Everyone tells you to soak up the sun and let rays bounce off your skin to absorb vitamin D naturally. However, few explain why you should soak vitamin D beyond how your skin naturally scoops it up from the sun. Is vitamin D good for your skin? You’d probably love to know what the responsibilities of vitamin D are while discovering the benefits for your skin. Why should you absorb vitamin D, take supplements, and use vitamin D oil? Let’s find out.
Get your personalized
meal plan!
Let’s Discover How Vitamin D For The Skin Works And Matters
Vitamin D is an incredible source of skin, hair, and health benefits. It’s important to understand why your skin needs the vitamin, how it works for skincare, and which benefits you can enjoy.
Why Do We Need Vitamin D For Our Skin?
The National Institute of Health published facts about vitamin D for health professionals (11). It helps you understand how vitamin D works in your body. When the skin is exposed to UV rays, it synthesizes vitamin D.
Meanwhile, the National Institute of Health recommends vitamin D in several ways (11). You’ll consume vitamin D3 in your diet and fortified foods or supplements with vitamins D2 and D3. You’ll likely get most of your vitamin D through sun exposure, but several factors can limit how much sun exposure you are able to get, which is where your diet comes in.
7 Vitamin D Benefits For Skin
Vitamin D plays an essential role in natural skin care and protection. How can you use vitamin D and benefit from it if it plays such a significant role in your largest organ? Let’s see what it does for your skin before discovering ways to use it.
Vitamin D Forms A Barrier To Protect The Skin
Cairo University examined your skin’s and vitamin D’s relationship (9). Vitamin D is involved in skin cell differentiation and proliferation, and regulates the production of glycosylceramides which form the skin barrier. This protects against pathogenic microbes and environmental toxins.
Vitamin D Enhances Skin Immunity
Cairo University suggested that vitamin D regulates B and T cells responsible for maintaining good immune functions (9). It also activates macrophages and monocytes. These two cells identify irregular or harmful cells to activate the immune system.
Read More: Vitamin K2 Benefits: Why This Little Known Nutrient Is Essential To Your Diet
Vitamin D May Reduce Acne
Ankara Occupational Diseases Hospital found that people with nodulocystic acne had lower vitamin D levels than those without it (4). This may be due to vitamin D’s role in the proliferation and differentiation of keratinocytes and sebocytes.
Vitamin D Heals Wounds And Repairs Skin Damage
Cairo University found that vitamin D regulates a protein called cathelicidin (9). The protein is an essential tool in repairing skin damage and healing wounds. It’s an antimicrobial that promotes the restoration of the protective barrier and activates repair.
Vitamin D Antioxidants Slow Skin Aging
The Medical University of Sofia suggested that vitamin D reduces oxidative stress in skin cells (7). Oxidative stress makes your skin age faster; reducing it can limit or delay skin aging. In addition, vitamin D plays a vital role in DNA repair to help slow skin aging.
Are Various Forms Of Vitamin D Good For Skin?
