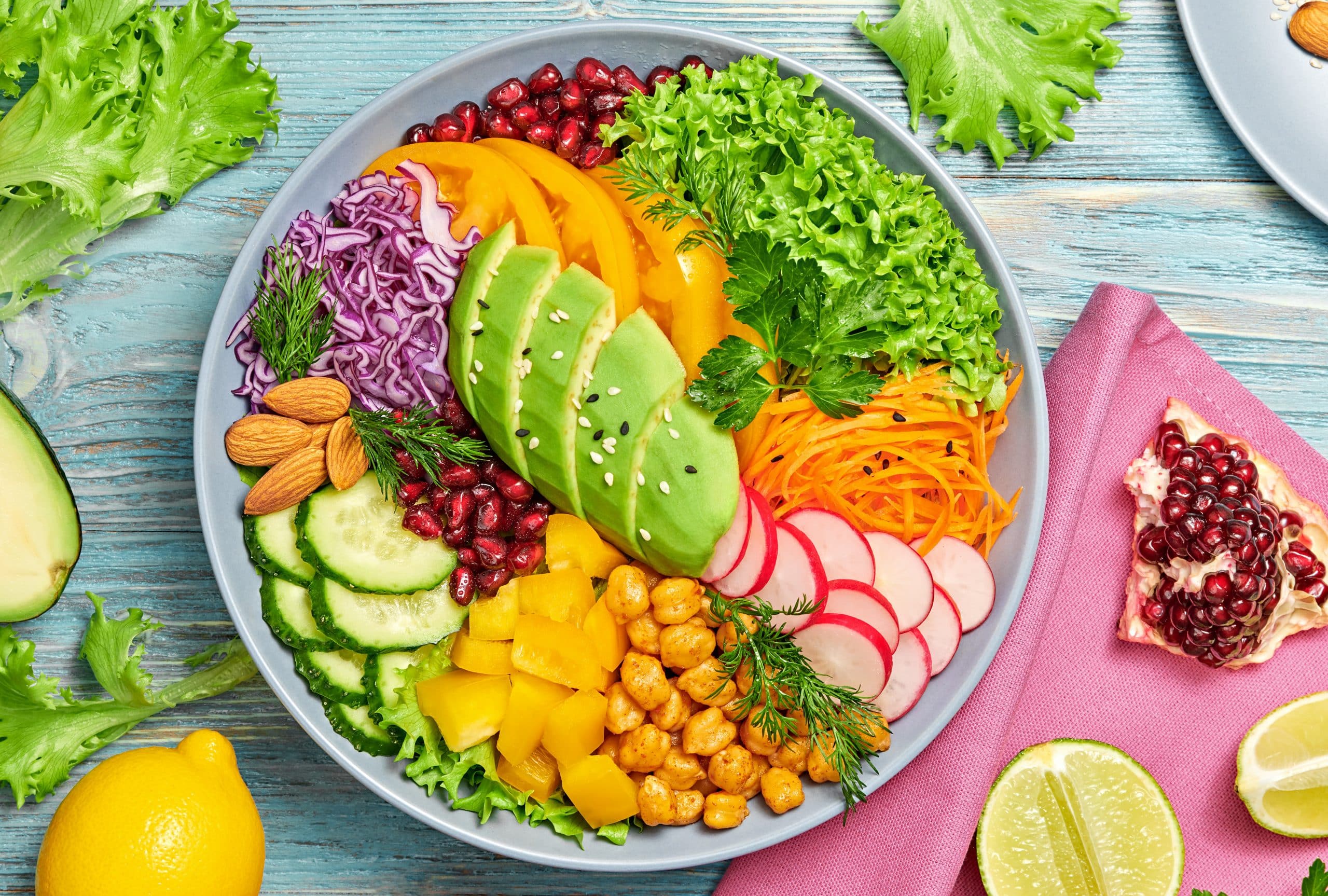
Getting on a Paleo diet plan may be one of the best decisions you’ve ever made if the hype is anything to go by. This dietary approach, which mimics the eating habits of our Paleolithic ancestors, has gained considerable attention for its supposed health benefits. This diet focuses on consuming whole, nutrient-dense foods such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, while avoiding processed foods, grains, dairy, and refined sugars. Advocates of the Paleo diet argue that this way of eating aligns better with our genetic makeup, and can therefore lead to significant improvements in health and well-being. From weight loss and improved energy levels to better digestion and reduced risk of chronic diseases, the purported benefits of the Paleo diet are compelling enough to make anyone reconsider their current eating habits.
