A glass of juice is an amazing way to add more nutrients to your daily diet. If you feel that you lack vitamins, minerals, and energy, in addition to the time for another meal, drinking some juice may just do the trick.
An interesting fact: many people choose to go on a 3-day juice cleanse or regularly drink as much juice as possible in the belief that it will help with weight loss.
This isn’t the safest or most sustainable way to lose weight, but some people choose to do it anyway.
In this guide, I’ll give you the low-down on such cleanses and whether they’re completely healthy. I’ll also give you a list of 20 great fruit and vegetable juices that taste great, keep you in a good mood, and make sure you get enough nutrients every day (as part of a healthy balanced diet).
How to Drink Juices for Weight Loss
First, let’s make one thing clear. Buying a juice drink at a grocery store that says “100% Natural” without looking into its contents won’t automatically bring you any health benefits. Branding is everything nowadays, and it should go without saying that the small print tells the true story.
Here are some tips on consuming juices as part of a diet for weight loss:
- Make juices at home using either a juicer or a blender, depending on the amount of fiber you want to consume daily.
- Try to drink freshly made juice as it has the most nutrients and will bring the most value to you.
- If you have to store the juice, put it in your refrigerator – you can keep it there for up to 3 days.
- Always close the bottle, jug, or other container you keep the juice in. If juice contacts air for too long, the oxidation process may decrease its nutritional value or it may be exposed to microbes.
- The best container for juice is a glass one with a lid you can close tightly.
- When using a juicer, make sure you don’t heat the juice as heat could make enzymes inactive and promote oxidation.
- Consider a cold-press method for making juice.
- If possible, don’t remove pulp and parts of fruit or vegetable skin from the drink, particularly if you need additional fiber.
Fruits and vegetables are rich in biologically active components that may help prevent cardiovascular disease (29) and provide other health benefits. Although eating fruits and vegetables whole is ideal, moderate consumption of juices made from them can help you get more of those compounds and other nutrients.
Are There Benefits of Juicing for Weight Loss?
Proponents of juicing claim that it can help with weight loss in several ways:
1. Increased Consumption of Fruits and Vegetables
Juicing involves extracting the juice from fruits and vegetables. Fruit juices are an excellent source of nutrients and polyphenols, which are good for your health (19).
By incorporating more fruits and vegetables into your diet through juicing, you may be able to reduce your overall calorie intake while still meeting your daily nutrient requirements. However, eating fruits and vegetables whole is still better than juicing them.
2. Improved Digestion
Some fruits and vegetables are rich in enzymes that may help with digestion. Juicing removes much of the insoluble fiber found in these foods, which makes it quicker and/or easier for the body to absorb and digest the nutrients. However, the fiber that is removed is very good for the digestive system and can help promote regularity as well as gut microbiome diversity.
3. Reduced Cravings for Unhealthy Foods
Juicing may help curb cravings for unhealthy foods. By consuming a variety of nutrient-dense fruits and vegetables, you may feel more satisfied and be less likely to reach for ultra-processed or high-calorie snacks.
Read More: Water-Rich Foods: Staying Hydrated Through Your Diet
4. Increased Hydration
Many people struggle to meet their daily fluid intake requirements, which can affect weight loss efforts. Juicing provides a convenient way to increase your fluid intake as most juices are primarily made up of water.
5. Customizable and Flexible
Juicing allows for flexibility in terms of what fruits and vegetables you incorporate into your diet. You can tailor your juices according to your taste preferences, dietary restrictions, and weight loss goals.
What Are the Negatives of Juicing for Weight Loss?
While there are potential benefits of juicing for weight loss, it’s important to be aware of the potential pitfalls too:
- Lack of Fiber: Juicing removes much of the fiber from fruits and vegetables, which is an essential nutrient for digestive health. A lack of fiber may lead to constipation or other digestive issues (37).
- High Sugar Content: Some fruits and vegetables that are used in juicing, such as apples and carrots, are high in natural sugars. While these are healthier than added sugars that are found in sugar-sweetened beverages, fruit juices are still a more concentrated source of those sugars and lack the fiber of whole fruits. To illustrate this point, one large longitudinal cohort study found the greater consumption of fruit juices to be associated with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes, while eating whole fruits was found to be associated with a lower risk (18).
