Protein is essential for building and repairing muscles, bones, and tissues.
It consists of amino acids, the body’s “building blocks,” which also help produce hormones and enzymes (1,2).
While protein can serve as an energy source, its primary role is to support:
Most people can meet their protein needs through a balanced diet, as many already consume more than enough from food alone.
High-protein diets are trending, with influencers promoting their benefits for muscle gain, weight management, and overall health. But what qualifies as “high” protein, and how much do you need?
A common misconception is that plant-based proteins are incomplete and require food pairing. However, research shows that our bodies store amino acids, meaning a variety of plant proteins throughout the day provides all essential amino acids—you don’t need to pair any foods intentionally (4).
This article explores everything you need to know about protein and how to create easy, high-protein meals that fuel your body.
What Are Some Meal Prep Ideas High-Protein-Focused?
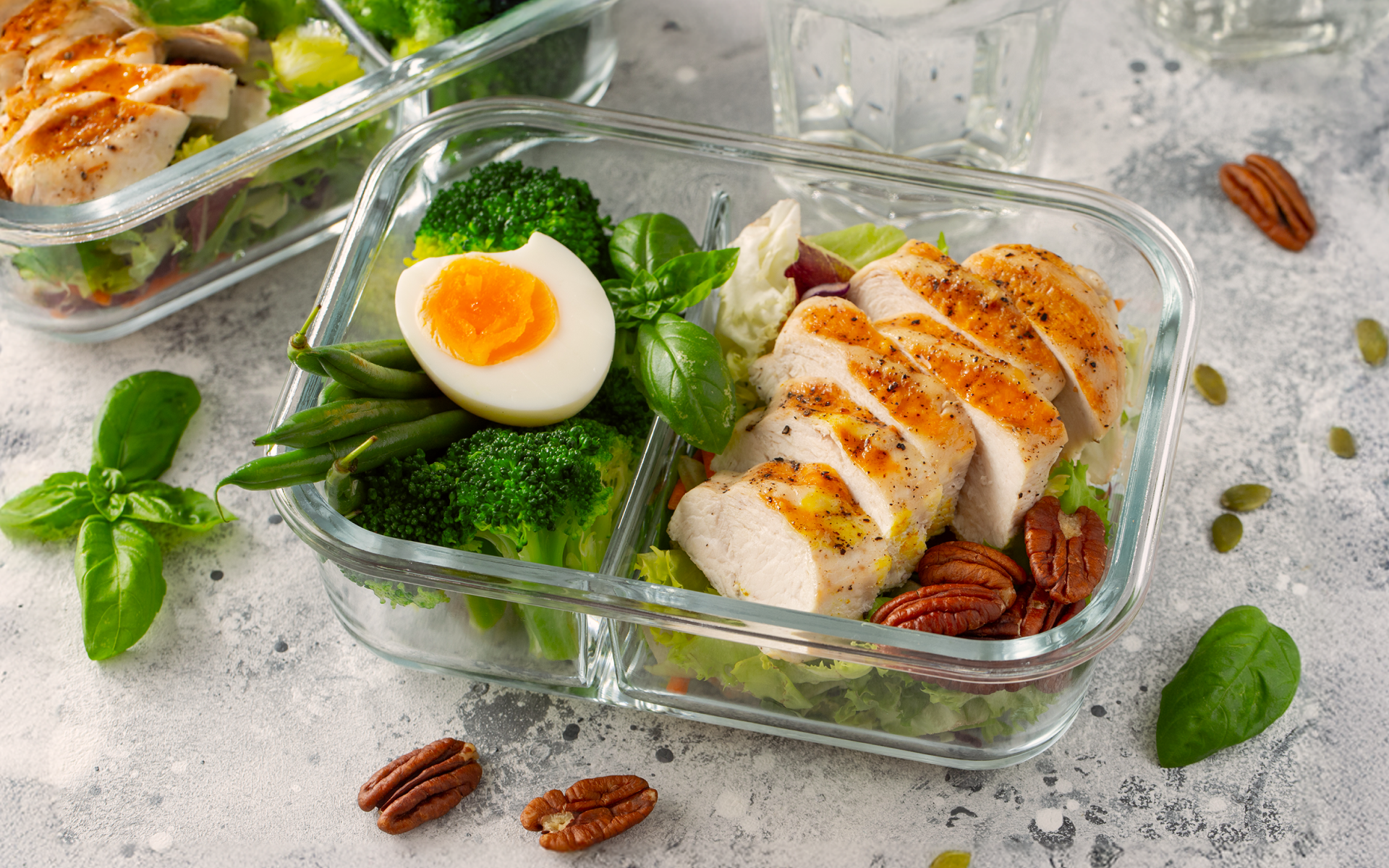
Simple high-protein meal prep ideas for muscle gain can be as easy as choosing different staples and batch-cooking them.
