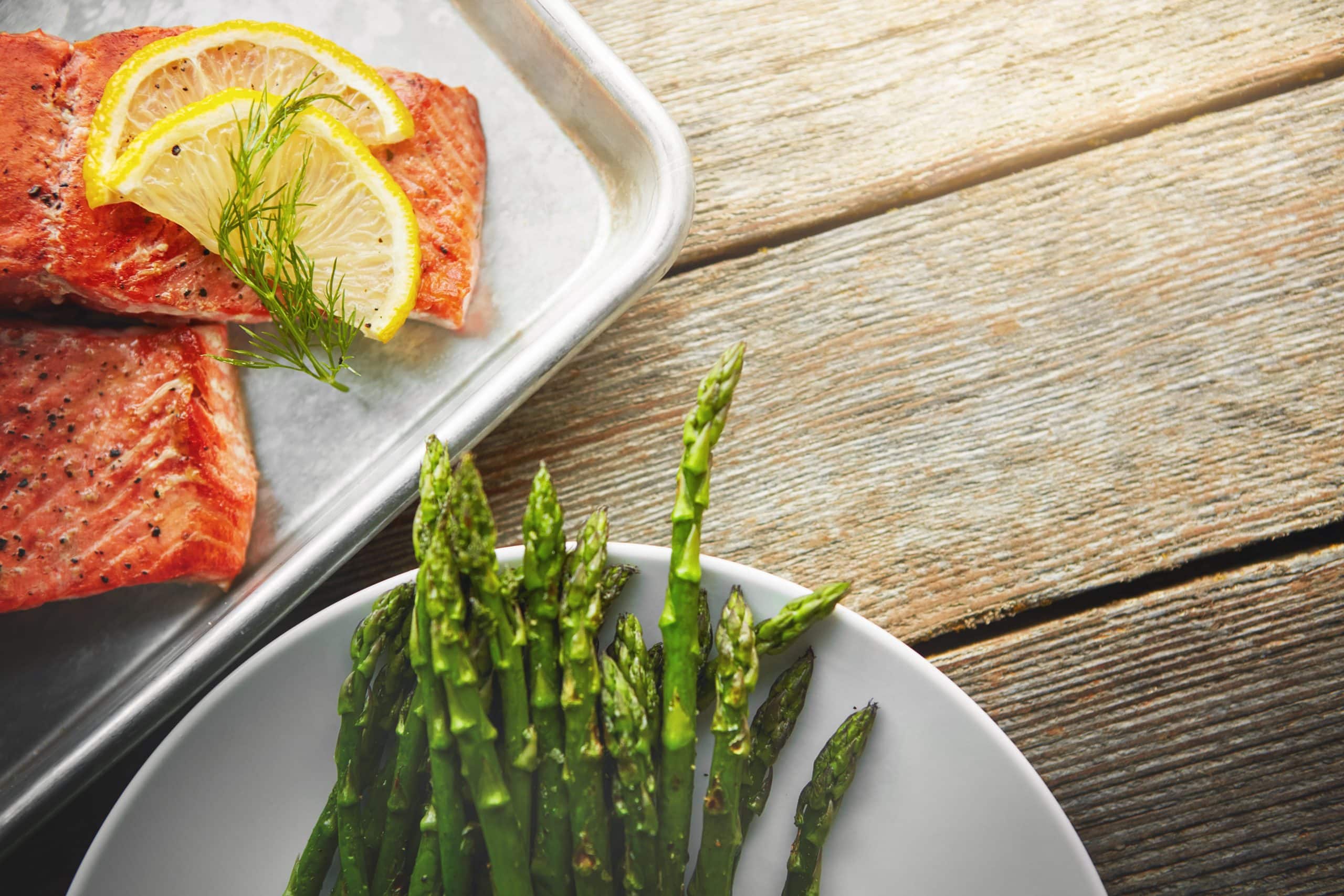
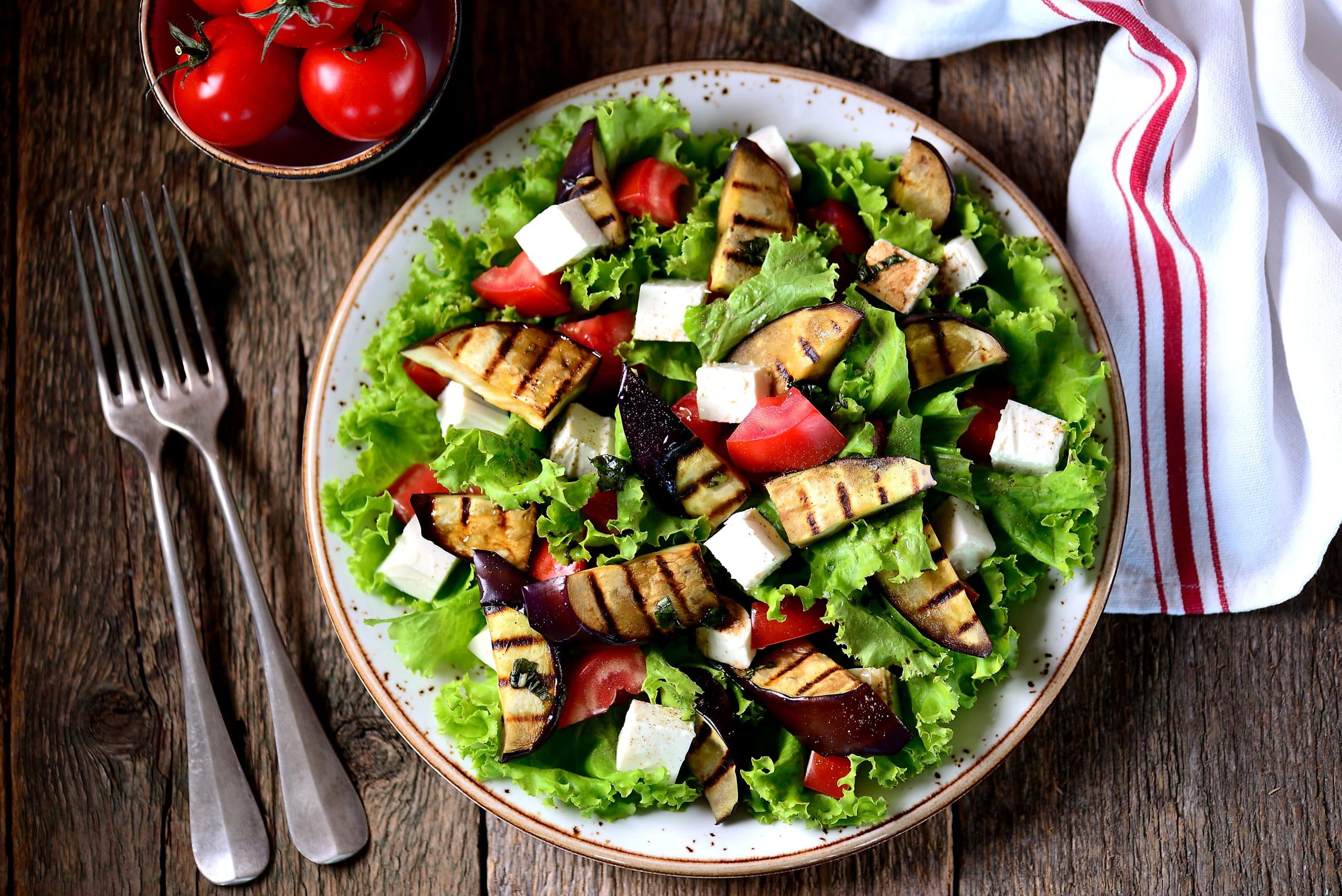
As far as diets go, the Mediterranean diet is one of the most well-researched and proven effective. This diet is based on the traditional foods and lifestyle of people living in countries along the Mediterranean Sea. There are many benefits associated with following a Mediterranean diet, including a lower risk of heart disease, cancer, diabetes, and stroke (27). The diet has also been shown to help improve cognitive function and memory, and reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases (24). If you’re interested in trying out the Mediterranean diet, knowing exactly what to eat and what to avoid is crucial for success. This Mediterranean diet food list will help you get started on the healthy eating plan.
How The Mediterranean Diet Works
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes specific foods that are rich in healthy fats, antioxidants, and fiber. This diet also limits red meat, refined grains, sweets, and sugary drinks (3). As a result, people who follow this eating pattern tend to have:
Lowers Rates Of Obesity
A recent study found that the Mediterranean diet was linked to a lower rate of obesity (1). This is attributable to the fact that the diet is rich in healthy foods that promote weight loss, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fish.