- Calorie Intake: Juices can be deceivingly high in calories, particularly if they contain a lot of fruit. It’s important to monitor your overall calorie intake and choose lower-calorie options when juicing, especially when trying to lose weight.
- Lack of Protein: Fruits and vegetables don’t provide sufficient amounts of protein, which is essential for satiety and muscle maintenance (38). This means that juicing alone may not be enough to satisfy hunger or support long-term weight loss goals, and it doesn’t provide adequate nutrition.
- Not a Sustainable Solution: Juicing may lead to short-term weight loss due to calorie restriction, but it isn’t a sustainable solution for long-term weight loss. A balanced diet with a variety of whole foods is the key to lasting weight management (13).
Are Bottled Juices Okay?
While bottled juices may seem like a convenient option, they often contain added sugars and other additives that may(3) (39):
- Negate the health benefits of juicing
- Contribute to weight gain
- Have negative effects on your overall health
It’s best to opt for freshly made juices or make your own at home using whole fruits and vegetables. This way, you can control the ingredients and ensure that you get the most nutrients from your juice.
If you must purchase bottled juices, make sure to read the label and choose options with minimal added sugars and preservatives.
Here’s how to properly read a bottled juice label:
- Look at the list of ingredients and make sure that fruits and vegetables are listed first.
- Check for added sugars such as high fructose corn syrup, cane sugar, or fruit juice concentrates.
- Be aware of artificial sweeteners or other additives.
- Be mindful of portion sizes; one bottle of juice may contain multiple servings.
By being aware of these factors and making informed choices, you can still incorporate bottled juices into your diet without sacrificing your weight loss goals.
Check out our previous blog – Fructose vs Sucrose – to learn the difference between these two simple sugars and the impact their consumption will have on your health
Lean and toned up body isn’t just a far-fetched fantasy. Check out the BetterMe app and watch it propel your weight loss journey into high gear!
Top 20 Best Juices for Weight Loss
What are the best juices for weight loss as part of a healthy balanced diet?
There are at least 20!
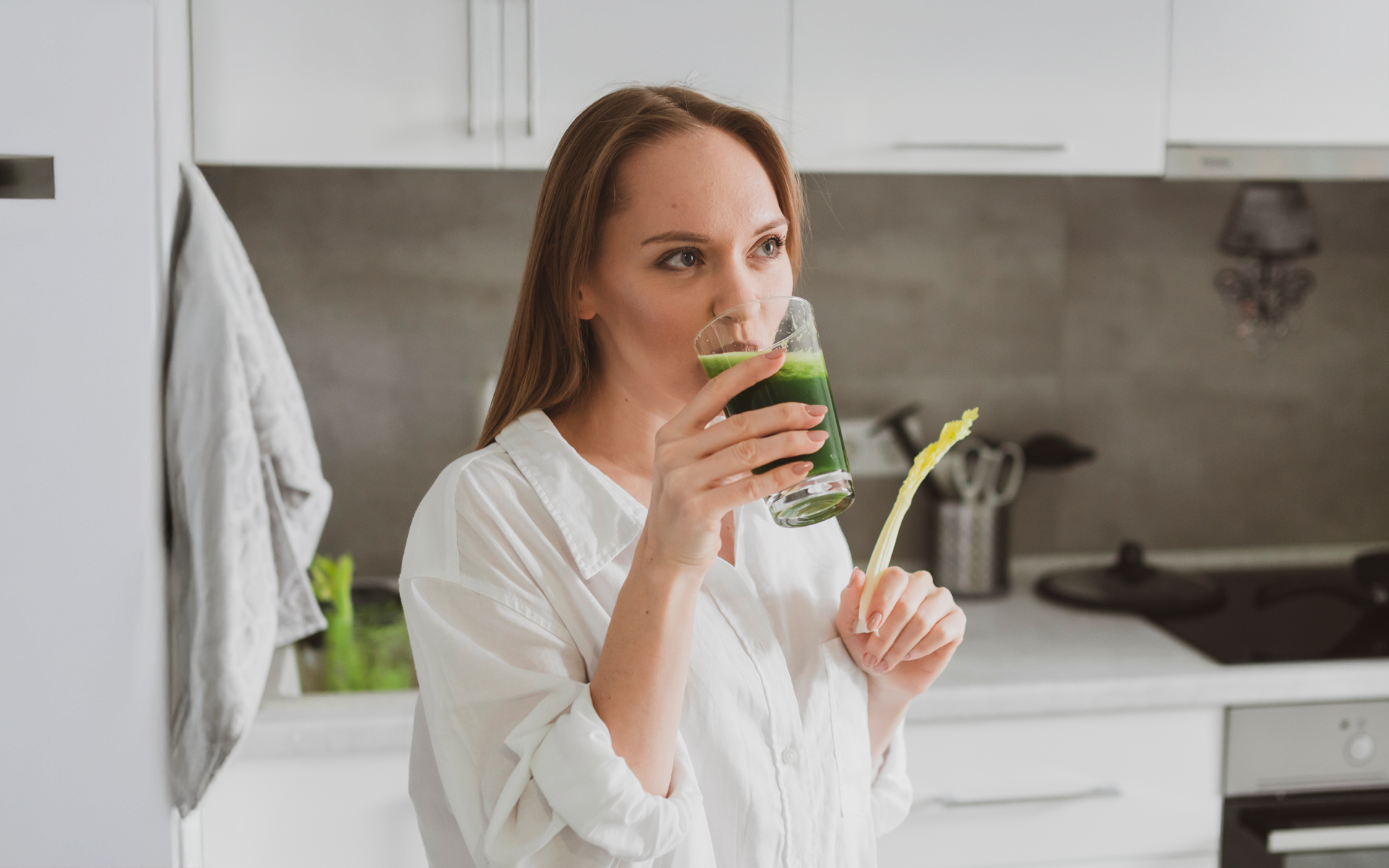
1. Celery Juice
Celery juice is one of the most popular among health enthusiasts. It’s incredibly low in calories and contains just 14 kcal per serving (21). Celery is rich in vitamins A, C, and K, potassium, and folate. It’s also 95% water (8).
Celery is rich in antioxidants and helps fight inflammation (5). In addition, due to its low calorie density, it can be beneficial for weight loss (26).
