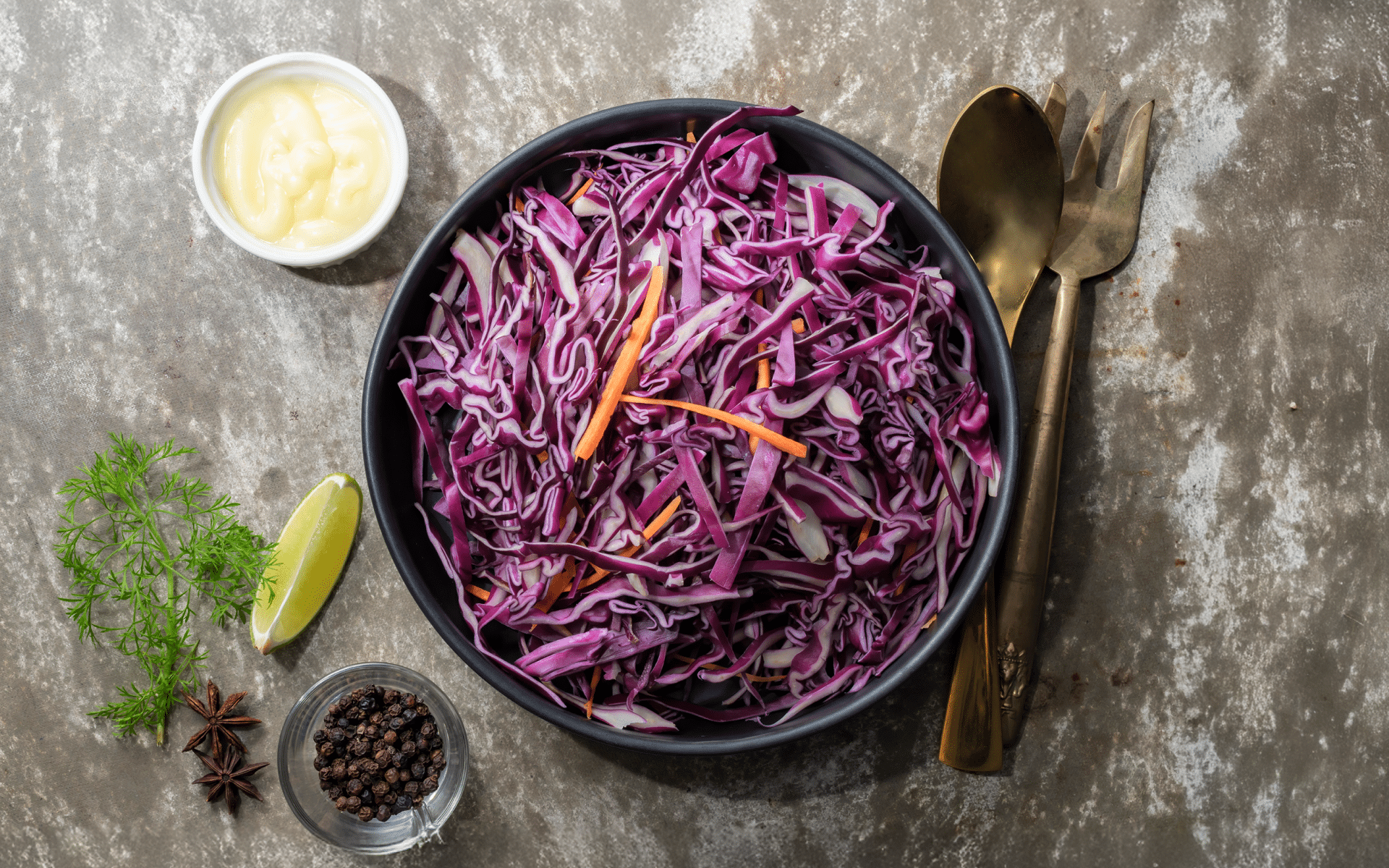
Purple cabbage is closely related to green cabbage; it’s simply a different variety of the cabbage plant. Surprisingly, they even taste similar – the main difference between the two is the color and nutritional profile.
