We often joke about back pain being a sign of ‘getting old’ but tight and aching back muscles are actually becoming more common, even among younger adults. The thing about such pain is you can easily ignore it for a while and dull it with medication, but it can lead to larger problems if left untreated. At the core, tight back muscles are a sign that you’re doing something, or multiple things that are causing too much strain on your back. There could be some underlying medical issues at play, but it’s more likely you have an imbalance in your lifestyle. So, what can you do? First off, read this article in which we cover; What causes tight back muscles, how to tell if there is an underlying medical issue, home remedies for tight muscles, whether over-the-counter (OTC) medication should be used to treat them, and methods to prevent them.
The Muscles In Your Back And How They Work
Do you know how many, or how big, or how strong the muscles in your back are? Your back is made up of several large and small muscles (1). I’ll try my best to paint a clear picture of how these muscles work together and why they become tight in the first place.
The largest muscle is the erector spinae, running from the lower neck to the tailbone. It supports posture, especially when standing up straight. The rhomboid muscles in your upper back keep your spine aligned and the trapezius muscles in your back and neck help you rotate and tilt your head.
The smaller muscles in your back are mainly responsible for stabilization. They help to maintain the position of your spine as you move and give it additional support when you lift things or strain yourself.
As you can see, almost every movement that you do on a day to day basis is supported by the muscles in your back. It’s no wonder why they can become overloaded, tight and achy!
Why Are My Back Muscles So Tight?
Pinpointing the exact cause of tight back muscles can be tricky since there are many different factors that can contribute to it. It’s rarely ever a single culprit, but rather a combination of factors.
You’re Sitting Or Standing Wrong
By far the most common cause of tight back muscles is poor posture. Poor posture is defined as any posture that puts additional strain on the spine and surrounding muscles. This can be anything from sitting in a hunched position for too long, to standing with your weight unevenly distributed.
Aside from static posture (sitting or standing in one position), dynamic posture (the way your body moves as you go about your day-to-day activities, such as bending, lifting and twisting) also plays a role in how tight your muscles become.
Ideally, with correct posture a line of gravity should pass through the ear, shoulder and hip. This position will ensure that your spine is in its correct anatomical position, thus preventing any additional strain on the muscles in your back.
But with posture misalignments, it’s common to experience tightness in your lower, mid and upper back.
Read More: How To Relax Back Muscles To Unwind And Melt Away Tension
Here are the common types of posture misalignments and how they affect your muscles:
- Lordotic posture – when the spine curves too much at the lower back, which in turn causes overstretching of your abdominal muscles and tightness in your lower back (6).
- Kyphotic posture – when the spine curves too much in the upper back, which leads to excessive tension on your upper back muscles (5).
- Flat back posture – when the spine is in too much of a neutral position, which causes tightness in the muscles that support your spine (3).
- Forward head posture – when the head protrudes forward and down, which leads to overstretching of your neck muscles (10).
While seated, the following faulty posture, which can contribute to tightness in the back muscles:
- Crossing your legs – when you cross one leg over the other, it can strain your hip muscles and tighten your lower back.
- Slouching – sitting in an unnatural curvature of the spine can cause overstretching and tightness in your abdominal muscles, leading to lower back pain.
- Sitting on your wallet – when you sit with a wallet in your back pocket, it misaligns your hips and causes your pelvis to tilt, leading to tightness in your lower back.
You’re Leading A Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle is defined as one that involves a lot of sitting and little to no physical activity (9). This can be detrimental to your spine health, as it doesn’t give the muscles in your back enough opportunity to move and stretch.
The recommended amount of physical activity for adults is 150 minutes per week, so if you’re getting less than that, you may be at risk for tight back muscles (4).
You’re Overweight
Being overweight has a cascading effect on our bodies, placing extra strain on the muscles and joints (2). Several things happen when you’re carrying extra weight:
- Your abdominal muscles weaken – under strain from the excess weight, they can no longer support your trunk as well, leading to compensation by other muscles in your back.