Read More: 4 Water Fasting Benefits and What to Expect
2. Green Vegetable Juice
Green juices for weight loss are some of the best. They vary by content, but most often, these juices contain cabbage, spinach, and/or kale. Sometimes they also contain avocados and look more like smoothies.
Most green vegetable juices are low in calories, high in fiber, and filled with antioxidants and other nutrients that may help fight inflammation (6) (25) (33).
According to studies, increasing your intake of fruits and vegetables can help you prevent weight gain over time and decrease current body weight, although this refers to whole fruits and vegetables rather than juices (23).
Another advantage of green vegetable juice is that you can change the ingredients to cater to your taste.
3. Beet Juice
Beets are high in fiber and help you feel fuller for a longer period of time, which promotes weight maintenance (4). They contain dietary nitrates that may help boost muscle function and reduce blood pressure (15).
Therefore, the juice may help you lose weight due to its low calorie content while also normalizing pressure and helping you have a better workout.
4. Pomegranate Juice
One of the most obvious benefits of pomegranate juice is its delicious taste. It’s also low in calories and may support your pound-shedding efforts (30). Components in this fruit may help regulate blood sugar, which may lead to hunger control (22) (36).
Pomegranate is rich in antioxidants and can help you boost weight loss deliciously.
5. Lemon-Ginger Green Juice
A variation of green juice with lemon and ginger may boost weight loss and other health benefits even further. In fact, lemon adds more antioxidants to your juice (9), while ginger may boost metabolism and reduce appetite (35). These features in a combo may promote weight loss and support your efforts.
In addition, if you don’t remove the pulp from the juice, you’ll boost your fiber intake.
6. Watermelon Juice
Watermelon is quite delicious, contains lots of nutrients, and is perfect as a refreshment. It’s rich in potassium, low in calories, and is a good source of vitamins A and C and other antioxidants (40).
It’s high in water, which means you’ll eat less and feel fuller.
A month-long study found that eating fresh watermelon daily helped reduce body weight, as well as being more filling than cookies (16). Again, this refers to the whole fruit, not the juice.
7. Kale-Apple Juice
Kale and apple juice is a wonderful substitute for store-bought sweet fruit juices. Both kale and apples are high in fiber, so you should consider leaving the pulp in your juice. Kale may also help with blood sugar stabilization (2) (24).