Purple cabbage’s rich color is credited to a number of beneficial plant compounds that make it a nutritional powerhouse. In this article, we’ll review the many health benefits of purple cabbage, according to science.
Purple Cabbage Nutrition Facts
According to the USDA database, One cup (89 grams) of chopped, raw, purple cabbage contains the following nutrients (1):
- Calories: 27.9
- Protein: 1.29 grams
- Carbs: 6.63 grams
- Fiber: 1.89 grams
- Vitamin C: 56% of the daily value (DV)
- Vitamin K: 28% of the DV
- Vitamin B6: 11% of the DV
- Vitamin A: 6% of the DV
- Potassium: 5% of the DV
- Thiamine: 5% of the DV
- Riboflavin: 5% of the DV
Purple cabbage also provides small amounts of iron, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, copper, and zinc.
Health Benefits of Purple Cabbage
Due to its nutritional profile, purple cabbage offers the following health benefits:
- Rich in Disease-Fighting Antioxidants
Purple cabbage is a great source of antioxidants and other beneficial plant compounds that help protect against cellular damage.
Vitamin C is the most well-known antioxidant in cabbage. It is a water-soluble vitamin, which means it isn’t stored in the body and must be replenished daily. It performs many essential functions in the body, including wound healing, strengthening blood vessels and tissues, maintaining healthy gums and teeth, and supporting the immune system (2).
In addition, purple cabbage contains other antioxidants including carotenoids such as beta-carotene, lutein, and zeaxanthin, which support eye health (3).
Purple cabbage is also a source of flavonoid compounds called anthocyanins, which are being studied for their antioxidant effects.
Anthocyanins are one of the most potent types of antioxidants that are found in plants (4). Their presence gives certain fruits and vegetables their dark color, including eggplant, grapes, hawthorn berries, blackberries, blueberries, raspberries, cherries, and purple cabbage.
Anthocyanins have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties (5). Therefore, they may help protect against and relieve the pain associated with arthritis and other types of inflammatory conditions.
In addition, cabbage is a good source of indoles and sulforaphanes, which are phytonutrients that help protect against cancer. Indole-3-carbinol (I3C) in particular has been studied extensively in the laboratory and in animal studies for its anti-cancer effects. In test tube studies, sulforaphane has been shown to inhibit the growth of cancer cells (6).
- Improved Heart Health
Purple cabbage has a number of nutrients that may be good for your heart.
The purple color is due to antioxidants called anthocyanins. These pigments are being studied for their potential role in cancer prevention and heart disease, in addition to other conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease (7).
Isoflavones may help reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke by blocking an enzyme that stimulates the production of cholesterol in the liver. They also may protect against cancer (8)
Carotenoids may lower blood pressure and increase “good” HDL cholesterol. Fiber, which is abundant in purple cabbage dishes, also helps lower “bad” LDL cholesterol (9).
Vitamin C is needed for collagen formation to maintain the wall of blood vessels, which may help prevent atherosclerosis. The American Heart Association suggests that people eat five to nine servings of fruits and vegetables a day to reduce their risk of heart disease through vitamin C consumption, in addition to fiber, potassium, and other heart-healthy nutrients (10).
- Improved Bone Health
Purple cabbage contains several bone-benefiting nutrients.
Vitamin C, a chemical necessary for the formation of collagen, is abundant in purple cabbage. Collagen is an important protein that makes up bone tissue and helps strengthen bones and connective tissues such as tendons (11).
Vitamin K, a fat-soluble vitamin, is found in purple cabbage. It helps the body with blood clotting and also helps move calcium into the bones where it can benefit bone health. Purple cabbage also contains smaller amounts of calcium, potassium, magnesium, and phosphorus (12)
Calcium is necessary for the development of healthy bones. It works to assist the body in balancing fluid levels. Magnesium is required for the formation of bones and teeth as well as the production of energy from carbohydrates. Phosphorus works with calcium to help build strong bones (12).
If you wish to free yourself from all the extra pounds that have been weighing you down for way too long, start using the BetterMe: Health Coaching app and overhaul your entire life!
- Improved Gut Health
Purple cabbage may help improve gut function due to the various nutrients it contains.