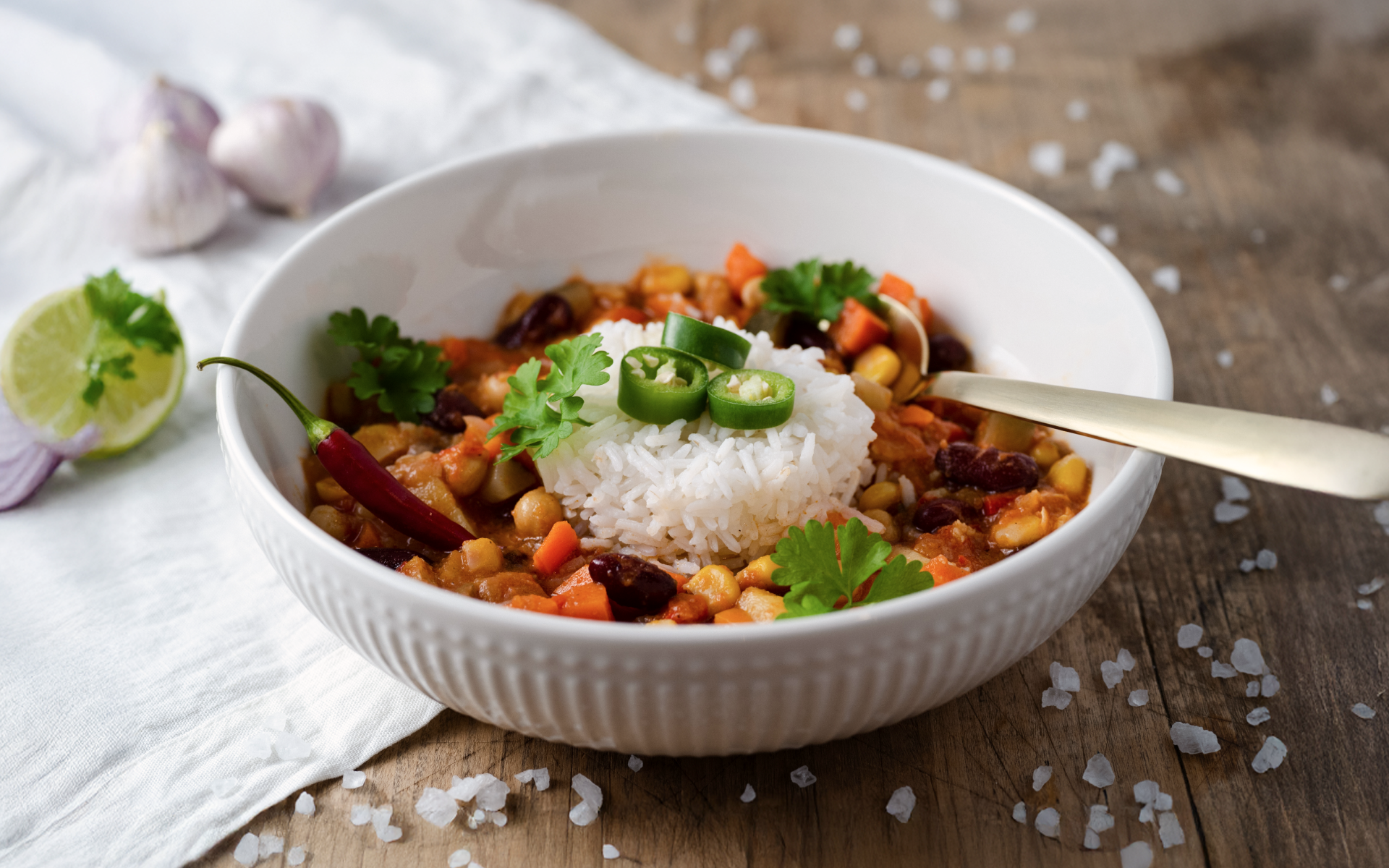
Think of meals such as overnight oats, mixed bean chili with quinoa, bean burritos, chicken burritos, salmon poke bowls with edamame, and tofu stir-fries—the list is endless!