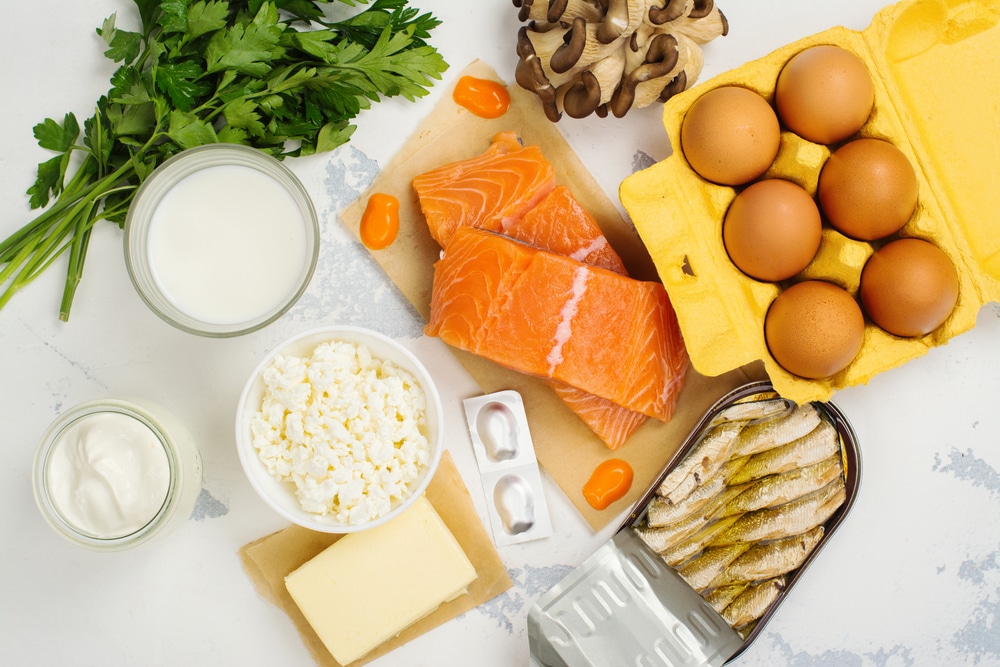
The National Institute of Health suggests various forms of vitamin D to benefit your skin (11). You can obtain vitamin D3 from fatty fish and cod liver oil. Trout, tuna, and salmon are excellent sources of vitamin D3. Fortified soy and almond milk or cereal also works.
Uses Of Vitamin D For Skin
You can surprisingly use vitamin D in various ways. The right amount of vitamin D brings all the benefits to your skin. However, each one requires some safety information because too much vitamin D isn’t a good thing. Everything needs balance, including your skincare habits.
Use Natural Vitamin D For Skin Care Safely
Oregon State University has shown how only sunlight or UVB rays can activate the precursor to vitamin D3 (8). The keratinocytes in your skin start processing pre-vitamin D3 to form the D3 that benefits your health, skin, and hair. However, too much exposure is harmful.
Getting too much vitamin D can work against your skin and health. So, be careful of how much exposure you get. The National Institute of Health lists the adverse side effects of vitamin D deficiency (11):
- Children’s vitamin D deficiencies can cause rickets, soft bones, poor skeletal formation, developmental delays, dental problems, and cardiomyopathy.
- Adult Vitamin D deficiencies can cause bone mineralization, weak bones, pain, seizures, and dental issues.
- Over-exposure to sunlight can lead to skin cancer, damage, premature aging, sunspots, and wrinkles.
Meanwhile, some people need more natural sun exposure than others. The National Institute of Health also suggests adding sufficient vitamin D intake to higher-risk groups, like (11):
- Anyone who doesn’t burn or tan quickly because they have natural melanin that acts as a sunscreen,
- Obese individuals with too many fat cells as it sequesters vitamin D,
- Older individuals because their skin can’t actively synthesize vitamin D as well as they did before,
- People who have limited sun exposure or use sunscreen daily.
If you’ve mustered up the courage to crush your weight loss goal, let Betterme take the sting out of this demanding process. Our app will help you restructure your habits, remold your life and crank up your fitness results!
How Much Skin Exposure To Vitamin D Is Recommended?
Nothing beats natural exposure, but too much will damage your skin or risk skin cancer. Dr. Robert Ashley at UCLA recommends exposure limits to benefit and avoid side effects (1). It depends on a few variables such as latitude and how much skin is exposed, so see the recommendations below:
- One study found that light-skinned individuals in Valencia, Spain produced enough vitamin D from 8-10 minutes of sun exposure at noon in the spring and summer when 25% of their bodies were exposed. They needed 2 hours in the winter when 10% of their bodies were exposed.,
- In Miami in the summer, individuals who tanned easily but still burned needed 3 minutes in the sun to produce enough vitamin D, but those same people would need 23 minutes in Boston in the winter.
- If the weather is cold and very little of the body is exposed, you will likely need longer.
- Darker skinned people likely need longer.
Ultimately, use sunscreen when sun exposure is longer to prevent sunburn and skin damage.
Use A Vitamin D Face Mask
A face mask may rejuvenate the skin and help protect it. You must use vitamin D ingredients to make the mask naturally, but you can also customize it with other ingredients. The National Institute of Health provides a list of ingredients rich in vitamin D (11):
Ingredients:
- 1 egg yolk
- ½ a teaspoon of Cod liver oil
- 2 tablespoons of oats
- 2 tablespoons plain yogurt
Directions:
- Mix the ingredients to form a paste.