It contains anti-inflammatory compounds that may help reduce intestinal inflammation and is a great addition to your diet if you suffer from autoimmune or inflammatory gut conditions, as long as you’re not having an active flare-up and can tolerate fiber (l). Cabbage contains fermentable fibers, which are fuel for the good bacteria in our guts. The insoluble fiber from purple cabbage can also help to reduce constipation (13).
In addition, antioxidants have been shown to protect the gut lining and reduce damage caused by free radicals (14). This may mean that antioxidant-rich purple cabbage can promote healthy digestion and prevent digestive issues like bloating gas, and constipation.
As a result, purple cabbage may improve overall gut health and support healthy bowel movements.
- Improved Skin Health
The nutrients in purple cabbage make it one of the best vegetables you can eat for skin health.
This vegetable contains antioxidants that are good for your complexion and that may help fight premature aging.
Purple cabbage also contains vitamins A, C, and E (more than spinach), which are excellent for your skin. Vitamin A helps prevent acne breakouts and wrinkles. Vitamin C brightens your skin tone and helps with hyperpigmentation. Vitamin E helps prevent collagen crosslinking and lipid peroxidation, which are linked again to skin (15).
- Helps Lower Blood Pressure
The reputation of cabbage as a blood-pressure-lowering food stems from its richness in two bioflavonoids – kaempferol and quercetin – which are potent antioxidants that may help protect the heart and lower blood pressure (16).
Antioxidants fight free radicals, which form in the body due to environmental exposures and as the byproducts of metabolic processes and can damage blood vessel linings. Some studies have suggested that cruciferous vegetable consumption may help prevent atherosclerosis (17).
Cabbage’s potential to lower cholesterol levels has also been well documented. It contains a number of phytochemicals, such as indoles and isothiocyanates, that have been shown to inhibit the body’s production of cholesterol, not to mention fiber, which also helps lower cholesterol (18).
- May Help with Weight Loss
As part of a balanced diet and along with exercise, purple cabbage can be a great weight-loss food. It contains a number of nutrients that aid weight loss.
Firstly, purple cabbage is high in fiber. This vegetable contains approximately 2 grams of dietary fiber per cup, which helps keep you full longer, thereby helping prevent overeating. Fiber also helps lower cholesterol (13).
Secondly, it’s low in calories. A cup of raw purple cabbage only contains approximately 28 calories. A reduced-calorie diet may help reduce the risk of obesity and weight gain, which are both associated with a number of health risks such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes (19).
Read more: Is the Plate Method for Weight Loss Effective?
- Headache and Migraine Relief
The antioxidants in purple cabbage may help reduce migraine headaches by reducing inflammation in blood vessels.
Eating vegetables that are high in magnesium may also be effective for relieving migraines (20).
When these nutrients combine in your body, they may help reduce inflammation and prevent blood vessel constriction, both of which are factors that can contribute to migraines and other types of headaches.
- Memory Loss Prevention
One of the benefits of purple cabbage is that it contains anthocyanin, an antioxidant that potentially helps protect cognitive function (22).
Anthocyanin may boost blood flow to the brain’s memory center, which may help improve short-term recall.
Purple Cabbage Side Effects
Being aware of the potential purple cabbage side effects is also important. Although this vegetable has many beneficial properties, there are some things about it you should know.
- May Inhibit Functioning of the Thyroid Gland
Purple cabbage contains goitrogens that may inhibit the functioning of the thyroid gland, particularly if you also don’t get enough iodine in your diet (23). This vegetable is safe for most people when it’s eaten in moderation and cooking it can help lessen the effects of goitrogens. If you have a thyroid condition, talk to your doctor about how cabbage and other cruciferous vegetables may affect you.
- May Cause Flatulence
Cabbage contains significant quantities of raffinose, an indigestible sugar. Eating too much of it can cause uncomfortable side effects such as gas and flatulence (24).
- Diarrhea
Cabbage contains high amounts of fiber, which is essential for the proper digestion of food. However, too much of it can lead to stomach aches and diarrhea (25). Always start slow when increasing your fiber intake and advance gradually, making sure you drink plenty of fluids as well.
