What Are Micros
Macros and micros are something you’ve heard a lot in the fitness world. People are always talking about counting macros, checking your macros, and all that. But, what are micros? Why are they important in our diet? Can you easily find them?
Get your personalized
meal plan!
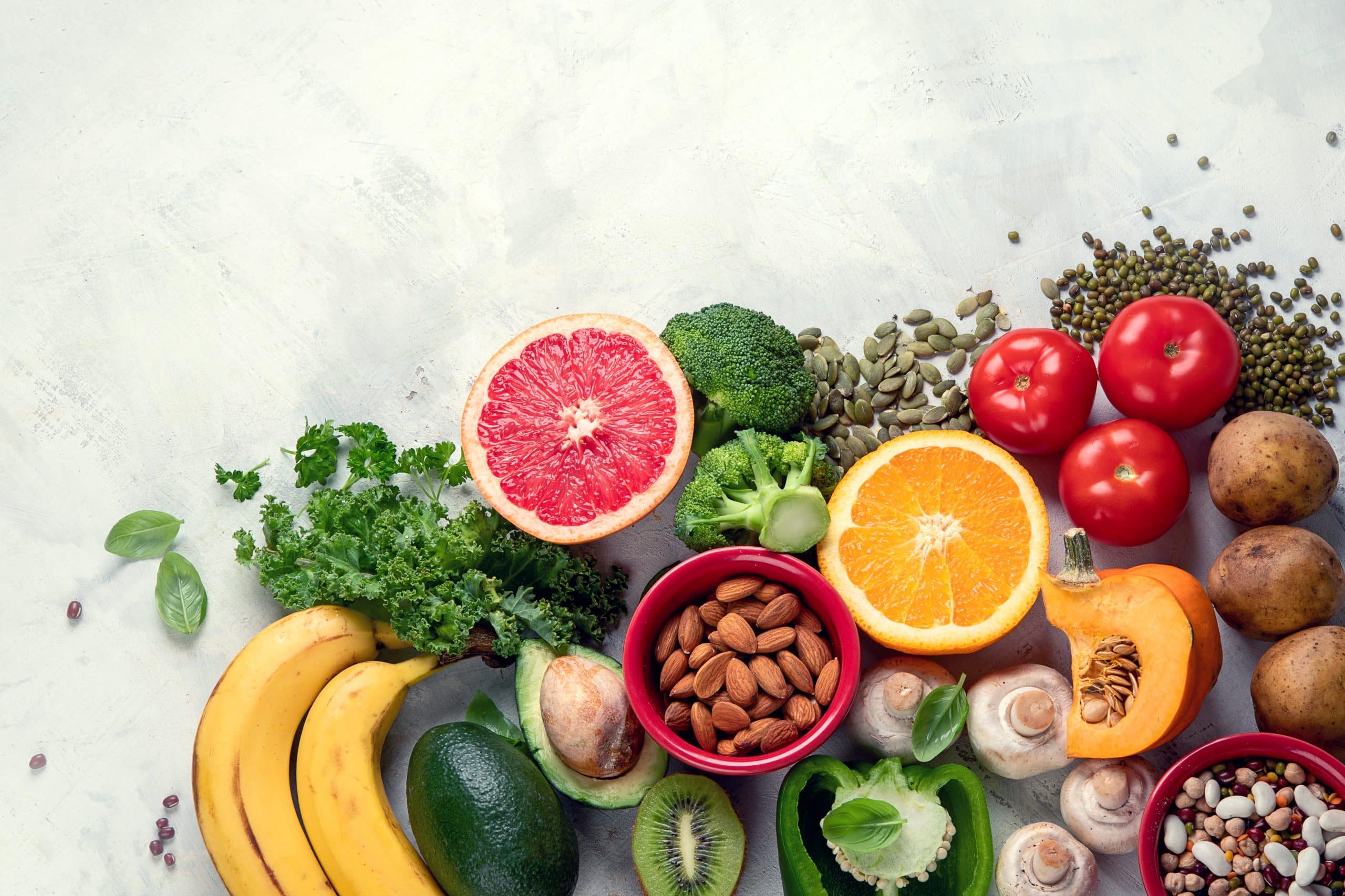
Micros are one of the two major nutrient groups. They are commonly referred to as Micronutrients. Micronutrients and macronutrients are both nutrients that our bodies need for different reasons. This then means that none of these two main categories of nutrients is more important than the other. We should always make sure to balance getting the right amount of macronutrients and micronutrients in our diet.