According to studies, apples help with weight loss and improve the quality of adult and children’s diets (42).
For more flavor, you can add celery, lemon, carrots, or ginger.
8. Carrot Juice
Carrot juice is a package of vitamin A and carotenoids (7). If you don’t remove the pulp, you’ll boost fiber intake, which will help you feel full for longer.
According to a study. carotenoid-rich vegetables may help reduce belly fat (14).
You can also add other fruits and vegetables to the mix to make it even more delicious. Carrot-apple juice is a rather popular mix.
BetterMe app is a foolproof way to go from zero to a weight loss hero in a safe and sustainable way! What are you waiting for? Start transforming your body now!
9. Ginger Curry Leaves Juice
Such a juice is rich in folate, which promotes the production of new healthy cells. It’s also rich in antioxidants, particularly if you choose to add lemon to it. You can add a little bit of honey if the taste is too powerful for you.
10. Amla Juice
Amla or Indian gooseberry juice contains antioxidants and may help improve endothelial function and reduce oxidative stress (10). Amla is also believed to boost immunity and improve digestion in traditional medicine, which can be an important part of your weight loss journey.
11. Orange Juice
Is orange juice great for weight loss?
Very much so, particularly if you choose to substitute sodas and colas with a small cup of freshly squeezed orange juice.
Orange juice can be included in a healthy balanced diet to improve diet quality and nutrient adequacy and potentially decrease the risks of obesity (1)
12. Pineapple Juice
Pineapple contains large amounts of vitamin C. Its phenolic compounds may also contribute to weight loss, at least in rats (28). This juice may help with appetite control and can be mixed with other juices for flavor.
13. Cucumber Juice
Maximum hydration and minimum calories are the most important things about cucumber juice. It’s also a great base for any other juice. You can add carrots, apples, berries, avocado, greens, etc. to this juice and boost hydration.
Cucumber is incredibly low in calories (only 8 kcal in one serving) (12).
14. Prune Juice
Prunes may help improve and optimize gastrointestinal function (34). It’s a juice that is believed to be great for treating and controlling bloating and constipation.
If you’re looking to buy prune juice, make sure it doesn’t contain added sugars or artificial flavorings.
Honorable Mentions
There are many more juices and mixes for you to try to boost weight loss that may help prevent various health conditions:
- Blackberry green juice – Blackberries have a high content of vitamin C and other antioxidants (32). They taste great in combination with greens, plant milk, banana, and pineapple.
- Grapefruit-fennel juice – A tasty mix with fiber-dense and low-glycemic grapefruit and fennel. You can also add avocado for a dose of healthy fats.
- Radish-apple-grapefruit juice – If you don’t like sweet juices, this is perfect for you. It’s hydrating and has a low glycemic index, which ensures your blood sugar won’t spike.
- Pomegranate-orange juice – Both kinds of fruit are full of fiber (when eaten whole) and antioxidants to fill your body (17) (27) and provide the feeling of fullness for a longer time. It’s also incredibly delicious.
- Tomato-vegetable juice – This so-called healthy (virgin) Bloody Mary will supply you with vitamins. If you’re not a fan of eating vegetables, why not try and drink this? If you buy it from the store, look for one that’s lower in sodium.
- Strawberry-cucumber juice – Cucumber is a universal vegetable that goes well with fruits and other vegetables. Mix it with strawberries, add some carrots and/or apples, and you’ll get hydrated and add antioxidants (32).
Is Juicing Healthier than Eating Whole Fruits or Vegetables?
Advocates of juicing claim that it allows for better absorption of nutrients and easier digestion due to the removal of fiber. They also argue that juicing allows for the consumption of a larger variety and quantity of produce, which leads to a more diverse intake of vitamins and minerals.
While juicing can be a convenient way to consume a variety of fruits and vegetables, it’s not necessarily healthier than eating whole produce. The loss of fiber and potential increase in sugar and calorie intake are important factors you need to consider.
Nutrient Loss
When fruits and vegetables are juiced, their fiber is removed. This means that some nutrients, particularly those that are found in the skin or pulp of produce, may be lost. Fiber also helps slow down the absorption of sugar from fruit juices, which can cause a spike in blood sugar levels (37).