- Your posture worsens – excess weight can push your body forward, causing you to hunch over and strain your back muscles.
- Your joint stability decreases – due to the extra strain, your joints become less stable and more prone to injury.
You Smoke
Research shows that smoking habits may have a long term effect on the posture control system. It increases the risk for lumbar disc degeneration (a common cause of back pain), which can lead to tight back muscles (8).
Furthermore, nicotine is known to constrict the blood vessels, which reduces the amount of oxygen and nutrients delivered to your muscles. Over time, this can lead to muscle tightness, spasms and pain.
You’re Injured
Injuries can also cause tightness in the back muscles. If you’ve recently had an accident or suffered through a muscle strain, it’s likely that your back muscles will become tight as they try to heal themselves.
Whether you’re a workout beast or just a beginner making your first foray into the world of fitness and dieting – BetterMe has a lot to offer to both newbies and experts! Install the app and experience the versatility first-hand!
How Can I Tell If There Is An Underlying Medical Issue?
While it’s true that tightness in the back muscles can be caused by poor posture and overuse, there can also be other underlying medical issues that could be the cause.
If you have tightness in your back muscles that is accompanied by any of the following symptoms, it’s best to see a chiropractor as soon as possible:
- Tingling or numbness in the lower back, legs and/or feet
- Weakness in the lower back, legs and/or feet
- Pain radiating down the back or legs
- Difficulty moving your lower back
How To Loosen Tight Lower Back Muscles
Fortunately, there are some simple home remedies that can help to loosen tight back muscles.
Posture Correction
Posture correction is a slow, gradual, yet multi-faceted approach to addressing tight back muscles. You’ll need to look at all the different aspects of your lifestyle that could be contributing, and make small changes to improve posture.
Follow these steps:
- Avoid holding static postures for long – including prolonged sitting and standing, take breaks often.
- While seated or standing maintain a neutral spine position, with your head and neck in line with the rest of your body.