Get your personalized
meal plan!
What Are The 7 Pillars Of The Paleo Diet?
The “7 Pillars of the Paleo Diet” is not a universally accepted or defined concept. Remember, the Paleo diet isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach. It’s more of a template to guide your eating habits, and it can be tailored to meet individual health needs and goals.
That said, based on various sources and interpretations of the Paleo diet, the following principles could be considered as its seven pillars:
- Whole Foods: Eating foods that are natural, unprocessed, and as close to their original state as possible.
- Lean Proteins: Consuming a good amount of lean meats, poultry, and fish which provide the necessary proteins for muscle growth and immune function.
- Fruits and Vegetables: These are a vital part of the diet providing essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Healthy Fats: Sourcing fats from foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fish, which are rich in Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids.
- Avoid Processed Foods and Sugars: Processed foods, artificial sweeteners, and high-fructose corn syrup are avoided.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity is a key part of the lifestyle, reflecting our ancestors’ active routines.
- Hydration and Sleep: Drinking plenty of water and ensuring adequate sleep are also crucial for overall health and wellness.
What Are Some Benefits Of The Paleo Diet?
The purported benefits of adopting this diet are numerous and, if true, might significantly impact one’s health and well-being:
1. Weight Loss
The Paleo diet promotes the consumption of nutrient-dense, whole foods and eliminates processed foods and added sugars, which tend to be high in calories and low in nutritional value.
When you replace these calorie-laden foods with healthier options, you naturally reduce your calorie intake, which can lead to weight loss (10). Additionally, the emphasis on protein-rich foods can increase satiety, helping to curb overeating and snacking between meals.
Furthermore, the Paleo diet encourages physical activity, which can also contribute to weight loss and overall health. Regular exercise not only helps burn calories but also builds muscle mass, which boosts your metabolism and further aids in weight loss (9).
By combining a healthy diet with regular exercise, the Paleo lifestyle offers a holistic approach to weight management. On the other hand, the Paleo diet is quite restrictive, which won’t work for everyone, especially long-term.
Read More: Paleo Chicken Pot Pie Recipe For Cold-Weather Comfort
2. Improved Blood Sugar Control
The Paleo diet eliminates refined carbohydrates and sugars, which can cause high blood sugar levels in people with impaired blood sugar control. Instead, it focuses on slower-burning sources of energy like fruits and vegetables, which helps regulate blood sugar level (10).
By promoting better blood sugar control, the Paleo diet may help manage blood sugar in people with insulin resistance and other metabolic disorders. You should always talk to your doctor before making any dietary changes, especially if you are on medication to lower your blood sugar.
3. Better Heart Health
Heart health is a major concern for many people, and the Paleo diet might offer several benefits in this area. The diet is rich in lean proteins and high in fiber, both of which are beneficial for heart health (2).
Lean meats provide essential nutrients without the saturated fats found in processed and fatty meats, while dietary fiber can help lower cholesterol levels.
In addition, the Paleo diet promotes the consumption of fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, all of which have been associated with improved cardiovascular health. Fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants that protect against heart disease, while healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health (5). You don’t have to be on the Paleo diet to get these benefits – simply focus on eating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and choosing healthy fats over unhealthy ones.
4. Reduced Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is increasingly being linked to a host of health problems, from heart disease to cancer. The Paleo diet promotes foods that are rich in anti-inflammatory nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in foods like fish and nuts, are believed to reduce inflammation in the body (7).