- May Interact with Blood Thinning Medication
This vegetable contains vitamin K, which can reduce the effectiveness of these kinds of medications (26). The most important thing is to keep your vitamin K intake consistent and not vary it widely from day to day.
Talk to your doctor and dietitian about vitamin K intake if you’re on warfarin or another blood-thinning medication. It’s always best to consult a healthcare provider before you change your diet if you’re taking any medication.
When it comes to weight loss, progress is made by inches, not miles, so it’s much harder to track and a lot easier to give up. The BetterMe: Health Coaching app is your personal trainer, nutritionist, and support system all in one. Start using our app to stay on track and hold yourself accountable!
How to Eat Cabbage for Proper Nutrition
Purple cabbage is a versatile vegetable that can be eaten in a variety of different dishes.
When buying purple cabbage, look for smaller heads that are firm and have a deep color. Avoid buying cabbage with limp leaves or those that have been bruised, as these can indicate that it’s nearing the end of its shelf life, and its quality and nutrient retention may be lessened.
Purple cabbage can be eaten raw or cooked for maximum nutritional benefits.
It’s best not to overcook the cabbage as this may reduce the benefits it has to offer. When cooking purple cabbage, you should always remove the outer leaves and cut them into small pieces before adding them to a dish. Although cooking the cabbage will make some of the nutrients easier for your body to absorb, cooking it can reduce the potency of some others.
Read more: Benefits Of Red Cabbage: Surprising Reasons You Should Add This Vegetable To Your Diet
Here are some meal ideas using purple cabbage:
- Use It Raw in Coleslaw
You can use purple cabbage to make a crunchy, refreshing slaw. Cut the cabbage into small pieces and add it to your favorite dressing. You can also top it with fruits or nuts for added flavor.
- Use It Raw in Salad
Cabbage blends well with other vegetables, so it’s recommended that you use it together with carrots, cucumbers, and onions. Add olive oil and vinegar to your favorite dressing and top your salad with some nuts or seeds for extra crunchiness.
- Add It to Your Soup
Purple cabbage can be blended into a smooth soup. Try adding it to a tomato base together with other vegetables such as carrots, green beans, and zucchini for an antioxidant-rich meal that’s easy to digest.
- Add It to Your Omelet
This delicious purple vegetable can be used to make low-carb omelets. Simply combine two beaten eggs with some spices and add some purple cabbage to enhance the flavor of your omelet.
- Stir Fry It with Your Meals
Add some color to your plate by stir-frying this vegetable with your favorite meat and other vegetables. You can also mix it in a salad, pasta or fried rice for added texture and flavor.
- Blend It in Your Smoothie
Purple cabbage can be added to your favorite smoothie for a healthy, delicious drink that’s great for breakfast or as an afternoon snack.
- Add It to Your Juice
If you’re looking for ways to incorporate purple cabbage into your diet, try using it as the base of your juice. This vegetable has a mild flavor that won’t overpower your juice ingredients.
Discover Cabbage Juice Benefits, including support for digestive health and a boost of essential nutrients such as vitamins C and K for overall wellness.
Both green and purple cabbage are nutritious, but purple cabbage has a slight edge due to its higher concentration of antioxidants. Purple cabbage is rich in anthocyanins, the compounds that give it its vibrant color, and these have anti-inflammatory and heart-protective properties (27). It also contains more vitamin C than green cabbage. However, both varieties are excellent sources of fiber, vitamins K and C, and various minerals, so the choice largely depends on your taste preference and specific nutritional needs. Mixing the two can create colorful salads and stir-fries, and then you don’t have to choose. We’ve discussed a 7-Day Cabbage Soup Diet, highlighting its focus on incorporating nutrient-rich vegetables for a simple and structured meal plan. No, purple cabbage isn’t high in sugar. A one-cup serving of raw purple cabbage contains approximately 2 grams of natural sugar (1). It’s a low-calorie, low-sugar vegetable that can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet without significantly impacting blood sugar levels. Its high fiber content also helps slow the absorption of sugar in the body, which makes it a good choice for those who are monitoring their blood sugar (28). Yes, purple cabbage is beneficial for skin health. It’s rich in antioxidants such as vitamin C and anthocyanins, which help protect the skin from damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin C boosts collagen production, improving skin elasticity and reducing signs of aging (15). In addition, its anti-inflammatory properties can help soothe skin conditions such as acne or redness. Including purple cabbage in your diet supports overall skin health from within. Yes, you can eat cabbage every day. It’s a nutrient-dense vegetable that provides essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, benefiting digestion and overall health. However, moderation is key, as excessive consumption of cabbage can cause bloating or gas due to its fiber content and certain natural compounds such as raffinose. If you have thyroid issues, it’s worth noting that cabbage contains goitrogens, which can interfere with thyroid function if consumed in very large quantities over a prolonged period. Talk to your healthcare provider to get individualized advice.Frequently Asked Questions
Which is healthier, green or purple cabbage?