- If you’re doing manual labor or heavy lifting, make sure to keep your back in a neutral position and engage your core so that your back is supported.
- Make sure you have an ergonomic workspace, with a chair that supports your back and encourages good posture.
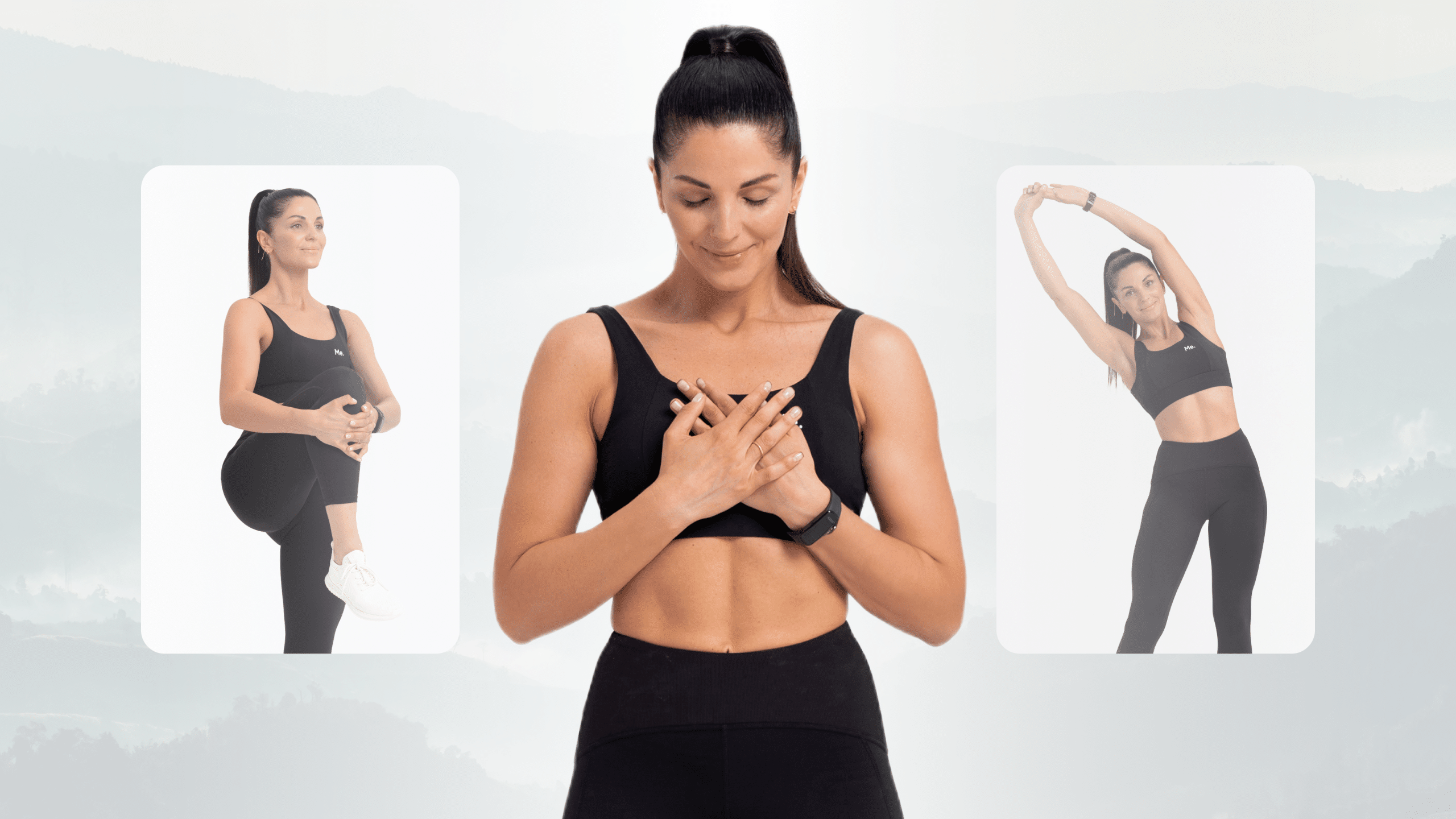
Stretches For Tight Back Muscles
Knowing how to loosen tight muscles in the lower back often comes down to doing the right stretches. These are best down when the pain is mild. If you’re feeling too much pain, then it may be best to see a chiropractor.
Here are some simple stretches you can do to loosen tight back muscles:
- Cat/Cow Stretch – Begin by getting on your hands and knees, and then arching your back up in a ‘cat’ position. Then, round your back in the opposite direction to create a ‘cow’ position, before returning to the initial cat position.
- Child’s Pose – This is a basic yoga pose that stretches the lower back muscles and can also help with relaxation. Begin by sitting on your heels, with your knees apart and ankles touching. Slowly lower yourself forward until your forehead is resting on the floor. Hold this pose for 5-10 breaths.
- Knee to Chest – Begin by lying on your back and bringing one knee up towards your chest, holding it there with your hands. Make sure to keep the other leg flat on the floor. Hold this position for 5-10 breaths, and then repeat with the other leg.
- Seated Twist – Begin by sitting on the floor with your legs straight in front of you. Then, cross one leg over the other and twist your body to the side, keeping your back as straight as possible. Hold this position for 5-10 breaths and then repeat on the other side.
Read More: Unwind With These Relaxing Yoga Poses While Lying On Your Back
Thermo-Therapy
Using heat or cold on a sore area of your back can be an effective way to loosen up tight muscles. Heat works by increasing circulation and relaxing muscles, while cold numbs any pain and can reduce inflammation (7).
Knowing when to use either heat or cold can be confusing, so here’s a quick guide to help you:
- If the area is swollen and inflamed, use cold packs (like a bag of frozen peas) for 15-20 minutes. The idea is to make the blood vessels constrict, to reduce swelling and inflammation.
- If the area is sore but not swollen, use heat packs. Applying a hot water bottle, heating pad or warm bath for 15-20 minutes can help to increase circulation and relax the muscles.