Protein Intake For Muscle Growth
Research suggests that to build muscle effectively, one should consume:
- 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily.
Distributing protein across multiple meals to further optimize intake helps maximize muscle protein synthesis (4).
- Other studies recommend 0.4g/kg per meal over 4 meals; individual needs can vary.
- 0.25-0.55g/kg per meal across 3-5 meals may also be adequate.
- A simple guideline that covers most individuals is 0.4g/kg per meal over 4 meals; this amount is most commonly used and suggested as the blanket target (4,5).
Eating more than 20g of protein in one sitting does not mean your body wastes the extra grams.
While MPS reaches a threshold per meal (~20-40g, depending on the individual), excess protein still plays a role in:
- Muscle repair
- Energy production
- Other physiological functions.
However, excessive protein intake does not accelerate muscle growth, as the body limits the amount of protein, it can use for muscle-building.
The key is to meet your protein needs while maintaining a well-balanced diet that supports overall health and performance (6).
Why Is Meal Prep A Good Idea For You?
Meal prep can be a fantastic idea as it can help you:
- Save time by reducing daily cooking and meal decisions.
- Lower stress by ensuring ready-to-eat, nutrient-dense meals
- Reduce food waste through better planning and portion control.
- Support health goals, whether muscle gain, fat loss, or maintenance.
- Help with consistency, making it easier to stick to a balanced diet.
When it comes to weight loss, progress is made by inches, not miles, so it’s much harder to track and a lot easier to give up. The BetterMe: Health Coaching app is your personal trainer, nutritionist, and support system all in one. Start using our app to stay on track and hold yourself accountable!
What Are The Benefits Of Meal Prepping High-Protein Foods?
- Can promote muscle growth and recovery by supplying an even spread of protein throughout the day (Read more about meal prep for muscle gain here)
- Optimize fat loss by providing a consistent eating schedule and optimizing your metabolism.
- Improves dietary consistency, eliminating last-minute unhealthy choices.
- Saves money by buying protein sources in bulk and reducing food waste.
- Adds variety with both animal and plant-based proteins for balanced nutrition.
- Can help support weight loss progress (especially by using meal prep ideas high protein low calorie)
How to Prepare High-Protein Meals In Advance?
- Plan meals based on your daily protein needs to meet fitness goals.
- Batch cook proteins like chicken, tofu, fish, or lentils to save time.
- Use diverse cooking methods – grill, bake, slow cook, or steam for variety.
- Balance macronutrients by pairing proteins with healthy fats and complex carbs.
- Store meals properly in airtight containers to maintain freshness and avoid waste.
Read more: High-Calorie Recipes for Weight Gain: Nutritious and Flavorful Options
What Are Some Easy High-Protein Meal Prep Recipes For Muscle Gain And Fat Loss?
Traditional Diet Options:
Scrambled Eggs with Spinach and Avocado on Whole-Grain or Sourdough Toast (~18-20g protein)
- Whole-grain/sourdough toast (1 slice) = ~4g
- Spinach (1 cup) = ~1g
- Eggs (2) = ~12g
- Avocado (½) = ~2g
- (Consider adding cheese (~5g) for extra protein.)
Greek Yogurt with Protein Granola and Berries (~24-26g protein)
- Protein granola (½ cup) = ~10g
- Greek yogurt (6 oz) = ~15g
- Berries (½ cup) = ~1g
Overnight Oats with Protein Powder, Flaxseeds/Chia Seeds, Nut Butter, and Fruit (~28-30g protein)
- Oats (½ cup) = ~5g
- Protein powder (1 scoop) = ~20g
- Chia or flaxseeds (1 tbsp) = ~2g
- Nut butter (1 tbsp) = ~3g
Plant-Based Options:
Overnight Oats with Protein Powder, Flaxseeds/Chia Seeds, Nut Butter, and Fruit (~28-30g protein)
- Same as above
Granola with Dairy-Free Yogurt (e.g., Soy Yogurt), Berries, and Hemp Seeds (~18-22g protein)
- Dairy-free yogurt (soy-based, 6 oz) = ~6g
- Granola (½ cup) = ~8-10g
- Hemp seeds (1 tbsp) = ~3g
Smoothie with Rolled Oats, Calcium-Fortified Plant-Based Milk, Protein Powder, Flaxseeds, and Berries/Banana (~30-35g protein)
- Oats (½ cup) = ~5g
- Fortified plant-based milk (soy/pea, 1 cup) = ~7-10g
- Protein powder (1 scoop) = ~20g
- Flaxseed (1 tbsp) = ~2g
Tofu Scramble with Spinach and Avocado on Whole-Grain or Sourdough Toast (~20-25g protein)
- Avocado (½) = ~2g
- Spinach (1 cup) = ~1g
- Tofu (high-protein, 4 oz) = ~14-18g
- Whole-grain toast (1 slice) = ~4g
- (Add nutritional yeast (~2 tbsp) for +5g protein.)