What are Micros and Macros in Nutrition?
It is better to differentiate these two major types of nutrients to better understand them. Macronutrients are nutrients that the body needs in large amounts. They practically make up your total calorie intake. They are measured in grams. They help provide an individual with the energy to carry out daily activities. They also help keep a person healthy. Macronutrients consist of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Carbohydrates can be found in foods like bread, pasta, potatoes, and the likes. Proteins can be found in foods like eggs, fish, beans, different dairy products, etc. Fats are found in oils, nuts, meats, avocados, and the likes.
Each macronutrient is important to the body for various reasons. Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body. When broken down, they provide the body with the needed energy to carry out all the day’s activities. Proteins on hand are required by the body as they are the building blocks of cells and our bodies (4). They also help build muscle tissues and also help in repairing cells. Fats can also be used to provide energy for the body. This is seen in individuals who follow low-carb, high-fat diet plans. Fats also help us absorb vitamins. They keep the cell membranes working, as well as keep our skin and hair healthy (7).
Read More: Do Vitamins Break A Fast: Exploring The Impact Of Supplements On Fasting
Amounts of macronutrients human body need
The different macronutrients are required by the body in different amounts. The body requires carbohydrates in the largest amount. It requires between forty-five percent to sixty-five percent of the total nutrients (1). About ten percent to thirty-five percent should come from proteins (1). Fats are required to be about twenty to thirty-five percent of the total calorie intake (5). The number of calories in a single gram of the various macronutrients differ. For proteins and carbohydrates, there are four calories in a single gram. For fats, one gram contains nine calories. These are the required amounts of each macronutrient. If you want to adopt a certain diet, you should consult an expert on the amounts of each macronutrient you need.
What are micros in food? The name gives you a hint as to what micronutrients are. They are nutrients that the body requires in small amounts. They are useful for many different functions in the body. They are necessary to support the body’s metabolism and functions. Micronutrients also make sure the body organs are working properly and efficiently. They also help digest the macronutrients. Micronutrients consist of vitamins and minerals. Examples of micronutrients are zinc, folate, vitamin B-6, vitamin B-12, vitamin C, vitamin D, calcium, iron, etc. Some micronutrients are easy to get like vitamin C, while others are difficult. An example is vitamin D whose primary source is the sun (3).
Micros are usually measured in either milligrams or micrograms (6).
If you struggle to even flirt with the idea of giving up your favorite foods or working out till your legs give way – BetterMe app is here to breathe a fresh perspective into the way you view the weight loss process! Check out the app and experience the fun side of fitness and dieting with BetterMe!
Effects of Lacking Micronutrients in Your Diet
Micros are very important to a human being. They are required for the various functions mentioned above as well as many other functions. Something else to note is that each micro is required for a different function. This helps drive the notion as to why you need all micronutrients and not just some, as all are equally important for an individual to be considered healthy. Lacking micronutrients can cause anemia, slow-thinking, and impotence (9). Lacking micronutrients or having them in fewer quantities than those required by the body can also cause constipation and bloating, or may even cause diarrhea. Lacking the micronutrients required may also lead to hair loss (9). If you are experiencing hair loss, you should check your diet to see what micronutrients you are missing.
Lack of micronutrients can also result in muscle cramping, as well as numbness (9).
How Much of Each Micronutrient Does Your Body Require?
Most people know the number of macros their bodies required but are not so keen when it comes to micros. You should know what amount of each nutrient your body needs so that you can work towards ensuring you get the required micronutrients. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015–2020 recommends taking the following amounts of vitamins and mineral salts (2).