To get the most benefit from either heat or cold therapy, it’s best to use them several times a day for around 20 minutes each.
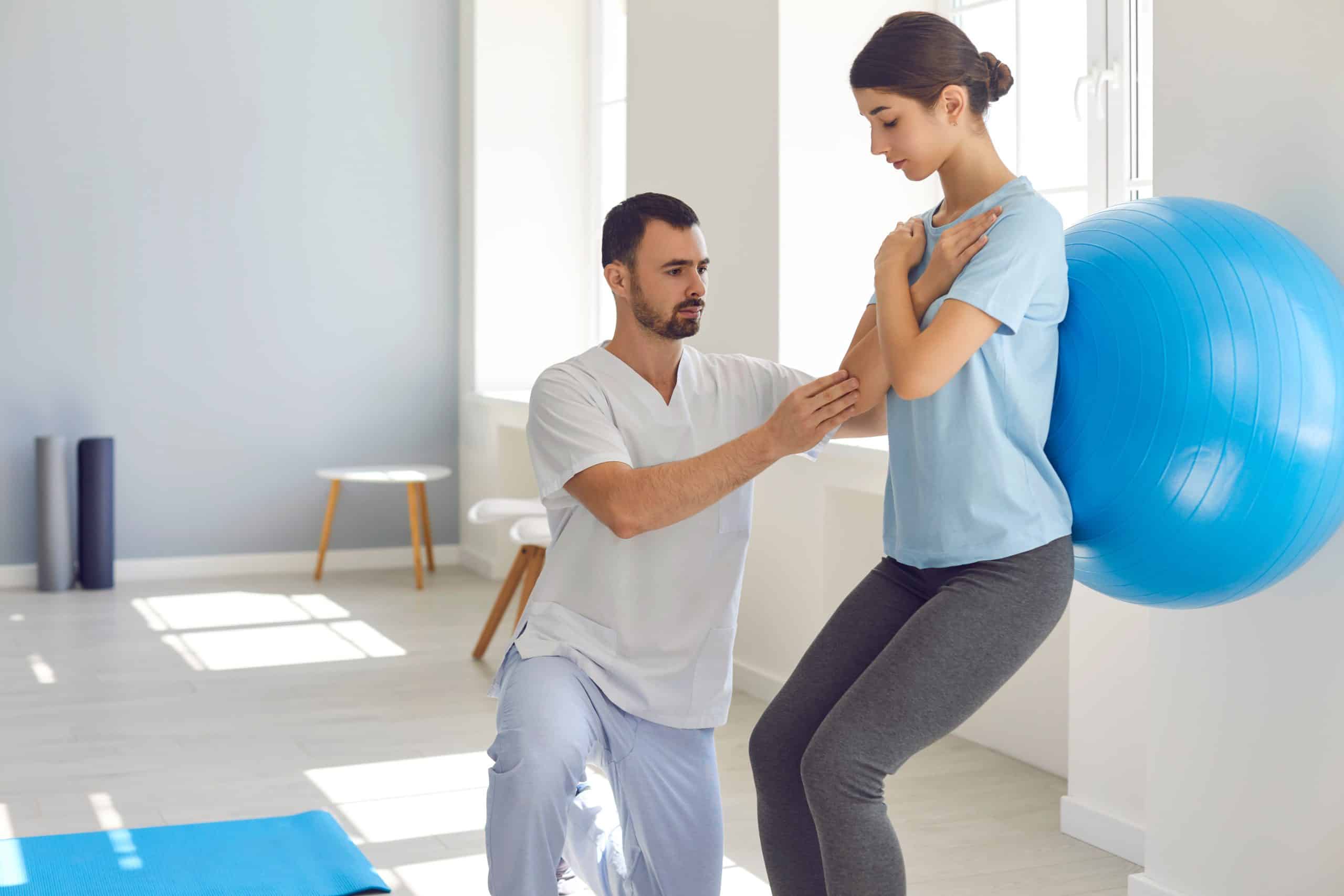
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a great way to address tight back muscles. The physiotherapist will be able to assess your condition, determine the cause of your tight muscles, and devise a tailored treatment plan.