This diet also eliminates processed foods and sugars, which are thought to contribute to inflammation. By focusing on anti-inflammatory foods and eliminating potential inflammatory triggers, the Paleo diet might help reduce chronic inflammation and its associated health risks, although there is not enough scientific evidence to demonstrate this. You can also include more omega-3s and antioxidants and reduce your intake of ultra processed foods and added sugars without the extreme restriction of the Paleo diet.
5. Improved Gut Health
The Paleo diet excludes foods that are hard on some people’s digestive systems, like dairy and grains. This is particularly beneficial for people with intolerances, allergies, or autoimmune sensitivities to those particular foods. However, a Paleo diet is not the only answer for people living with those conditions – they can simply avoid the specific food that triggers their condition.
By focusing on nutrient-dense, whole foods, the Paleo diet is likely to be high in fiber which promotes a healthy gut microbiome (13). A healthy gut microbiome is crucial for overall health, aiding in everything from digestion and nutrient absorption to immune function and even mood regulation.
6. Increased Energy Levels
One of the most commonly reported benefits of the Paleo diet is increased energy levels. They feel that by cutting out highly processed foods and focusing on nutrient-dense whole foods, the diet provides a steady supply of energy throughout the day (8).
Eating a balance of protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates from fruits and vegetables can provide energy, but the Paleo diet is missing a key energy source by cutting out whole grains and legumes.
Whether you’re looking to simply pep up your fitness routine, jazz up your diet with mouth-watering low-calorie recipes or want to get your act together and significantly drop that number on your scale – BetterMe app has got you covered! Improve your body and revamp your life with us!
7. Enhanced Mental Clarity
Some people who follow the Paleo diet report improved mental clarity and focus. This is subjective and it is unclear whether, how, or why the Paleo diet in particular might improve cognitive function.
The diet’s focus on nutrient-dense foods might help your brain get some of the nutrients it needs to function optimally. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, for example, are crucial for brain health and cognitive function. On the other hand, the Paleo diet is very restrictive and might not provide enough carbohydrates for your brain to function optimally.
8. Improved Skin Health
The Paleo diet might theoretically improve skin health. It promotes the intake of fresh fruits and vegetables, which are loaded with antioxidants and other nutrients that can help protect and repair the skin (5). These foods also have high water content, which can help keep your skin hydrated.
In addition, this diet eliminates common dietary triggers for skin issues, like dairy and added sugar. Some studies suggest a link between these types of foods and skin conditions like acne. By removing potential triggers, the Paleo diet might help clear up skin problems.
9. Reduced Allergies
The Paleo diet may help reduce allergies since it eliminates some common allergens from the diet, such as dairy, wheat, and soy. These foods can trigger allergic reactions in some people (12).
By focusing on whole foods and avoiding known allergens (if you are allergic to them), the Paleo diet could potentially alleviate allergy symptoms. However, it’s important to note that everyone is different. What works for one person may not work for another. The Paleo diet is a pretty drastic measure if you really only need to avoid the foods you specifically are allergic to. Always consult with a healthcare provider or an allergist if you’re considering dietary changes to manage allergies.
10. Better Sleep
The Paleo diet, combined with regular exercise, may contribute to better sleep. Eating a nutritious diet may help regulate your hormones, which can impact your sleep quality (6). Consuming more fruits and vegetables and fewer ultra processed foods might help you get better sleep, but the Paleo diet is an extreme version of that, where smaller adjustments to your diet might do the trick.
There is evidence that physical activity can promote better sleep. Regular exercise may help you fall asleep faster and enjoy better quality sleep (3). Therefore, the Paleo lifestyle, with its emphasis on exercise, might help improve your sleep habits.
11. Sustained Physical Performance
The Paleo diet might support sustained physical performance. It is rich in protein, essential for muscle recovery after workouts, and healthy fats, which provide a long-lasting source of energy. This makes it a popular choice among athletes and those who lead an active lifestyle.