In addition, juicing often requires large quantities of produce to make just one glass of juice. This can lead to a higher intake of calories and sugar than you would consume by eating whole fruits and vegetables.
Lack of Fiber
Fiber plays an important role in maintaining digestive health and promoting satiety (37). Without fiber, our bodies may not feel as full and satisfied after drinking juice as after eating whole fruits and vegetables. This can potentially lead to overconsumption of calories and affect weight management.
Cost
Juicing can be an expensive habit, particularly if you do it regularly or use more exotic produce. Eating whole fruits and vegetables is typically more affordable than buying a large quantity and juicing them.
Time-consuming
Preparing fruits and vegetables for juicing can be time-consuming, especially if you use a traditional juicer that requires peeling and chopping before juicing. This may make it less convenient for those who have busy schedules.
Safety Concerns
While fresh fruit and vegetable juices can be a nutritious addition to your diet, there are safety concerns that must be considered. Improperly washed produce or contaminated equipment can lead to foodborne illnesses. It’s important to properly clean and sanitize all equipment used for juicing, in addition to thoroughly washing all produce before juicing.
Our blog post Can You Eat Coffee Beans? explores the benefits and side effects of coffee beans when they’re consumed in excess in great detail.
FAQs
Is a 3-day juice cleanse beneficial?
One small study found that 3 days of such a cleanse altered the gut microbiome of participants, but these changes started to reverse once the cleanse was over. They also lost weight, but the study only followed them for 2 weeks after the cleanse, so it is unknown whether they maintained their weight loss in the long term (20). Most healthcare providers would recommend against juice cleanses of any kind.
Why are juices beneficial for health?
They contain polyphenols, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. All of these may help decrease the risk of cancer, improve skin condition, and nourish your body. However, all these and more benefits can be gained by eating whole fruits and vegetables instead.
Can juice be bad for you?
Yes, if you substitute regular healthy meals with juice. Juice cannot provide all the nutrients a human needs, although you will get some vitamins and minerals from the juice itself. In addition, juicing removes most or all of the fiber, so you don’t get much of a feeling of fullness from them. If you can, it’s actually better to eat the whole fruit for the nutritional benefits you’re looking for from the juice.
Is juicing for weight loss effective in the long term?
No. Similar to detox diets, juicing only works short-term and will likely only help you lose water weight. Once you return to your regular diet, the weight usually comes back (31). Such diets work due to a dramatic reduction in caloric intake for short periods of time.
Your body then uses up its glycogen stores, which causes water release. This water release is likely what is responsible for any initial weight loss experienced and will come back once you start to eat again and replenish your glycogen stores.
Find tips on how to meal prep and eat healthy meals even with a busy work schedule in our previous blog post, Best Frozen Meals for Weight Loss.
Which juice can reduce belly fat?
There’s no specific juice that can target belly fat as spot reduction of fat is not possible. However, nutrient-dense juices can be incorporated into a balanced, reduced-calorie diet and exercise routine, which can help with overall weight loss and may lead to a reduction in belly fat over time.
Various herbal remedies have been used to reduce waist circumference and body weight in overweight individuals, although these uses are not always backed by rigorous scientific research (11). Some ingredients that have been linked to potential weight loss benefits include green tea, ginger, turmeric, and apple cider vinegar.
However, it’s important to note that these results are based on limited research and should be treated with caution. A healthy, balanced diet and regular exercise are the most effective ways to reduce overall body fat and improve overall health (41). Juicing can be an occasional part of this lifestyle, but it shouldn’t be relied upon as your sole solution for weight loss or reducing belly fat.
The Bottom Line
There are many juices that can help you get more nutrients, improve the condition of your skin, and even promote weight loss. However, before you start on a super detox course where you can only drink juice, you should consider the potential dangers.
You should also understand that even a 3-day juice cleanse is only a temporary fix. If you want to lose weight and maintain the result, you need a balanced meal plan, proper physical activity, and healthy sleep.
Juices, gum-chewing, and other life hacks are only additional helpers on your journey. The key to healthy pound-shedding is consistency. Take small steps toward your goal every day and you’ll enjoy the process and maintain the result for many years.
DISCLAIMER:
This article is intended for general informational purposes only and does not serve to address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional advice or help and should not be relied on for making any kind of decision-making. Any action taken as a direct or indirect result of the information in this article is entirely at your own risk and is your sole responsibility.