Lunch Meal Prep Ideas High-Protein
Grilled Chicken with Quinoa and Roasted Vegetables (~40g protein)
- Chicken breast (4 oz) = ~30g
- Quinoa (1 cup cooked) = ~8g
- Roasted vegetables = ~2g
Tuna Salad with Chickpeas and Avocado (~30-34g protein)
- Tuna (3 oz) = ~25g
- Chickpeas (½ cup) = ~7g
- Avocado = ~2g
BetterMe is your fast-track ticket to long-lasting weight loss! Tailor your fitness journey and maximize your results with just a couple of swipes!
Plant-Based Options:
Toasted Turkish Bread Roll with Avocado, Rocket, Mock meat (e.g. Seitan or Fava Bean-Based Vegan Chicken) (~32-35g protein)
- Turkish roll = ~8g
- Mock meat (seitan, ~3 oz) = ~21g
- Avocado = ~2g
- Rocket = ~1g
Wholemeal Pita Bread with Black Beans, Spinach, Tofu, Sweet Chili Sauce, Avocado (~26-28g protein)
- Wholemeal pita = ~6g
- Black beans (½ cup) = ~7g
- Tofu (3 oz) = ~10g
- Spinach = ~1g
- Avocado = ~2g
Chickpea, Pea, and Sweet Potato Curry with Brown Rice (~22-25g protein)
- Chickpeas (½ cup) = ~7g
- Sweet potato (½ cup) = ~2g
- Brown rice (1 cup) = ~5g
- Green beans (1 cup) = 8g
- (Consider adding tempeh or tofu for a higher-protein variation)
Lentil Bolognese with Pasta and Nutritional Yeast (~30-32g protein)
- Lentils (1 cup cooked) = ~18g
- Whole-wheat pasta (1 cup cooked) = ~8g
- Nutritional yeast (2 tbsp) = ~5g
- Tempeh (3 oz) = ~19g
Roasted Vegetables with Sautéed Broccolini, Spinach, Quinoa or Wild Rice, Tempeh or Seitan ~32-34g protein)
- Roasted vegetables = ~2g
- Broccolini (1 cup) = ~3g
- Quinoa (1 cup cooked) = ~8g
- Tempeh (3 oz) = ~19g
Dinner High-Protein Meal Prep Recipes
Baked Salmon with Roasted Brussels Sprouts and Farro (~34g protein)
- Salmon (4 oz) = ~25g
- Brussels sprouts (1 cup) = ~3g
- Farro (1 cup cooked) = ~6g
Ground Turkey Lettuce Wraps with Black Beans (~30g protein)
- Ground turkey (4 oz) = ~22g
- Black beans (½ cup) = ~7g
- Lettuce wraps = ~1g
Tempeh Stir-Fry with Edamame and Wild Rice (~34g protein)
- Tempeh (3 oz) = ~19g
- Edamame (½ cup) = ~9g
- Wild rice (1 cup) = ~6g
Black Bean and Tofu Chili (~35-40g protein)
- Black beans (1 cup cooked) = ~14g
- Tofu (4 oz, firm or extra firm) = ~14g
- Red kidney beans (½ cup cooked) = ~7g
- Tomatoes (1 cup diced) = ~2g
- Nutritional yeast (2 tbsp) = ~5g
- Onion, garlic, and spices
Snack Ideas For Muscle Gain And Fat Loss
- Edamame (½ cup): ~9g
- Hard-boiled eggs (2 eggs): ~12g
- Cottage cheese with nuts: ~18g
- Roasted chickpeas (½ cup): ~7g
- Protein smoothie with plant-based protein powder: ~25g
Discover more easy meals for the week in this article here.
Read more: How to Build a Healthy Dinner Plate, According to Experts
How Can I Incorporate More Protein Into My Meal Prep?
Remember, protein is actually in almost all foods, in varying quantities.
If you are eating enough energy from calories, you should naturally meet your baseline protein requirements from various key food groups.