However, it will require effort and planning to get enough carbohydrates to support physical performance given the highly restrictive nature of the diet.
12. Balanced Mood
Many whole foods promoted in the Paleo diet, such as fatty fish and fruits and vegetables, contain nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which have been linked to improved mood and reduced risk of depression (4). Meanwhile, sugar-sweetened beverages, which are avoided on the Paleo diet, may be associated with an increased risk of depression. However, you don’t need to be on the Paleo diet to increase your fruit, vegetable, and fish intake or to reduce your intake of sugar-sweetened beverages.
Why Do I Feel Better On Paleo?
The Paleo diet is often referred to as the “caveman” diet because it omits processed foods, grains, legumes, and dairy, which are not believed to have been eaten by humans in the Paleolithic era.. Here may be why many people report feeling better when following this diet:
1. Improved Digestion
The Paleo diet emphasizes whole foods and eliminates some common allergens and triggers for intolerances, like dairy and grains. This can lead to improvements in digestion for select people who have these intolerances, reducing symptoms like bloating, gas, and irregular bowel movements.
Read More: Paleo-Friendly Grain-Free Pancakes To Enrich Your Diet
2. Weight Loss And Body Composition
Many people find they lose weight on the Paleo diet without having to count calories or feel hungry. This may be partly due to the high protein and fiber content of the diet, which can help keep you feeling full, but a bigger factor is more likely the restrictive nature of the diet, which results in a reduced calorie intake (10).
3. Reduced Inflammation
The Paleo diet is rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats (5). Reducing inflammation may improve various aspects of health, from cognitive function to joint pain and skin clarity.
4. Mental Clarity
Some people report experiencing clearer thinking and improved mental focus on the Paleo diet. This is highly subjective, however.
5. Improved Sleep
Some followers of the Paleo lifestyle report that they sleep more soundly. This could be due to a combination of factors, including increased fruit and vegetable intake, and regular physical activity.
As with any dietary approach, individual experiences with the Paleo diet vary. It’s essential to listen to your body and consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have any medical conditions or are taking any medication.
What Are 3 Disadvantages Of The Paleo Diet?
While the Paleo diet has several purported benefits, it’s important to note that it also has some downsides:
1. Restrictive And Hard To Follow
The Paleo diet eliminates several food groups, including grains, legumes, and dairy. This can make it challenging to follow, especially for long-term commitment. It can also be difficult when dining out or attending social events where these types of foods are typically served.
2. Potential Nutrient Deficiencies
By eliminating entire food groups, you might miss out on essential nutrients. For instance, cutting out dairy can lead to a deficiency in calcium and vitamin D unless adequately compensated with other foods. Similarly, avoiding grains can result in missing out on dietary fiber, complex carbohydrates, and other beneficial compounds found in whole grains.
3. Can Be Expensive
The Paleo diet emphasizes high-quality proteins like grass-fed meats and organic fruits and vegetables, which can be more expensive than their conventional counterparts. This makes the diet less accessible for some people due to cost constraints.
If you struggle to even flirt with the idea of giving up your favorite foods or working out till your legs give way – BetterMe app is here to breathe a fresh perspective into the way you view the weight loss process! Check out the app and experience the fun side of fitness and dieting with BetterMe!
What Are Pros And Cons Of The Paleo Diet? (List)
In summary, here are the pros and cons of the Paleo diet:
Pros
- Simplicity: The Paleo diet doesn’t require calorie counting or portion control, just a simple understanding of which foods to embrace and which to avoid.
- Elimination of Processed Foods: One of the biggest advantages is the elimination of ultra processed and fast foods, which are often high in unhealthy fats, added sugars, and artificial ingredients.
- Focus on Quality Proteins: The emphasis on lean meats provides a good source of quality protein, essential for muscle growth and repair.
Cons
- Restrictive: The diet excludes several food groups, making it difficult to follow for some people, especially over the long term.