| VITAMINS | FEMALES AGED 19-30 YEARS | MALES AGED 19-30 YEARS | FEMALES AGED 31-50 YEARS | MALES AGED 31-50 YEARS | FEMALES AGED 51 AND ABOVE | MALES AGED 51 AND ABOVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A (RAE) | 700mcg | 900mcg | 700mcg | 900mcg | 700mcg | 900mcg |
| Vitamin E | 15mg | 15mg | 15mg | 15mg | 15mg | 15mg |
| Vitamin D | 600IU | 600IU | 600IU | 600IU | 600IU | 600IU |
| Vitamin C | 75mg | 90mg | 75mg | 90mg | 75mg | 90mg |
| Thiamin | 1.1mg | 1.2mg | 1.1mg | 1.2mg | 1.1mg | 1.2mg |
| Riboflavin | 1.1mg | 1.3mg | 1.1mg | 1.3mg | 1.1mg | 1.3mg |
| Niacin | 14mg | 16mg | 14mg | 16mg | 14mg | 16mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.3mg | 1.3mg | 1.3mg | 1.3mg | 1.5mg | 1.7mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.4mcg | 2.4mcg | 2.4mcg | 2.4mcg | 2.4mcg | 2.4mcg |
| Choline | 425mg | 550mg | 425mg | 550mg | 425mg | 550mg |
| Vitamin K | 90mcg | 120mcg | 90mcg | 120mcg | 90mcg | 120mcg |
| Folate | 400mcg | 400mcg | 400mcg | 400mcg | 400mcg | 400mcg |
How Much of Each Micronutrient Does Your Body Require?
| MINERALS | FEMALES AGED 19-30 YEARS | MALES AGED 19-30 YEARS | FEMALES AGED 31-50 YEARS | MALES AGED 31-50 YEARS | FEMALES AGED 51 AND ABOVE | MALES AGED 51 AND ABOVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 1000mg | 1000mg | 1000mg | 1000mg | 1200mg | 1000mg |
| Iron | 18mg | 8mg | 18mg | 8mg | 8mg | 8mg |
| Magnesium | 310mg | 400mg | 320mg | 420mg | 320mg | 420mg |
| Phosphorous | 700mg | 700mg | 700mg | 700mg | 700mg | 700mg |
| Potassium | 4700mg | 4700mg | 4700mg | 4700mg | 4700mg | 4700mg |
| Sodium | 2300mg | 2300mg | 2300mg | 2300mg | 2300mg | 2300mg |
| Zinc | 8mg | 11mg | 8mg | 11mg | 8mg | 11mg |
| Copper | 900mcg | 900mcg | 900mcg | 900mcg | 900mcg | 900mcg |
| Manganese | 1.8mg | 2.3mg | 1.8mg | 2.3mg | 1.8mg | 2.3mg |
| Selenium | 55mcg | 55mcg | 55mcg | 55mcg | 55mcg | 55mcg |
These tables show the amount of each micronutrient that everyone needs. You should try as much as possible to make sure your diet consists of these micros. The easiest way to make sure you consume as many vitamins and minerals are by eating lots of fruits and vegetables, and a wide variety of them (10).
Whether you’re looking to simply pep up your fitness routine, jazz up your diet with mouth-watering low-calorie recipes or want to get your act together and significantly drop that number on your scale – the BetterMe app has got you covered! Improve your body and revamp your life with us!
What Each Micronutrient is used for?
It is clear that micros are important in our diets. Here are the reasons they are essential to each person’s diet:
Vitamin B1: Thiamin
Vitamin B1 is important as it helps (8):
- Release energy from food
- Prevent beriberi
This vitamin can be found in whole grains, dried beans, peas, and animal proteins e.g. beef.
Vitamin B2: Riboflavin
Riboflavin is essential to the body as it is required to build and maintain body tissues.
Some places you are likely to get this vitamin include whole grains, green and yellow vegetables, and animal proteins (8).
Vitamin B6: Pyridoxine
This vitamin plays several useful roles in the human body (8).
- Firstly, it helps develop the nervous system.
- It also helps with food production.
- Lastly, it helps produce fuel for the body by helping break down proteins and glucose.
It can be obtained from eating potatoes, chickpeas, yeast, nuts, bulgur, fish, rice, and bananas.
Vitamin B12: Cobalamin
Cobalamin is used to promote proper growth and development of the nervous system.
It can be found in animal products as well as fortified cereals, nutritional yeast, and algae. (8).
Vitamin C: Ascorbic Acid
This is one of the commonly known vitamins. It is used to (8):
- Help form growth hormones
- Help build strong gums, teeth, and bones
- Function as an antioxidant
Vitamin C can be found in citrus fruits, cabbage, berries, and peppers.