Reduces Risk Of Heart Disease
The Mediterranean diet has also been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease (26). This is likely due to the fact that the diet is high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease.
Its high-fiber content may also play a role in heart health by reducing cholesterol levels (12).
Prevents Alzheimer’s And Parkinson’s Diseases
Studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet may help to prevent Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases (24).
This is likely due to the fact that the diet is high in antioxidants, which protect the brain from damage. The healthy fats in the diet may also play a role in preventing cognitive decline.
Staves Off Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition that can lead to complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems (5).
The Mediterranean diet has been shown to help prevent the development of type 2 diabetes (18). This is likely due to the fact that the diet helps to keep blood sugar levels in check.
In fact, some research has shown that the Mediterranean diet is more effective at managing blood sugar levels than low-glycemic, low-carb, and high-protein diets (17).
Helps Fight Inflammation
The Mediterranean diet is also thought to help lessen inflammation (25). This is due to the fact that the diet is rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as olive oil, fish, and nuts. The antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables in the diet may also play a role in reducing inflammation.
Read More: Healthy Mediterranean Eggplant Salad Recipe
May Protect You From Cancer
Cancer is a complex disease that can be difficult to prevent. However, the Mediterranean diet may help to lower your risk of developing cancer (2). This is likely due to the fact that the diet is high in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods, which have been linked to a reduced risk of cancer.
May Ease Depression Symptoms
Depression is a common mental health disorder that can cause a wide range of symptoms, such as fatigue, insomnia, and loss of interest in activities (4).
The Mediterranean diet has been shown to help ease depression symptoms. This is likely due to the fact that the diet is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been linked to improved mental health (16).
The diet’s high content of antioxidants may also play a role in alleviating depression (21).
What To Eat On The Mediterranean Diet
Certain food groups are central to the Mediterranean diet, including:
Brightly-Colored Fruits And Vegetables
The Mediterranean diet is rich in fruits and vegetables, which are loaded with antioxidants and other nutrients that are beneficial for health (9). Some of the best fruits and vegetables to include in your diet are:
- Green-colored fruits and vegetables (broccoli, lettuce, celery, green peppers, kiwi, okra) – contain chlorophyll, fiber, lutein, zeaxanthin, calcium, folate, vitamin C, iron, calcium, and Beta-carotene. These nutrients are important for vision, bone health, and cancer prevention.
- Yellow and Orange-colored fruits and vegetables (carrots, sweet potatoes, squash, mangoes, oranges, apricots) – contain Beta-carotene, zeaxanthin, flavonoids, lycopene, potassium, and vitamin C. These nutrients are important for heart health, immunity, bone health, and cancer prevention.
- Red-colored fruits and vegetables (tomatoes, watermelons, pink grapefruit, strawberries, red peppers) – contain lycopene, flavonoids, ellagic acid, quercetin, and vitamin C. These nutrients are important for heart health, immunity, and cancer prevention.
- Purple and blue-colored fruits and vegetables (blueberries, blackberries, plums, purple cabbage, and eggplant) – contain anthocyanins, ellagic acid, resveratrol, and vitamin C. These nutrients are important for brain health, gut health, immunity, fighting inflammation and cancer prevention.
- White-colored fruits and vegetables (garlic, onions, white potatoes, bananas, cauliflower) – contain quercetin, selenium, allicin, and sulfur. These nutrients are important for fighting inflammation, balancing hormones and cancer prevention.
Looking for a way to break the vicious cycle of weight loss and tone up all the jiggly parts? Watch the extra pounds fly off and your muscles firm up with the BetterMe app!
Legumes
Legumes are a rich source of protein for people on the Mediterranean diet. They are also a good source of fiber, which can help improve digestive health and regulate blood sugar levels (15). Some of the best legumes to include in your diet are:
- Black beans
- Chickpeas
- Kidney beans
- Lentils
- Soybeans
Note that a side effect of high-fiber diets like the Mediterranean diet is increased flatulence. To minimize this side effect, start slowly with legumes and increase your intake gradually over time.
Whole Grains
The Mediterranean diet includes whole grains as a source of healthy carbohydrates.