- Potential Nutrient Deficiencies: Without careful planning, the exclusion of dairy, grains, and legumes could lead to deficiencies in nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and fiber. It also may not provide enough carbohydrates for optimal functioning and performance.
- May Be Expensive: The emphasis on grass-fed meats, organic fruits, and vegetables can make this diet more costly than others.
- Not Vegetarian/Vegan-Friendly: The focus on animal proteins makes it challenging for vegetarians or vegans to follow.
- Lack of Long-Term Research: There is limited research on the long-term effects and benefits of the Paleo diet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Paleo Actually Healthy?
The Paleo diet is touted as healthy because it promotes the consumption of whole foods and eliminates processed foods, which often contain unhealthy fats, added sugars, and artificial ingredients.
However, it’s important to note that the diet excludes some food groups like dairy and legumes, which can lead to potential nutrient deficiencies if not properly managed. Therefore, it’s crucial to consult with a dietitian or healthcare provider before starting the Paleo diet.
How Successful Is The Paleo Diet?
The success of the Paleo diet can vary greatly depending on individual goals and adherence to the diet. Some people find success in terms of weight loss, improved energy levels, and better digestive health due to the focus on whole foods and elimination of processed ones.
However, the restrictive nature of the diet can make it difficult for some people to stick to it long-term. Therefore, its success often depends on how well an individual adapts to the dietary changes and maintains them in the long run.
Who Should Avoid Paleo?
While many people can safely follow the Paleo diet, certain individuals should avoid it or seek medical advice before starting.
These include people with chronic conditions like kidney disease due to the diet’s high protein content, individuals with certain food allergies or intolerances, and those at risk of eating disorders due to the diet’s restrictive nature. Anyone on chronic medications such as blood sugar lowering medication, blood pressure medication, or blood thinners should speak to their healthcare provider before making any major changes to their diet.
Also, vegetarians or vegans may find the diet challenging due to its heavy emphasis on animal proteins.
Are There Any Side Effects To The Paleo Diet?
While the Paleo diet is said to have several health benefits, there are also potential side effects to be aware of. Some people may experience fatigue, headaches, and irritability during the initial transition period as their body adapts to the new way of eating.
The diet’s restrictiveness can also lead to nutrient deficiencies if not properly planned. Additionally, the high intake of meat and other animal products can potentially increase the risk of heart disease if these foods are high in saturated fat. Always consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before starting any new diet.
The Bottom Line
The Paleo diet, centered around whole foods and the elimination of processed items, is said to offer several potential benefits. From weight loss and improved digestion to reduced inflammation and better heart health, the Paleo lifestyle could be a game-changer for many.
Please know that it’s important to consider its potential drawbacks and consult with a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- Dietary fats and prevention of type 2 diabetes (2010, nih.gov)
- Dietary Fiber, Atherosclerosis, and Cardiovascular Disease (2019, nih.gov)
- Exercising for Better Sleep (n.d., hopkinsmedicine.org)
- Linking What We Eat to Our Mood: A Review of Diet, Dietary Antioxidants, and Depression (2019, nih.gov)
- Health Benefits of Fruits and Vegetables1 (2012, nih.gov)
- Nutrition and Sleep (2023,sleepfoundation.org)
- Omega-3 in fish: How eating fish helps your heart (2022, mayoclinic.org)
- Postprandial energy expenditure in whole-food and processed-food meals: implications for daily energy expenditure (2010,nih.gov)
- Physical Activity for a Healthy Weight (2023, cdc.gov)
- Paleo diet: What is it and why is it so popular? (2022, nih.gov)
- The Paleo Diet: Pros and Cons According to NUNM (2019, nunm.edu)
- Ultra-processed foods and allergic symptoms among children and adults in the United States: A population-based analysis of NHANES 2005–2006 (2022,nih.gov)
- Whole Food-Based Approaches to Modulating Gut Microbiota and Associated Diseases (2020, nih.gov)