To dial this in even further, ensuring that each of your main meals contains a prominent protein source will provide you with an even distribution throughout the day (2):
- Animal Proteins: Chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, cottage cheese, Greek yogurt
- Plant-Based Proteins: Tofu, tempeh, lentils, beans, quinoa, chia seeds, nuts, nutritional yeast
Considerations For Choosing Your Protein Sources
While we know protein is essential, we must also consider its role in our overall health (7). Rigorous research has consistently shown that there are some key considerations regarding protein sources. Not all protein sources are created equal, and what comes with protein (such as fat, sodium, fiber, and micronutrients) affects health (8, 9, 10).
Eat more of these:
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas): High in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Nuts & seeds: Rich in healthy fats and plant-based protein.
- Seafood: High in protein and omega-3 fatty acids (good for heart health).
- Poultry (chicken, turkey): Lower saturated fat than red meats
- Dairy: In moderation
- Plant proteins: Quinoa, chia seeds, etc.
Eat less of these:
- Red meat (beef, pork, lamb): High in saturated fat; linked to heart disease, diabetes, and cancer (8,9,10)
- Processed meats (bacon, hot dogs, sausages, deli meats): High in sodium and preservatives; increase cancer risk (8,9,10)
- Fast food meats: Often deep-fried and highly processed
Tips To Store High-Protein Meal Preps For The Week
- Refrigeration vs. Freezing: Keep refrigerated meals for 3-5 days; freeze meals for up to 3 months for more extended storage.
- Use Airtight Containers: Prevents spoilage, maintains freshness, and avoids freezer burn.
- Label Meals: Mark preparation dates to track freshness and reduce waste.
- Reheat Properly: Use gentle reheat.
Yes! Meal prep ideas for weight loss help control portions, reduce mindless snacking, and ensure balanced, nutritious meals, making it easier to stay on track with weight loss goals. You can read more about meal prep for weight loss female-focused here. Great options include Greek yogurt, boiled eggs, cottage cheese, nuts, protein bars, hummus with veggies, vegan jerky, tuna packs, and edamame. Refrigerated meals stay fresh for 3-5 days, while properly stored frozen meals can last up to 3 months. Yes! You can save money with high protein meal prep on a budget by buying in bulk, batch cooking, and using budget-friendly protein sources like eggs, beans, canned fish, and tofu.Frequently Asked Questions
Can meal prep help with weight loss?
What are the best high-protein snacks for meal prep?
How long can high-protein meal preps be stored?
Is meal prepping for high-protein diets cost-effective?
The Bottom Line
Meal prepping high-protein meals is one of the most effective ways to stay consistent, save time, and reach your fitness goals. Whether your focus is muscle gain, fat loss, or overall health, having pre-planned, protein-rich meals helps ensure you stay on track.
For optimal health and longevity, prioritize high-quality protein sources, including:
Best Choices:
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas)
- Nuts & seeds (almonds, walnuts, chia seeds)
- Seafood (salmon, tuna, shrimp)
- Poultry (chicken, turkey)
- Eggs (rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals)
- Whole grains (quinoa, oats, brown rice)
Limit Intake Of:
- Red meat (consumed occasionally)
- Dairy (moderation; opt for yogurt over cheese/milk)
- Processed meats (avoid as much as possible)
Avoid Completely:
- Fried meats (high in unhealthy fats)
- Highly processed meats (bacon, hot dogs, sausages)
- Excessively salted meats (linked to high blood pressure)
Start small – choose 1-2 recipes, plan weekly meals, and build from there.
Experiment with different protein sources to keep your meals nutritious, satisfying, and enjoyable.
Remember, variety is key!
A balanced, high-protein diet will support muscle growth, fat loss, and long-term well-being, whether you prefer lean meats, seafood, or plant-based proteins.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- Protein (2024, betterhealth.vic.gov)
- Protein (2023, nutrition.org.uk)
- Protein (2025, nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu)
- How much protein can the body use in a single meal for muscle-building? Implications for daily protein distribution (2018, nih.gov)
- Is It Time to Reconsider the U.S. Recommendations for Dietary Protein and Amino Acid Intake? (2023,nih.gov)
- A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression of the effect of protein supplementation on resistance training-induced gains in muscle mass and strength in healthy adults (2017, nih.gov)
- Diet Quality as Assessed by the Healthy Eating Index- Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies (2017, nih.gov)
- Cancer incidence and mortality during the intervention and postintervention periods of the Women’s Health Initiative dietary modification trial (2014, nih.gov)
- American Cancer Society guideline for diet and physical activity for cancer prevention (2020, nih.gov))