Is purple cabbage high in sugar?
Is purple cabbage good for your skin?
Can I eat cabbage every day?
The Bottom Line
Purple cabbage is a nutrient-rich vegetable that can help boost your health. It contains an array of vitamins and minerals that are beneficial for your body. However, it should be eaten in moderation to avoid getting indigestion or an upset stomach, particularly if you’re not used to a high fiber intake.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- Cabbage, red, raw (2020, fdc.nal.usda.gov)
- Vitamin C in Disease Prevention and Cure: An Overview (2013, nih.gov)
- A Mechanistic Review of β-Carotene, Lutein, and Zeaxanthin in Eye Health and Disease (2020, mdpi.com)
- Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits (2017, nih.gov)
- Daily Consumption of an Anthocyanin-Rich Extract Made From New Zealand Blackcurrants for 5 Weeks Supports Exercise Recovery Through the Management of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: A Randomized Placebo Controlled Pilot Study (2020, frontiersin.org)
- Cruciferous Vegetables and Human Cancer Risk: Epidemiologic Evidence and Mechanistic Basis (2009, nih.gov)
- A Review of the Properties of Anthocyanins and Their Influence on Factors Affecting Cardiometabolic and Cognitive Health (2021, mdpi.com)
- Flavonoids and Their Metabolites: Prevention in Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes (2017, nih.gov)
- How to Lower Cholesterol with Diet (2024, medlineplus.gov)
- Fruit and Vegetable Intake and Mortality: Results From 2 Prospective Cohort Studies of US Men and Women and a Meta-Analysis of 26 Cohort Studies (2021, ahajournals.org)
- Biochemistry, Collagen Synthesis (2023, nih.gov)
- Minerals and vitamins in bone health: the potential value of dietary enhancement (2009, cambridge.org)
- Health benefits of dietary fiber (2009, academic.oup.com)
- Antioxidants in Health and Disease (2017, sciencedirect.com)
- Discovering the link between nutrition and skin aging (2012, tandfonline.com)
- Dietary Quercetin and Kaempferol: Bioavailability and Potential Cardiovascular-Related Bioactivity in Humans (2019, mdpi.com)
- Cruciferous and Total Vegetable Intakes Are Inversely Associated With Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Older Adult Women (2018, ahajournals.org)
- Mechanisms Underlying Biological Effects of Cruciferous Glucosinolate-Derived Isothiocyanates/Indoles: A Focus on Metabolic Syndrome (2020, frontiersin.org)
- Complications of obesity (2018, academic.oup.com)
- Magnesium in headache (2011, nih.gov)
- Vitamin K2 Status and Arterial Stiffness Among Untreated Migraine Patients: A Case-Control Study (2020, nih.gov)
- Intake of Products Containing Anthocyanins, Flavanols, and Flavanones, and Cognitive Function: A Narrative Review (2021, frontiersin.org)
- Various Possible Toxicants Involved in Thyroid Dysfunction: A Review (2016, nih.gov)
- Review article Flatulence — Causes, relation to diet and remedies (1988, onlinelibrary.wiley.com)
- Dietary fiber in irritable bowel syndrome (Review) (2017, nih.gov)
- Warfarin and Vitamin K (2023, uofmhealth.org)
- 8 Impressive Benefits of Purple Cabbage (2024, medicinenet.com)
- Fiber: The Carb That Helps You Manage Diabetes (2024, cdc.gov)