This can include manual therapy techniques, such as massage and mobilization, to help loosen tight back muscles, as well as exercises to strengthen and stretch the affected area.
Some advantages of working with a physiotherapist include:
- A tailored treatment plan to address your specific needs
- Access to specialized techniques and treatments, such as dry needling and kinesio taping
- The ability to monitor your progress over time
- A professional opinion on the cause of your tight muscles and any underlying issues.
At your first physiotherapist appointment, you will be asked to provide a detailed medical history and complete an assessment. Your physiotherapist may also use special tests to determine the origin of your problem and how best to treat it.
Should I Use Over-the-Counter Medication For Back Pain?
Over-the-counter medications for back pain can provide temporary relief, but it is best to speak with a healthcare professional to determine the cause and find out if stronger medications or other treatments are necessary.
We advise against using over-the-counter medication as the first line of defense when it comes to treating tight back muscles, since they will only mask the pain and not provide lasting relief.
However, if you are in significant pain or the pain persists for more than a few days, it may be beneficial to speak with your healthcare provider about taking a short course of over-the-counter medication.
Dropping pounds by the dozens without putting yourself through the wringer is everyone’s weight loss pipe dream. But what if we told you that the BetterMe app can make that happen? Keep yourself in prime shape with our fat-blasting workouts, delicious budget-sparing recipes, and body-transforming challenges with our app!
How Can I Prevent Tight Back Muscles?
Prevention is certainly better than cure when it comes to tight back muscles. Here are some tips for avoiding this issue in the first place:
Maintaining A Healthy Weight
Weight management comes down to proper diet and exercise. Eating a balanced diet, reducing your intake of processed foods, and doing some form of physical activity such as walking or swimming will go a long way towards helping you reach and stay at a healthy weight.
Lead An Active Lifestyle
A common misconception is that exercise is only necessary for weight loss. In reality, exercise plays an important role in maintaining overall good health and preventing a range of conditions, including tight back muscles. It helps in the following ways:
- Increasing muscle strength – when done correctly, exercise builds strength in your back muscles and core. This helps support your spine, reducing the risk of injury
- Improving flexibility – flexibility exercises such as yoga and pilates can help keep your muscles loose and supple
- Improving posture – moves such as deadlifts and planks help strengthen your core, which will improve your posture and reduce back strain
Of course, it is important to practice proper form when exercising, as poor form can lead to injury. If you’re unsure of how to perform a particular exercise, it’s always best to ask a fitness professional for advice.
Lifting Correctly
It is important to use correct form when performing any type of lift, as incorrect technique can put undue strain on your back. This includes lifting objects from the floor as well as picking up children or pets.
When lifting, keep your feet shoulder-width apart and bend your knees, not your back. Tighten your abdominal muscles and lift with your legs, not your back. Breathe out with the exertion and keep your back as straight as possible.
Conclusion
Tight back muscles can be very painful, but luckily there are steps you can take to both treat the problem and prevent it from occurring in the first place. An active lifestyle, healthy eating habits, and regular exercise are all important ways to keep your back muscles strong and healthy.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on to make decisions of any kind. Any action you take upon the information presented in this article is strictly at your own risk and responsibility!
SOURCES:
- Anatomy, Back, Muscles (2022, nih.gov)
- Clinical Problems Caused by Obesity (2018, nih.gov)
- Flatback Syndrome (n.d., neurosurgery.columbia.edu)
- How much physical activity do adults need? (2022,cdc.gov)
- Kyphosis (2022, nih.gov)
- Lumbar lordosis (2014, nih.gov)
- Mechanisms and efficacy of heat and cold therapies for musculoskeletal injury (2015, nih.gov)
- Smoking habits and postural stability (1994, nih.gov)
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Overview of Updated Evidence of Potential Health Risks (2020, nih.gov)
- The Relationship Between Forward Head Posture and Neck Pain: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (2019, nih.gov)