Folic Acid
The folic acid is useful because it (8):
- Helps build proteins
- Helps build a person’s DNA
- Is useful in aiding bone growth
- Helps prevent nervous system birth defects
It can be found in dark green leafy vegetables, yeast, as well as wheat germ.
Vitamin A: Retinal
Vitamin A helps keep your hair and skin healthy, as well as promotes good eyesight. It can be found in animal products. The body is also able to make its own vitamin A from vegetables that have carotene, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, and other red-orange vegetables (8).
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is another common vitamin. It is used to (8):
- Prevent rickets (Rickets is a disease caused by a lack of getting enough vitamin D)
- Help create strong teeth and bones
It can be found in mushrooms, egg yolks, salmon, tuna, cod liver oil, fortified cereals, dairy milk, and fortified non-dairy milk. The body is also able to produce vitamin D when exposed to the sun.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is another essential vitamin. It is used to (8):
- Prevent damage to cell membranes
- Protect vitamin A
- Aid in the production of blood
It can be found in seeds, nuts, and vegetable oil.
Read More: Essential Vitamins and Foods That Provide Them
Vitamin K
This vitamin helps add the clotting of blood. It can be found in green leafy vegetables. It can also be produced by bacteria in the large intestine (8).
Calcium
This is yet another micronutrient to the human body. It can be used to (8):
- Maintain teeth and bones
- Help in the clotting of blood
- Help nerves and muscles to function
It can be found in dairy milk, fortified non-dairy milk, dark green vegetables, sardines, clams, oysters, legumes, almonds, etc.
Potassium
Potassium can be found in a diverse array of plant-based foods, especially potatoes, oranges, bananas, cereals, and dried beans. It is useful for (8):
- Regulating water balance in cells
- Helping nerves function
- Controlling the heart rhythm
Sodium
Just like potassium, it helps regulate water balance as well as stimulate nerves. It is commonly found in salt and bread (8). We need sodium, but many of us get too much in our diets and it is common for people to focus on reducing sodium intake.
Iron
Iron is quite important to the human body. It is useful for (8):
- Forming blood cells
- Transporting oxygen throughout the body
It can be found in animal proteins, dark green vegetables, whole-grain cereals, legumes, lentils, nuts, seeds, and dried fruits.
Zinc
Zinc is useful for (8):
- Aiding in the transport of carbon dioxide
- Aiding in the healing of wounds
- Forming enzymes
It can be acquired from eating whole grains, dairy milk, and fortified non-dairy milk and legumes.
Micros and Weight Loss
Micros do not really have a big effect on your weight. This is because they are required in such small quantities. If you want to check your weight, it is advisable to check your macros as they constitute your total calorie intake. Micros helps ensure you are eating all the nutrients required by your body, hence promoting healthy eating. Micros do not also affect your weight because they don’t have calories. When you take a cup of yogurt, you will absorb the proteins, carbs, as well as fats in the drink. In addition to that, your body will also absorb calcium. The proteins, carbs, and fats might have calories but the calcium won’t (3).
The Bottom Line
If you ever find yourself answering the question, what are micros? Those are exactly what micros (micronutrients) are. They are quite essential to our bodies and, hence, we should ensure our diet consists of foods that are rich in the various micronutrients needed in the body.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on to make decisions of any kind. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any medical conditions. Any action you take upon the information presented in this
SOURCES:
- A Breakdown of Macros and Micros (2019, rwjbh.org)
- Appendix 7. Nutritional Goals for Age-Sex Groups Based on Dietary Reference Intakes and Dietary Guidelines Recommendations (n.d., health.gov)
- Macronutrients vs Micronutrients: Which Matters Most? (2020, barbend.com)
- Macros vs. Micros (2018, winnipegfreepress.com)
- Micros vs. macros: Everything you need to know (2020, medicalnewstoday.com)
- Mayo Clinic Minute: The difference between micronutrients and macronutrients (2018, mayoclinic.org)
- Nutrients (Macro vs. Micro) (n.d., wit.edu)
- NUTRITION BASICS (n.d., mynutrition.wsu.edu)
- What does it mean, hit your ‘micros vs. macros nutrients?‘ (2015, chicagonow.com)
- What’s the Difference Between Micronutrients and Macronutrients? (2019, healthline.com)