Whole grains are a good source of fiber, which can help improve digestive health and regulate blood sugar levels. The germ and bran of whole grains contain important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants (8).
In addition, the slow release of carbohydrates from whole grains can help maintain energy levels and prevent spikes in blood sugar (19). Some of the best whole grains to include in your diet are:
- Oats
- Brown rice
- Rye
- Barley
- Buckwheat
- Quinoa
- Millet
Nuts And Seeds
Nuts and seeds are a good source of protein, healthy fats, and fiber. They are also a good source of vitamins and minerals, including magnesium, zinc, and selenium (10).
Nuts and seeds can help improve heart health, cognitive function, and blood sugar control (10). Some of the best nuts and seeds to include in your diet are:
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Pistachios
- Hazelnuts
- Macadamia nuts
- Pumpkin seeds
Note that nuts and seeds are typically calorie-dense. Therefore, it is important to practice portion control when including them in your diet. This is especially true if you’re using the Mediterranean diet to lose weight.
Olive Oil And Other Healthy Fats
Extra-virgin olive oil is the cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet. It is a good source of healthy monounsaturated fats and antioxidants. The health benefits of olive oil include improved heart health, cognitive function, and blood sugar control (29).
When using olive oil, it is important to choose a high-quality olive oil and to use it in moderation.
In addition to olive oil, the Mediterranean diet includes other healthy fats, such as avocados and nuts. These foods are also a good source of antioxidants and monounsaturated fats.
Fish And Seafood
Fish is a good source of protein, healthy fats, and omega-3 fatty acids. The health benefits of fish include improved heart health, cognitive function, and joint pain relief (11). Some of the best fish to include in your diet are:
- Salmon
- Tuna
- Trout
- Sardines
- Anchovies
- Shrimp
- Crab
- Lobster
- Mussels
- Oysters
Read More: The Gluten-Free Mediterranean Diet: How It Works, Benefits, And Tips For Getting Started
Dairy
Dairy products are a good source of calcium, vitamin D, and protein. The health benefits of dairy include improved bone health, reduced inflammation, and lower blood pressure (6). Some of the best dairy products to include in your diet are:
- Milk
- Cheese
- Yogurt
- Butter
- Kefir
Note that dairy products are typically high in saturated fat. Therefore, it is important to choose low-fat or nonfat dairy products when possible.
Herbs And Spices
Herbs and spices are a good source of antioxidants. They can also help to improve cognitive function and relieve joint pain (22). Some of the best herbs and spices to include in your diet are:
- Garlic
- Rosemary
- Thyme
- Oregano
- Basil
- Cumin
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Chili pepper
What To Avoid On The Mediterranean Diet
While there are many healthy foods to include in your diet, there are also some unhealthy foods that you should avoid.
Added Sugar
Added sugar refers to any sugar that is not naturally found in food. Examples of added sugar include table sugar, honey, molasses, and syrups. In contrast, natural sugars are found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products.
Studies have shown that consuming too much added sugar can lead to an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease (23). Therefore, it is important to limit your intake of foods that contain added sugar.
The Mediterranean diet limits all foods that have been sweetened with sugar, including ice cream, candy, cake, cookies, and pastries.
Refined Grains
Refined grains are grains that have been stripped of their outer layer (the bran) and inner layer (the germ). This process removes some of the fiber, vitamins, and minerals from the grain.
Studies have shown that consuming too many refined grains can lead to an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease (14). That’s because refined grains are typically high in sugar and low in fiber.
Consuming them causes a spike in blood sugar and later cravings for more sugary foods.
The Mediterranean diet limits all refined grains, including white bread, pasta made with white flour, and white rice.
If you tend to let yourself off the hook, raise the white flag when things get tougher than you expected, send yourself on an unconscious binge-eating trip – BetterMe app is here to help you leave all of these sabotaging habits in the past!
Trans Fats
Of all dietary fats, trans fats are the most harmful to your health. Trans fats are created when manufacturers add hydrogen to vegetable oils in order to solidify them. This process is called hydrogenation.
Trans fats are often found in processed foods, such as:
- Margarine
- Vegetable shortening
- Fried foods
- Baked goods
- Snack foodsPackaged goods
Studies have shown that consuming trans fats can lead to an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. That’s because trans fats are associated with an increase in “bad” LDL cholesterol and a decrease in “good” HDL cholesterol (28).