BetterMe, its content staff, and its medical advisors accept no responsibility for inaccuracies, errors, misstatements, inconsistencies, or omissions and specifically disclaim any liability, loss or risk, personal, professional or otherwise, which may be incurred as a consequence, directly or indirectly, of the use and/or application of any content.
You should always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or your specific situation. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of BetterMe content. If you suspect or think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor.
SOURCES:
- 100% Orange juice consumption is associated with better diet quality, improved nutrient adequacy, decreased risk for obesity, and improved biomarkers of health in adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2003-2006 (2012, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Antidiabetic Properties of an Apple/Kale Extract In Vitro, In Situ, and in Mice Fed a Western-Type Diet (2017, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Artificial food additives: hazardous to long-term health (2024, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Beets, raw (2019, fdc.nal.usda.gov)
- Beneficial effects of celery (Apium graveolens) on metabolic syndrome: A review of the existing evidences (2019, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Cabbage, raw (2019, fdc.nal.usda.gov)
- Carrot juice, 100% (2020, fdc.nal.usda.gov)
- Celery juice (2020, fdc.nal.usda.gov)
- Citrus limon (Lemon) Phenomenon—A Review of the Chemistry, Pharmacological Properties, Applications in the Modern Pharmaceutical, Food, and Cosmetics Industries, and Biotechnological Studies (2020, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Clinical evaluation of Emblica Officinalis Gatertn (Amla) in healthy human subjects: Health benefits and safety results from a randomized, double-blind, crossover placebo-controlled study (2020, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Comprehensive Study of Scientific Evidence and Potential Risk of Herbal Medicine Use for Body Weight Reduction in North West Saudi Arabia (2020, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Cucumber (2020, webmd.com)
- Defining a Healthy Diet: Evidence for the Role of Contemporary Dietary Patterns in Health and Disease (2020, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Dietary Intake of Carotenoid-Rich Vegetables Reduces Visceral Adiposity in Obese Japanese men—A Randomized, Double-Blind Trial (2020, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Dietary Nitrate and Physical Performance (2018, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Effects of Fresh Watermelon Consumption on the Acute Satiety Response and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Overweight and Obese Adults (2019, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Food Applications and Potential Health Benefits of Pomegranate and its Derivatives (2020, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Fruit consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes: results from three prospective longitudinal cohort studies (2013, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Fruit Juices: Are They Helpful or Harmful? An Evidence Review (2021, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Health benefit of vegetable/fruit juice-based diet: Role of microbiome (2017, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Health Benefits of Celery (2020, webmd.com)
- Hypoglycemia (2022, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Improving fruit and vegetable intake attenuates the genetic association with long-term weight gain (2019, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Intake of kale suppresses postprandial increases in plasma glucose: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study (2016, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Kale, raw (2019, fdc.nal.usda.gov)
- Meal replacements, reduced energy density eating and weight loss maintenance in primary care patients: A randomized controlled trial (2014, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Nutritional benefits of oranges (2012, link.springer.com)
- Physiological and molecular study on the anti-obesity effects of pineapple (Ananas comosus) juice in male Wistar rat (2018, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Polyphenol-based nutraceuticals for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease: Review of human evidence (2016, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Pomegranate juice, 100% (2020, fdc.nal.usda.gov)
- Popular Weight Loss Strategies: a Review of Four Weight Loss Techniques (2017, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Review of Functional and Pharmacological Activities of Berries (2021, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Spinach, raw (2019, fdc.nal.usda.gov)
- Systematic review: the effect of prunes on gastrointestinal function (2014, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The effects of ginger intake on weight loss and metabolic profiles among overweight and obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (2019, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The Glycemic Effects of Pomegranate Juice (2020, academic.oup.com)
- Therapeutic Benefits and Dietary Restrictions of Fiber Intake: A State of the Art Review (2022, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- The role of protein in weight loss and maintenance (2015, sciencedirect.com)
- The sweet danger of sugar – Harvard Health (2022, health.harvard.edu)
- Watermelon, raw (2019, fdc.nal.usda.gov)
- Weight-Loss and Maintenance Strategies – Weight Management (2004, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
- Weight Loss Associated With Consumption of Apples: A Review (2018, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)