- Apply it to your face without rubbing, as the oats may scratch your skin.
- Rinse it off after 15 minutes using lukewarm water.
- Wash your face with gentle soap to remove any excess oil.
Recommended Vitamin D Daily Intake And Sources
Cairo University explains how your skin helps to produce vitamin D3 while your intestines absorbD2 and D3 from your diet (9). How much vitamin D should you consume in your diet? The National Institute of Health recommends the following international units by circumstance (11):
- Adult men and women should have 600 IU daily, which remains the same for pregnant or lactating women,
- People over 70 require a higher daily intake of 800 IU.
The recommended daily intake is average. Circumstances like climate, season, geographic location, gender, skin type, or BMI may also change how much you consume (9). It helps to get a recommended dose from your physician or nutritionist.
Foods With Vitamin D2 And D3
The National Institute of Health lists foods high in vitamin D (11). Add these products to your daily diet to help you absorb vitamins D2 and D3. Check the labels to see the UIs and mcgs. However, these common foods contain roughly this amount per serving size:
- Beef Liver: 42 IU or 1 mcg per 3 0z.,
- Canned Sardines: 46 IU or 1.2 mcg per two sardines,
- Cod Liver Oil: 1,360 IU or 34 mcg per tablespoon,
- Egg: 44 IU or 1.1 mcg per large size,
- Fortified Cereal: 80 IU or 2.4 mcg per package serving size,
- Fortified Milk: 120 IU or 2.9 mcg per cup,
- Trout: 645 IU or 16.2 mcg per 3 oz.,
- Tuna: 40 IU or 1 mcg per 3 0z.,
- Salmon: 570 IU or 14.2 mcg per 3 oz.,
- White Mushrooms: 366 IU or 9.2 mcg per ½ cup.
Read More: Discover 6 True Vitamin E Benefits For Hair And Scalp
FAQs
What Does Vitamin D Do For Your Skin?
Cairo University examined the benefits of vitamin D on your skin (9). Vitamin D protects your skin by creating an external barrier, supporting your skin’s immune system..
What Are The Benefits Of Vitamin D For The Skin And Hair?
Cairo University shows many skin benefits with vitamin D (9). It improves immunity and creates a barrier. However, Nishtar Medical University examined how it helps with hair loss (2). Oral vitamin D3 helped people with hair loss caused by telogen effluvium deficiency.
Meanwhile, the Venkat Center for Skin and Plastic Surgery confirmed how vitamin D is important for hair follicles (6). This means by absorbing more vitamin D in your diet and with sunlight you might prevent hair loss.
The Bottom Line
Vitamin D is the famous sunshine vitamin everyone talks about, but do you know how to use it? Follow safety guidelines and recommended exposure to ensure you don’t damage your skin. Instead, you’ll want healthier skin with fewer infections and inflammation.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- Ask the Doctors: How Much Sunshine Do I Need for Enough Vitamin D? (2018, uclahealth.org)
- Efficacy of Oral Vitamin D3 Therapy in Patients Suffering From Diffuse Hair Loss (Telogen Effluvium) (2021, nih.gov)
- Plant Oils as Potential Sources of Vitamin D (2016, nih.gov)
- Preliminary Evidence for Vitamin D Deficiency in Nodulocystic Acne (2014, nih.gov)
- Psoriasis: Psoriatic Arthritis (n.d., medicineplus.net)
- Role of Vitamin D in Hair Loss: A Short Review (2021, nih.gov)
- The Impact of Vitamin D on Skin Aging (2021, nih.gov)
- Vitamin D and Skin Health (n.d., lpi.oregonstate.edu)
- Vitamin D and the Skin: Focus on a Complex Relationship: A Review (2015, nih.gov)
- Vitamin D Increases Cell Turnover and Functionally Restores the Skeletal Muscle in Rats (2023, nih.gov)
- Vitamin D: Fact Sheet for Health Professionals (2022, nih.gov)