Refined Oils
Refined oils are oils that have been processed to remove impurities. The process of refining oils often involves the use of chemicals and high temperatures. This can damage the nutrients in the oil and make them less healthy (7).
Examples of refined oils include:
- Soybean oil
- Corn oil
- Canola oil
- Vegetable oil
The Mediterranean diet limits all refined oils. Instead, it recommends using olive oil, which is a type of unrefined oil.
Processed Meat
The meat industry has come up with many different ways to process meat, including curing, salting, smoking, and adding chemicals.
Processed meat is often high in sodium, which can lead to high blood pressure. It is also associated with an increased risk of cancer (13).
Therefore, it is best to limit your intake of processed meat. The Mediterranean diet recommends eating mostly unprocessed meat, such as free range chicken and grass-fed beef.
Convenience Foods
Convenience foods are foods that are quick and easy to prepare. They often come in packages or boxes and can be microwaved or eaten on the go.
Examples of convenience foods include:
- Frozen dinners
- Packaged snacks
- Canned soups
- Chips
- Pretzels
Convenience foods are often high in calories, unhealthy fats, and added sugar. They are also low in nutrients (20).
Therefore, it is best to limit your intake of convenience foods. The Mediterranean diet recommends eating mostly whole, unprocessed foods.
The Bottom Line
The Mediterranean diet is a healthy way of eating that limits processed foods, refined grains, and refined oils. Instead, it focuses on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and unprocessed meat. This diet has been shown to reduce the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
Get your personalized
meal plan!
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, Five-Year Weight Change, and Risk of Overweight and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies (2022, academic.oup.com)
- Cancer and Mediterranean Diet: A Review (2019, mdpi.com)
- Definition of the Mediterranean Diet; A Literature Review (2015, mdpi.com)
- Depression (2022, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Diabetes, Heart Disease, & Stroke (2021, niddk.nih.gov)
- Effects of Dairy Products Consumption on Health: Benefits and Beliefs—A Commentary from the Belgian Bone Club and the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (2016, link.springer.com)
- Evaluation of the deleterious health effects of consumption of repeatedly heated vegetable oil (2016, sciencedirect.com)
- Health Benefits of Dietary Whole Grains: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses (2017, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Health Benefits of Fruits and Vegetables (2012, academic.oup.com)
- Health Benefits of Nut Consumption (2010, mdpi.com)
- Health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids (2004, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet: Metabolic and Molecular Mechanisms (2018, academic.oup.com)
- Human risk of diseases associated with red meat intake: Analysis of current theories and proposed role for metabolic incorporation of a non-human sialic acid (2016, sciencedirect.com)
- Increased consumption of refined carbohydrates and the epidemic of type 2 diabetes in the United States: an ecologic assessment (2004, academic.oup.com)
- Legumes: Health Benefits and Culinary Approaches to Increase Intake (2015, diabetesjournals.org)
- Mediterranean Diet and its Benefits on Health and Mental Health: A Literature Review (2020, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Mediterranean Diet and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Perpetual Inspiration for the Scientific World. A Review (2021, mdpi.com)
- Mediterranean Diet Effects on Type 2 Diabetes Prevention, Disease Progression, and Related Mechanisms. A Review (2020, mdpi.com)
- Physiology, Carbohydrates (2022, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Relationship between Consumption of Convenience Foods and Health Status of the Working Women (2020, academia.edu)
- Role of antioxidants in generalised anxiety disorder and depression (2012, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Spices and herbs: Natural sources of antioxidants – a mini review (2015, sciencedirect.com)
- Sugars, obesity, and cardiovascular disease: results from recent randomized control trials (2016, link.springer.com)
- The Association between the Mediterranean Dietary Pattern and Cognitive Health: A Systematic Review (2017, mdpi.com)
- The Immune Protective Effect of the Mediterranean Diet against Chronic Low-grade Inflammatory Diseases (2016, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The Mediterranean Diet and Cardiovascular Health (2019, ahajournals.org)
- The Mediterranean diet and health: a comprehensive overview (2021, onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- Trans fats—sources, health risks and alternative approach – A review (2011, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Virgin Olive Oil and Health: Summary of the III International Conference on Virgin Olive Oil and Health Consensus Report, JAEN (Spain) 2018 (2019, mdpi.com)